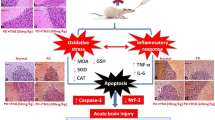
Abstract
Preservation of the brain is important to reducing recurrent seizures and other neurological sequelae after status epilepticus (SE). Medical ozone (MedO3) shows antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties in the human body. In this study, it was aimed to understand the neuroprotective potential of MedO3 in the acute period after SE. Mature rats of Wistar Albino were used for the study. Group design O3 + SE: SE induced after MedO3, O3: MedO3 alone was given, SE: SE only induced, SE + O3; MedO3 given after SE, C: control and S: sham control group. SE was induced with lithium-pilocarpine experimental model and evaluated on the Racine scale. Peripheral blood samples and brain tissue samples were taken before decapitation. Histopathological evaluation of the hippocampus of the rats given medical O3 before and after SE were studied. The highest peripheral blood oxidative stress index (OSI) was found in SE group. The OSI level in O3 + SE and SE + O3 was significantly higher than SE/C/S. Gene expressions of TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA were significantly higher in SE compared to other groups. Histopathologically; eosinophilia, cellular shrinkage and interstitial oedema were detected in the most severe SE and to a lesser extent in O3 + SE/ SE + O3. MedO3 reduced SE-induced oxidative damage, neuroinflammation and neuronal injury and contributed positively to neuroprotection.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SE:
-
status epilepticus
- MedO3 :
-
medical ozone
- OSI:
-
oxidant stress index
- TNF-α:
-
tumour necrosis factor- alpha
- IL-1β:
-
interleukine-1beta
- Li-Pi:
-
lithium-pilocarpine
- (q)PCR:
-
(quantitative) real-timepolymerase chain reaction
- TAC:
-
total antioxidant capacity
- TOC:
-
total oxidant capacity
- H&E:
-
hematoxylin-eosin
- Group 1:
-
O3 + SE
- Group 2:
-
O3
- Group 3:
-
SE
- Group 4:
-
SE+ O3
- Group 5-control group:
-
C
- Group 6-sham control group:
-
(S)
References
Basavappa S, Ellory JC (1996) The role of swelling-induced anion channels during neuronal volume regulation. Mol Neurobiol 13(2):137–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740638
Chen JWY, Naylor DE, Wasterlain CG (2007) Advances in the pathophysiology of status epilepticus. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 186:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2007.00803.x
Clavo B, Rodriguez-Esparragon F, Rodriguez-Abreu D et al (2019) Modulation of oxidative stress by ozone therapy in the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced toxicity: review and prospects. Antioxidants (Basel) 8(12):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120588
Clavo B, Suarez G, Aguilar Y et al (2011) Brain ischemia and hypometabolism treated by ozone therapy. Forsch Komplementmed 18(5):283–287. https://doi.org/10.1159/000333795
Clifford DB, Olney JW, Maniotis A, Collins RC, Zorumski CF (1987) The functional anatomy and pathology of lithium-pilocarpine and high-dose pilocarpine seizures. Neuroscience 23(3):953–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(87)90171-0
Colton CA (2009) Heterogeneity of microglial activation in the innate immune response in the brain. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 4(4):399–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-009-9164-4
Di Filippo C, Trotta MC, Maisto R et al (2015) Daily oxygen/O3 treatment reduces muscular fatigue and improves cardiac performance in rats subjected to prolonged high intensity physical exercise. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2015:190640. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/190640
Eastman CL, D’Ambrosio R, Ganesh T (2019) Modulating neuroinflammation and oxidative stress to prevent epilepsy and improve outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Neuropharmacology 172:107907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107907
Elvis AM, Ekta JS (2011) Ozone therapy: a clinical review. J Nat Sci Biol Med 2(1):66–70. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-9668.82319
Fellin T (2009) Communication between neurons and astrocytes: relevance to the modulation of synaptic and network activity. J Neurochem 108(3):533–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05830.x
Fountain NB (2000) Status epilepticus: risk factors and complications. Epilepsia 41(Suppl 2):S23–S30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.2000.tb01521.x
Gastaut H (1970) Clinical and electroencephalographical classification of epileptic seizures. Epilepsia 11(1):102–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1970.tb03871.x
Glien M, Brandt C, Potschka H, Voigt H, Ebert U, Löscher W (2001) Repeated low-dose treatment of rats with pilocarpine: low mortality but high proportion of rats developing epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 46(2):111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-1211(01)00272-8
Gordon S, Martinez FO (2010) Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity 32(5):593–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2010.05.007
Honchar MP, Olney JW, Sherman WR (1983) Systemic cholinergic agents induce seizures and brain damage in lithium-treated rats. Science 220(4594):323–325. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6301005
Kal A, Kal O, Akillioglu I, Celik E, Yilmaz M, Gonul S, Solmaz M, Onal O (2017) The protective effect of prophylactic ozone administration against retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 36(1):39–47. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569527.2016.1156120
Kim J-E, Ryu HJ, Choi SY, Kang TC (2012) Tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated threonine 435 phosphorylation of p65 nuclear factor-κB subunit in endothelial cells induces vasogenic edema and neutrophil infiltration in the rat piriform cortex following status epilepticus. J Neuroinflammation 9:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-6
Kim JE, Ryu HJ, Kang TC (2013) Status epilepticus induces vasogenic edema via tumor necrosis factor-α/ endothelin-1-mediated two different pathways. PLoS One 8(9):e74458. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0074458
Koca K, Yurttaş Y, Yıldız C, Caycı T, Uysal B, Korkmaz A (2010) Effect of hyperbaric oxygen and ozone preconditioning on oxidative/nitrosative stress induced by tourniquet ischemia/reperfusion in rat skeletal muscle. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 44(6):476–483. https://doi.org/10.3944/AOTT.2010.2327
Lemos T, Cavalheiro EA (1995) Suppression of pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus and the late development of epilepsy in rats. Exp Brain Res 102(3):423–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230647
Librizzi L, Noè F, Vezzani A, de Curtis M, Ravizza T (2012)Seizure-induced brain-borne inflammation sustains seizure recurrence and blood-brain barrier damage. Ann Neurol 72(1):82–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23567
Logroscino G, Hesdorffer DC, Cascino G et al (2005) Mortality after a first episode of status epilepticus in the United States and Europe. Epilepsia 46(11):46–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.00409.x
Maroso M, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Iori V, Ian Wright C, French J, Vezzani A (2011)Interleukin-1β biosynthesis inhibition reduces acute seizures and drug resistant chronic epileptic activity in mice. Neurotherapeutics 8(2):304–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-011-0039-z
McNamara JO, Huang YZ, Leonard AS (2006) Molecular signaling mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis. Sci STKE 2006(356):re12. https://doi.org/10.1126/stke.3562006re12
Pasantes-Morales H, Tuz K (2006) Volume changes in neurons: hyperexcitability and neuronal death. Contrib Nephrol 152:221–240. https://doi.org/10.1159/000096326
Pearson-Smith JN, Patel M (2017) Metabolic dysfunction and oxidative stress in epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci 18(11):2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112365
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation II Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32(3):281–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(72)90177-0
Sagai M, Bocci V (2011) Mechanisms of action involved in ozone therapy: is healing induced via a mild oxidative stress? Med Gas Res 1:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-9912-1-29
Sánchez Fernández I, Goodkin HP, Scott RC (2019) Pathophysiology of convulsive status epilepticus. Seizure 68:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2018.08.002
Shin EJ, Jeong JH, Chung YH et al (2011) Role of oxidative stress in epileptic seizures. Neurochem Int 59(2):122–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2011.03.025
Shorvon S, Trinka E, Walker M (2019) The seventh London-Innsbruck colloquium on status epilepticus and acute seizures. Epilepsy Behav 101(Pt B):106532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.106532
Sun Y, Ma J, Li D et al (2019)Interleukin-10 inhibits interleukin-1β production and inflammasome activation of microglia in epileptic seizures. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1452-1
Terrone G, Frigerio F, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Vezzani A (2019) Inflammation and reactive oxygen species in status epilepticus: biomarkers and implications for therapy. Epilepsy Behav 101(Pt B):106275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.04.028
Vasquez A, Farias-Moeller R, Tatum W (2019) Pediatric refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus. Seizure 68:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2018.05.012
Verhoog QP, Holtman L, Aronica E, van Vliet EA (2020) Astrocytes as guardians of neuronal excitability: mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis. Front Neurol 11:591690. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.591690
Viviani B, Bartesaghi S, Gardoni F et al (2003)Interleukin-1beta enhances NMDA receptor-mediated intracellular calcium increase through activation of the Src family of kinases. J Neurosci 23(25):8692–8700. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-25-08692.2003
Walker MC (2018) Pathophysiology of status epilepticus. Neurosci Lett 667:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.12.044
Wang L, Chen H, Liu XH, Chen ZY, Weng XD, Qiu T (2014) The protective effect of ozone oxidative preconditioning against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in rat kidney cells. Ren Fail 36(9):1449–1454. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2014.950934
Wang M, Deng X, Xie Y, Chen Y (2020) Astaxanthin attenuates neuroinflammation in status epilepticus rats by regulating the ATP-P2X7R signal. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:1651–1662. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S249162
Yamanel L, Kaldirim U, Oztas Y et al (2011) Ozone therapy and hyperbaric oxygen treatment in lung injury in septic rats. Int J Med Sci 8(1):48–55. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.8.48
Funding
The financial funding of this study was supported by Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (Project ID: 2697). All researchers thank the Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was obtained for the study from Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University Animal Experiments Local Ethics Committee for the study on 03.08.2018 with the file number 2018/1800109498. All the procedures performed in this study were carried in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration standards.
Conflict of interest
There have no conflict of interest between authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cokyaman, T., Oztopuz, O., Coskun, O. et al. The effect of medical ozone on oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in the early stage after experimental status epilepticus. Biologia 76, 3875–3882 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00911-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00911-w