Abstract
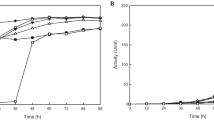
Streptokinase (SK) is one of the essential fibrinolytic agents and is commonly employed to treat myocardial infarction or heart attack. Despite its significance as an anti-clot agent, SK exhibits certain drawbacks, including limited half-life in the bloodstream, non-specific to fibrin, and may cause process workers to develop undesirable immune responses. Acknowledging the high specificity of staphylokinase (SAK) towards fibrin and the powerful recombinant DNA technology, this study was carried out to evaluate the fibrinolytic activity of a recombinant staphylokinase-streptokinase (SAK-SK) protein in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Briefly, the SAK gene isolated from Staphylococcus aureus was ligated at the 5’end of the SK gene using the pGEM®-3Zf (+) cloning vector and transformed into the expression host E. coliBL21(DE3) before being induced with isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG).Subsequently, the produced recombinant SK protein was analyzed using 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).The biological performance of the recombinant SK protein was then examined via caseinolytic and fibrinolytic assays and compared to that of the native SK protein. Based on the results, the recombinant SK protein contained 563 amino acid residues with a molecular weight of approximately 63.1 kDa. The hybrid SK protein was more active in the casein lysis experiment compared to the native SK, with a more significant halo zone formation. Moreover, the hybrid SK protein demonstrated a complete clot lysis compared to the poor clot lysis of the native SK protein. In conclusion, this study successfully developed a recombinant hybrid SK protein with enhanced affinity to fibrin, making it a potential anti-clot agent.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E. coli :
-
Escherichia coli
- F:
-
Forward
- R:
-
Reverse
- PCR:
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Rpm:
-
Revaluation per minute
- SK:
-
Streptokinase
- SAK:
-
Staphylokinase
References
Assiri AS, El-Gamal BA, Hafez EE, Haidara MA (2014) Production of recombinant streptokinase from Streptococcus pyogenes isolate and its potential for thrombolytic therapy. Saudi Med J 35:1482–1488
Banerjee A, Chisti Y, Banerjee UC (2004) Streptokinase—a clinically useful thrombolytic agent. Biotechnol adv 22:287–307. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2003.09.004
Buniya HK, Murugan V, Thangadurai C (2014) Cloning and expression of hybrid streptokinase towards clot-specific activity. J Microbiol methods 98:84–88. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2014.01.006
Buniya HK, Farhan HA (2016) Cloning and Expression of Staphylokinase gene produced from Staphylococcus aureus in E. coli DH5α. Al-Anbar J Vet Sci 9: 7–14
Collen D (1998) Staphylokinase: a potent, uniquely fibrin-selective thrombolytic agent. Nat Med 4:279–284. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0398-279
Collen D, Lijnen RH (2005) Thrombolytic agents. Thrombo and haemost 93:627–630. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1160/TH04-110724
Diwan D, Usmani Z, Sharma M, Nelson JW, Thakur VK, Christie G, …, Gupta VK (2021) Thrombolytic enzymes of Microbial Origin: a review. Inter. J Mol Sci 22:10468. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910468
Ghosh S, Qureshi A, Purohit HJ (2019) Microbial degradation of plastics: Biofilms and degradation pathways. Contaminants in agriculture and environment: health risks and remediation, 1: 184–199. DOI:https://doi.org/10.26832/AESA-2019-CAE-0153-014
Goldhaber SZ, Bounameaux H (2012) Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. The Lancet 379:1835–1846. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61904-1
Jackson KW, Tang J (1982) Complete amino acid sequence of streptokinase and its homology with serine proteases. Biochemistry 21:6620–6625. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00269a001
Kotb E (2012) Fibrinolytic bacterial enzymes with thrombolytic activity. Fibrinolytic bacterial enzymes with thrombolytic activity. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 1–74. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24980-8.
Labarrere CA, Dabiri AE, Kassab GS (2020) Thrombogenic and inflammatory reactions to biomaterials in medical devices. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:123. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00123
Mandel M, Higa A (1970) Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J of Mol Biol 53:159–162. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3
Mican J, Toul M, Bednar D, Damborsky J (2019) Structural biology and protein engineering of thrombolytics. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 17:917–938
Prasad S, Kashyap RS, Deopujari JY, Purohit HJ, Taori GM, Daginawala HF (2006) Development of an in vitro model to study clot lysis activity of thrombolytic drugs. Thrombo J 4:1–4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-9560-4-14
Yau JW, Teoh H, Verma S (2015) Endothelial cell control of thrombosis. BMC Cardiovasc disord 15:1–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-015-0124-z
Acknowledgements
For their assistance in completing this work, the authors are grateful to all of the employees at the Department of Biology, College of Education for Pure Science, University Of Anbar, as well as their colleagues at the Molecular Biology Lab.
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Authors of the manuscript declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not Applicable.
Informed consent
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Buniya, H.K., Hameed, A.K. & Al-Hayawi, A.Y. Cloning and expression of staphylokinase-streptokinase recombinant protein in E. coli BL21(DE3). Biologia 78, 1113–1117 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01311-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01311-y