Abstract
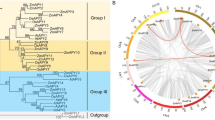
Sucrose non-fermenting-1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase2s (SnRK2s) were reported to be one of the critical factors in abscisic acid (ABA) signaling, playing important roles in response to biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is one of the most important protein crops, but little is known about SnRK2s (PvSnRK2s) in common bean. In this study, we identified and characterized PvSnRk2s at the genome-wide level. We identified 10 PvSnRK2 genes, which were divided into 4 groups by phylogenetic analysis. Stress response element (TC-rich repeats), MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility (MBS), and low-temperature responsiveness element (LTR) were identified in the promoter regions of PvSnRK2s. Real-time fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to verify the expression profiles of 10 genes at 5 time points under high salt, drought and low temperature stresses. Results showed that the expression levels of PvSnRK2.2/2.9 of group II were much higher than that of the other groups’ members under drought stress, implying these genes might play an important role in the response of common bean to water deficiency. Furthermore, PvSnRK2.4 was significantly up-regulated under NaCl, Mnt (mannitol) and low-temperature stresses, indicating the gene may be one of the essential regulatory genes of common bean in response to the adverse external environment. This is the first comprehensive analysis of the SnRK2 genes in the common bean, which provided a basis for further elucidating the function of PvSnRK2 genes in the common bean.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
After publication online, all data are available and used in the supplementary materials.
References
Anderberg RJ, Walker-Simmons MK (1992) Isolation of a wheat cDNA clone for an abscisic acid-inducible transcript with homology to protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(21):10183–10187. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.21.10183
Annaira F, Muhammad JK, Hassaan MA, Malik NA, Nazia B, Kalsoom S, Muhammad RK, Raza A, Muhammad I, Jamshaid H, Irfan S (2020) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of SnRK2 gene family in mung bean (Vigna radiata) in response to drought stress. Crop Pasture Sci 71(5):469–476. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP19392
Bai J, Mao J, Yang H, Khan A, Fan A, Liu S, Zhang J, Wang D, Gao H, Zhang J (2017) Sucrose non-ferment 1 related protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) genes could mediate the stress responses in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). BMC Genet 18:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-017-0506-6
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucl Acids Res 37:W202–W208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp335
Beebe SE, Rao IM, Blair MW, Acosta-Gallegos JA (2013) Phenotyping common beans for adaptation to drought. Front Physiol 4:35. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2013.00035
Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Laurière C (2004) Identification of nine sucrose nonfermenting 1-related protein kinases 2 activated by hyperosmotic and saline stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 279(40):41758–41766. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M405259200
Broughton WJ, Hernández G, Blair M, Beebe S, Gepts P, Vanderleyden J (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.)-model food legumes. Plant Soil 252(1):55–128
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R (2020a) TB tools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13(8):1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chen K, Li G, Bressan RA, Song C, Zhu J, Zhao Y (2020b) Abscisic acid dynamics, signaling, and functions in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 62(1):25–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12899
Chen Z, Zhou L, Jiang P, Lu R, Halford NG, Liu C (2021) Genome-wide identification of sucrose nonfermenting-1-related protein kinase (SnRK) genes in barley and RNA-seq analyses of their expression in response to abscisic acid treatment. BMC Genom 22(1):300. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07601-6
Diédhiou CJ, Popova OV, Dietz KJ, Golldack D (2008) The SNF1-type serine-threonine protein kinase SAPK4 regulates stress-responsive gene expression in rice. BMC Plant Biol 8(1):49
Finkelstein R (2013) Abscisic acid synthesis and response. The Arabidopsis Book 11, e0166. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0166
Fujii H, Zhu J (2009) Arabidopsis mutant deficient in 3 abscisic acid-activated protein kinases reveals critical roles in growth, reproduction, and stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(20):8380–8385. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0903144106
Fujita Y, Nakashima K, Yoshida T, Katagiri T, Kidokoro S, Kanamori N, Umezawa T, Fujita M, Maruyama K, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Nakasone S, Yamada K, Ito T, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009) Three SnRK2 protein kinases are the main positive regulators of abscisic acid signaling in response to water stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50(12):2123–2132. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcp147
Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2013) Pivotal role of the AREB/ABF-SnRK2 pathway in ABRE-mediated transcription in response to osmotic stress in plants. Physiol Plant 147(1):15–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01635.x
Furihata T, Maruyama K, Fujita Y, Umezawa T, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Abscisic Acid-Dependent Multisite Phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(6):1988–1993. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0505667103
Halford NG, Hardie DG (1998) SNF1-related protein kinases: global regulators of carbon metabolism in plants. Plant Mol Biol 37(5):735–748
Henry RJ, Harris PJ (1997) Molecular distinction between Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons: more than a simple dichotomy. Plant Mol Biology Report 15:216–218. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007498823211
Hey SJ, Byrne E, Halford NG (2010) The interface between metabolic and stress signalling. Ann Bot 105(2):197–203. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcp285
Hrabak EM, Chan CWM, Gribskov M, Harper JF, Choi JH, Halford N, Kudla J, Luan S, Nimmo HG, Sussman MR, Thomas M, Walker-Simmons K, Zhu J, Harmon AC (2003) The Arabidopsis CDPK-SnRK superfamily of protein kinases. Plant Physiol 132(2):666–680. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.011999
Hsu PK, Dubeaux G, Takahashi Y, Schroeder JI (2020) Signaling mechanisms in abscisic acid-mediated stomatal closure. Plant J 105(2):307–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15067
Hu Q, Jiang B, Wang L, Song Y, Tang X, Zhao Y, Fan X, Gu Y, Zheng Q, Cheng J, Zhang H (2022) Genome-wide analysis of growth-regulating factor genes in grape (Vitis vinifera L.): identification, characterization and their responsive expression to osmotic stress. Plant Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02939-x
Hu W, Yan Y, Shi H, Liu J, Miao H, Tie W, Ding Z, Ding X, Wu C, Liu Y, Wang J, Xu B, Jin Z (2017) The core regulatory network of the abscisic acid pathway in banana: genome-wide identification and expression analyses during development, ripening, and abiotic stress. BMC Plant Biol 17(1):145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1093-4
Islam M, Inoue T, Hiraide M, Khatun N, Jahan A, Kuwata K, Katagiri S, Umezawa T, Yotsui I, Sakata Y, Takezawa D (2021) Activation of SnRK2 by raf-like kinase ARK represents a primary mechanism of ABA and abiotic stress responses. Plant Physiol 185(2):533–546. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiaa046
Kamiyama Y, Katagiri S, Umezawa T (2021) Growth Promotion or osmotic stress response: how SNF1-Related protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) kinases are activated and manage Intracellular Signaling in plants. Plants 10(7):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071443
Katsuta S, Masuda G, Bak H, Shinozawa A, Kamiyama Y, Umezawa T, Takezawa D, Yotsui I, Taji T, Sakata Y (2020) Arabidopsis Raf-like kinases act as positive regulators of subclass III SnRK2 in osmostress signaling. Plant J 103(2):634–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14756
Kawa D, Meyer AJ, Dekker HL, Abd-El-Haliem AM, Gevaert K, Van De Slijke E, Maszkowska J, Bucholc M, Dobrowolska G, De Jaeger G, Schuurink RC, Haring MA, Testerink C (2020) SnRK2 protein kinases and mRNA decapping Machinery Control Root Development and Response to Salt. Plant Physiol 182(1):361–377. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00818
Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Minami H, Kagaya Y, Hattori T (2004) Differential activation of the rice sucrose nonfermenting1-related protein kinase2 family by hyperosmotic stress and abscisic acid. Plant Cell 16(5):1163–1177. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.019943
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Laskar P, Bhattacharya S, Chaudhuri A, Kundu A (2021) Exploring the GRAS gene family in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): characterization, evolutionary relationships, and expression analyses in response to abiotic stresses. Planta 254(4):84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03725-x
Letunic I, Copley RR, Schmidt S, Ciccarelli FD, Doerks T, Schultz J, Ponting CP, Bork P (2004) SMART 4.0: towards genomic data integration. Nucl Acids Res 32(1):D142–D144. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh088
Lin Z, Li Y, Zhang Z, Liu X, Hsu CC, Du Y, Sang T, Zhu C, Wang Y, Satheesh V, Pratibha P, Zhao Y, Song Ch, Tao WA, Zhu J, Wang P (2020) A RAF-SnRK2 kinase cascade mediates early osmotic stress signaling in higher plants. Nat Commun 11(1):613. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14477-9
Lin Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Liu X, Ma L, Zhang Z, Mu C, Zhang Y, Peng L, Xie S, Song C, Shi H, Zhu J, Wang P (2021) Initiation and amplification of SnRK2 activation in abscisic acid signaling. Nat Commun 12(1):2456. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41467-021-22812-X
Liu Z, Ge X, Yang Z, Zhang C, Zhao G, Chen E, Liu J, Zhang X, Li F (2017) Genome-wide identification and characterization of SnRK2 gene family in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). BMC Genom 18(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-017-0517-3
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆Ct method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Long T, Xu B, Hu Y, Wang Y, Mao C, Wang Y, Zhang J, Liu H, Huang H, Liu Y, Yu G, Zhao C, Li Y, Huang Y (2021) Genome-wide identification of ZmSnRK2 genes and functional analysis of ZmSnRK2.10 in ABA signaling pathway in maize (Zea mays L). BMC Plant Biol 21(1):309. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03064-9
Mach J (2009) Alternative splicing produces a JAZ protein that is not broken down in response to jasmonic acid. Plant Cell 21(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.210111
Marchler-Bauer A, Bo Y, Han L, He J, Lanczycki CJ, Lu S, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Lu F, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Wang Z, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Zheng C, Geer LY, Bryant SH (2017) CDD/SPARCLE: functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucl Acids Res 45(D1):D200–D203. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1129
Mazur R, Maszkowska J, Anielska MA, Garstka M, Polkowska-Kowalczyk L, Czajkowska A, Zmienko A, Dobrowolska G, Kulik A (2021) The SnRK2.10 kinase mitigates the adverse effects of salinity by protecting photosynthetic machinery. Plant Physiol 187(4):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab438
McLoughlin F, Galvan-Ampudia CS, Julkowska MM, Caarls L, van der Does D, Laurière C, Munnik T, Haring MA, Testerink C (2012) The Snf1-related protein kinases SnRK2.4 and SnRK2.10 are involved in maintenance of root system architecture during salt stress. Plant J 72(3):436–449. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05089.x
Miyazono KI, Miyakawa T, Sawano Y, Kubota K, Kang HJ, Asano A, Miyauchi Y, Takahashi M, Zhi Y, Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Kodaira KS, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Tanokura M (2009) Structural basis of abscisic acid signalling. Nature 462(7273):609–614. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08583
Mizoguchi M, Umezawa T, Nakashima K, Kidokoro S, Takasaki H, Fujita Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2010) Two closely related subclass II SnRK2 protein kinases cooperatively regulate drought-inducible gene expression. Plant Cell Physiol 51(5):842–847. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcq041
Mustilli AC, Merlot S, Vavasseur A, Fenzi F, Giraudat J (2002) Arabidopsis OST1 protein kinase mediates the regulation of stomatal aperture by abscisic acid and acts upstream of reactive oxygen species production. Plant Cell 14(12):3089–3099. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.007906
Park SY, Fung P, Nishimura N, Jensen DR, Fujii H, Zhao Y, Lumba S, Santiago J, Rodrigues A, Chow TF, Alfred SE, Bonetta D, Finkelstein R, Provart NJ, Desveaux D, Rodriguez PL, McCourt P, Zhu JK, Schroeder JI, Volkman BF, Cutler SR (2009) Abscisic acid inhibits type 2 C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START Proteins. Science 324(5930):1068–1071. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1173041
Rombauts S, Déhais P, Van MM, Rouzé P (1999) PlantCARE, a plant cis-acting regulatory element database. Nucl Acids Res 27(1):295–296. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/27.1.295
Schmutz J, McClean PE, Mamidi S, Wu GA, Cannon SB, Grimwood J, Jenkins J, Shu S, Song Q, Chavarro C, Torres-Torres M, Geffroy V, Moghaddam SM, Gao D, Abernathy B, Barry K, Blair M, Brick MA, Chovatia M, Gepts P, Goodstein DM, Gonzales M, Hellsten U, Hyten DL, Jia G, Kelly JD, Kudrna D, Lee R, Richard M, M.Miklas PN, Osorno JM, Rodrigues J, Thareau V, Urrea CA, Wang M, Yu Y, Zhang M, Wing RA, Cregan PB, Rokhsar DS, Jackson SA (2014) A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat Genet 46(7):707–713. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3008
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Shin R, Alvarez S, Burch AY, Jez JM, Schachtman DP (2007) Phosphoproteomic identification of targets of the Arabidopsis sucrose nonfermenting-like kinase SnRK2.8 reveals a connection to metabolic processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(15):6460–6465. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610208104
Soma F, Takahashi F, Suzuki T, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2020) Plant raf-like kinases regulate the mRNA population upstream of ABA-unresponsive SnRK2 kinases under drought stress. Nat Commun 11(1):1373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15239-3
Szymanska KP, Polkowska-Kowalczyk L, Lichocka M, Maszkowska J, Dobrowolska G (2019) SNF1-Related protein kinases SnRK2.4 and SnRK2.10 modulate ROS Homeostasis in Plant response to salt stress. Int J Mol Sci 20(1):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010143
Tian S, Mao X, Zhang H, Chen S, Zhai C, Yang S, Jing R (2013) Cloning and characterization of TaSnRK2.3, a novel SnRK2 gene in common wheat. J Exp Bot 64(7):2063–2080. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert072
Umezawa T, Yoshida R, Maruyama K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2004) SRK2C, a SNF1-related protein kinase 2, improves drought tolerance by controlling stress-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(49):17306–17311. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407758101
Umezawa T, Sugiyama N, Mizoguchi M, Hayashi S, Myouga F, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Ishihama Y, Hirayama T, Shinozaki K (2009) Type 2 C protein phosphatases directly regulate abscisic acid-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(41):17588–17593. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907095106
Vlad F, Droillard MJ, Valot B, Khafif M, Rodrigues A, Brault M, Zivy M, Rodriguez PL, Merlot S, Laurière C (2010) Phospho-site mapping, genetic and in planta activation studies reveal key aspects of the different phosphorylation mechanisms involved in activation of SnRK2s. Plant J 63(5):778–790. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04281.x
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93(1):77–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Wang Y, Wang X, Gu M, Kang H, Zeng J, Fan X, Sha L, Zhang H, Yu K, Zhou Y (2015) Cloning and characterization of four novel SnRK2 genes from Triticum polonicum. Biol Plant 59:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-015-0501-6
Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J (2010) KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a Toolkit incorporating Gamma-Series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics Proteom Bioinf 8(1):77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-0229(10)60008-3
Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, Lee TH, Jin H, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH (2012) MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucl Acids Res 40(7):e49. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1293
Wang Y, Yan H, Qiu Z, Hu B, Zeng B, Zhong C, Fan C (2019) Comprehensive Analysis of SnRK Gene Family and their responses to salt stress in Eucalyptus grandis. Int J Mol Sci 20(11):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112786
Wasternack C (2007) Jasmonates: an update on biosynthesis, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. Ann Bot 100(4):681–697. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcm079
Wu P, Wang W, Duan W, Li Y, Hou X (2017) Comprehensive Analysis of the CDPK-SnRK Superfamily genes in Chinese Cabbage and its evolutionary implications in plants. Front Plant Sci 8:162. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.0016
Xu M, Huang L, Zhang F, Zhu L, Zhou Y, Li Z (2013) Genome-wide phylogenetic analysis of stress-activated protein kinase genes in Rice (OsSAPKs) and expression profiling in response to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzicola infection. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31(4):877–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0559-2
Yin P, Fan H, Hao Q, Yuan X, Wu D, Pang Y, Yan C, Li W, Wang J, Yan N (2009) Structural insights into the mechanism of abscisic acid signaling by PYL proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16(12):1230–1236. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1730
Zhang H, Li W, Mao X, Jing R, Jia H (2016) Differential activation of the wheat SnRK2 family by Abiotic stresses. Front Plant Sci 7:420. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00420
Zhang H, Zhang H, Jing R, Mao X (2017) Functional characterization of TaSnRK2.8 promoter in response to Abiotic stresses by deletion analysis in transgenic Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 8:1198. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01198
Zhang Y, Wan S, Wang W, Chen J, Huang L, Duan M, Yu Y (2018) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the CsSnRK2 family in Camellia sinensis. Plant Physiol Biochem 132:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.09.021
Zhang Y, Wan S, Liu X, He J, Cheng L, Duan M, Liu H, Wang W, Yu Y (2020) Overexpression of CsSnRK2.5 increases tolerance to drought stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 150:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.035
Zhao W, Cheng Y, Zhang D, Shen X, You Q, Guo W, Li X, Song X, Zhou X, Jiao Y (2017) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the GmSnRK2 family in soybean. Int J Mol Sci 18(9):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091834
Zhu W, Wu D, Jiang L, Ye L (2020) Genome-wide identification and characterization of SnRK family genes in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol 20(1):287. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02484-3
Acknowledgements
We thank the Institute of Crop Science, The Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences for the kind donation of certified F4321 seeds; we also grateful for the financial support from the Science and Technology Project of Henan Province, Graduate Education Reform and Quality Improvement Project of Henan Province.
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (grant number 212102110248) and Postgraduate Education Reform and Quality Improvement Project of Henan Province (grant number YJS2021JD17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC conceived and designed the study. DC, XS, YZ, SY and JZ performed the experiments. DC, XS and JC analyzed the data. DC and JC wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial or non-financial interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
There are no ethical issues involved in this study.
Informed consent
All individual participants were included in the study with informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, DB., Sun, XY., Zhang, YP. et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of SnRK2 gene family in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in response to abiotic stress. Biologia 78, 2013–2027 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01343-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01343-4