Abstract
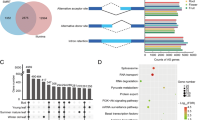
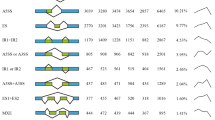
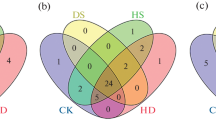
Tea, the important cash crop and globally most consumed beverage, are precariously sensitive to the climatic conditions. Numerous biotic and abiotic stress challenges are upsetting their growth and quality to a severe extent in recent years. Alternative splicing is a leading molecular mechanism to increase the transcript diversity and regulate the gene expression to cope with stress injuries. Members of WRKY gene family play an essential role in safeguarding the plant during such biotic and abiotic hassles. This study aimed to explore the dynamics of splicing and differential expression in tea plant WRKY genes under diverse conditions. A total of 61 transcriptomes across different tissues and conditions were selected to identify the novel splicing event and expression profile within 80 WRKY genes of the tea plant. Almost half of the total WRKY genes differentially expressed and 37.5% genes are alternatively spliced across tissues and stress responses. Finally, TEA028167, TEA017542, TEA002467, TEA023777, and TEA008808 were elucidated to have most significant variations in expression and splicing along the physiological ascents. Functional consequences of the WRKY gene spliced variants are predicted to play an important role through compensation or competition with their corresponding full-length transcripts.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data retrieved from the global database (mentioned in the text), not deposited any.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Andrews S (2010) FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Babraham Bioinformatics, Babraham Institute, Cambridge
Babicki S, Arndt D, Marcu A, Liang Y, Grant JR, Maciejewski A, Wishart DS (2016) Heatmapper: web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W147–W153. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw419
Balazadeh S, Riaño-Pachón D, Mueller‐Roeber B (2008) Transcription factors regulating leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol 10:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2008.00088.x
Cao H, Yue C, Zhou Y, Wang L, Hao X, Yang Y, Wang X (2014) Molecular cloning and expression of a bZIP transcription factor gene CsbZIPl in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Acta Agron Sin 40:1702–1709
Chen F, Hu Y, Vannozzi A, Wu K, Cai H, Qin Y, Mullis A, Lin Z, Zhang L (2017) The WRKY transcription factor family in model plants and crops. Crit Rev Plant Sci 36:311–335. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2018.1441103
Cheng Y, Ahammed GJ, Yu J, Yao Z, Ruan M, Ye Q, Li Z, Wang R, Feng K, Zhou G (2016) Putative WRKYs associated with regulation of fruit ripening revealed by detailed expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in pepper. Sci Rep 6:39000. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39000
Denti L, Rizzi R, Beretta S, Della Vedova G, Previtali M, Bonizzoni P (2018) ASGAL: aligning RNA-Seq data to a splicing graph to detect novel alternative splicing events. BMC Bioinform 19:444. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2436-3
Ding Y, Wang Y, Qiu C, Qian W, Xie H, Ding Z (2020) Alternative splicing in tea plants was extensively triggered by drought, heat and their combined stresses. PeerJ 8:e8258. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8258
Dong J, Chen C, Chen Z (2003) Expression profiles of the Arabidopsis WRKY gene superfamily during plant defense response. Plant Mol Biol 51:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020780022549
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Frey K, Pucker B (2020) Animal, fungi, and plant genome sequences harbor different non-canonical splice sites. Cells 9:458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020458
Hazra A, Dasgupta N, Sengupta C, Das S (2018) Next generation crop improvement program: Progress and prospect in tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Ann Agrar Sci 16:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aasci.2018.02.002
Hazra A, Dasgupta N, Sengupta C, Kumar R, Das S (2018) On some biochemical physiognomies of two common Darjeeling tea cultivars in relation to blister blight disease. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 51:915–926. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235408.2018.1522696
Hazra A, Kumar R, Sengupta C, Das S (2021) Genome-wide SNP discovery from Darjeeling tea cultivars-their functional impacts and application toward population structure and trait associations. Genomics 113:66–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.11.028
Hazra A, Saha S, Dasgupta N, Kumar R, Sengupta C, Das S (2021) Ecophysiological traits differentially modulate secondary metabolite accumulation and antioxidant properties of tea plant [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze]. Sci Rep 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-82454-3
Kim D, Paggi JM, Park C, Bennett C, Salzberg SL (2019) Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat Biotechnol 37:907–915. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0201-4
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Laloum T, Martín G, Duque P (2018) Alternative splicing control of abiotic stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 23:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.09.019
Li C-F, Zhu Y, Yu Y, Zhao Q-Y, Wang S-J, Wang X-C, Yao M-Z, Luo D, Li X, Chen L (2015) Global transcriptome and gene regulation network for secondary metabolite biosynthesis of tea plant (Camellia sinensis). BMC Genomics 16:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1773-0
Li W, Wang H, Yu D (2016) Arabidopsis WRKY transcription factors WRKY12 and WRKY13 oppositely regulate flowering under short-day conditions. Mol Plant 9:1492–1503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.08.003
Li Y, Mi X, Zhao S, Zhu J, Guo R, Xia X, Liu L, Liu S, Wei C (2020) Comprehensive profiling of alternative splicing landscape during cold acclimation in tea plant. BMC Genomics 21:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6491-6
Liu J, Chen X, Liang X, Zhou X, Yang F, Liu J, He SY, Guo Z (2016) Alternative splicing of rice WRKY62 and WRKY76 transcription factor genes in pathogen defense. Plant Physiol 171:1427–1442. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01921
Maeo K, Hayashi S, Kojima-Suzuki H, Morikami A, Nakamura K (2001) Role of conserved residues of the WRKY domain in the DNA-binding of tobacco WRKY family proteins. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:2428–2436. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.65.2428
Ner-Gaon H, Halachmi R, Savaldi‐Goldstein S, Rubin E, Ophir R, Fluhr R (2004) Intron retention is a major phenomenon in alternative splicing in Arabidopsis. Plant J 39:877–885. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02172.x
Qiao D, Yang C, Chen J, Guo Y, Li Y, Niu S, Cao K, Chen Z (2019) Comprehensive identification of the full-length transcripts and alternative splicing related to the secondary metabolism pathways in the tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Sci Rep 9:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39286-z
Ramamoorthy R, Jiang S-Y, Kumar N, Venkatesh PN, Ramachandran S (2008) A comprehensive transcriptional profiling of the WRKY gene family in rice under various abiotic and phytohormone treatments. Plant Cell Physiol 49:865–879. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcn061
Reddy AS, Marquez Y, Kalyna M, Barta A (2013) Complexity of the alternative splicing landscape in plants. Plant Cell 25:3657–3683. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.117523
Richardson DN, Rogers MF, Labadorf A, Ben-Hur A, Guo H, Paterson AH, Reddy AS (2011) Comparative analysis of serine/arginine-rich proteins across 27 eukaryotes: insights into sub-family classification and extent of alternative splicing. PLoS One 6:e24542. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024542
Scarpeci TE, Zanor MI, Mueller-Roeber B, Valle EM (2013) Overexpression of AtWRKY30 enhances abiotic stress tolerance during early growth stages in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 83:265–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0090-8
Shi C-Y, Yang H, Wei C-L, Yu O, Zhang Z-Z, Jiang C-J, Sun J, Li Y-Y, Chen Q, Xia T (2011) Deep sequencing of the Camellia sinensis transcriptome revealed candidate genes for major metabolic pathways of tea-specific compounds. BMC Genomics 12:131. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-131
Thorvaldsdóttir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP (2013) Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform 14:178–192. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbs017
Ülker B, Somssich IE (2004) WRKY transcription factors: from DNA binding towards biological function. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:491–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2004.07.012
Vera Alvarez R, Pongor LS, Mariño-Ramírez L, Landsman D (2019) TPMCalculator: one-step software to quantify mRNA abundance of genomic features. Bioinformatics 35:1960–1962. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty896
Wang X, Yan Y, Li Y, Chu X, Wu C, Guo X (2014) GhWRKY40, a multiple stress-responsive cotton WRKY gene, plays an important role in the wounding response and enhances susceptibility to Ralstonia solanacearum infection in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS One 9:e93577. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093577
Wang Y, Shu Z, Wang W, Jiang X, Li D, Pan J, Li X (2016) CsWRKY2, a novel WRKY gene from Camellia sinensis, is involved in cold and drought stress responses. Biol Plant 60:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0618-2
Wang L, Cao H, Qian W, Yao L, Hao X, Li N, Yang Y, Wang X (2017) Identification of a novel bZIP transcription factor in Camellia sinensis as a negative regulator of freezing tolerance in transgenic arabidopsis. Ann Bot 119:1195–1209. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx011
Wang P, Yue C, Chen D, Zheng Y, Zhang Q, Yang J, Ye N (2019) Genome-wide identification of WRKY family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Genes Genomics 41:17–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0734-9
Wei K-F, Chen J, Chen Y-F, Wu L-J, Xie D-X (2012) Molecular phylogenetic and expression analysis of the complete WRKY transcription factor family in maize. DNA Res 19:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsr048
Wu GA, Terol J, Ibanez V, López-García A, Pérez-Román E, Borredá C, Domingo C, Tadeo FR, Carbonell-Caballero J, Alonso R (2018) Genomics of the origin and evolution of Citrus. Nature 554:311–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25447
Xia EH, Li FD, Tong W, Li PH, Wu Q, Zhao HJ, Ge RH, Li RP, Li YY, Zhang ZZ (2019) Tea Plant Information Archive: a comprehensive genomics and bioinformatics platform for tea plant. Plant Biotechnol J 17:1938–1953. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13111
Xie Z, Zhang Z-L, Hanzlik S, Cook E, Shen QJ (2007) Salicylic acid inhibits gibberellin-induced alpha-amylase expression and seed germination via a pathway involving an abscisic-acid-inducible WRKY gene. Plant Mol Biol 64:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9152-0
Yan H, Jia H, Chen X, Hao L, An H, Guo X (2014) The cotton WRKY transcription factor GhWRKY17 functions in drought and salt stress in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana through ABA signaling and the modulation of reactive oxygen species production. Plant Cell Physiol 55:2060–2076. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu133
Yan X, Sablok G, Feng G, Ma J, Zhao H, Sun X (2015) nagnag: Identification and quantification of NAGNAG alternative splicing using RNA-Seq data. FEBS Lett 589:1766–1770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.05.029
Zheng J, Liu F, Zhu C, Li X, Dai X, Yang B, Zou X, Ma Y (2019) Identification, expression, alternative splicing and functional analysis of pepper WRKY gene family in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. PlLoS One 14:e0219775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219775
Zhu J, Wang X, Guo L, Xu Q, Zhao S, Li F, Yan X, Liu S, Wei C (2018) Characterization and alternative splicing profiles of the lipoxygenase gene family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Cell Physiol 59:1765–1781. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy091
Zhu J, Wang X, Xu Q, Zhao S, Tai Y, Wei C (2018) Global dissection of alternative splicing uncovers transcriptional diversity in tissues and associates with the flavonoid pathway in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). BMC Plant Biol 18:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1497-9
Hazra A, Dasgupta N, Sengupta C, Bera B, Das S (2019) Tea: A worthwhile, popular beverage crop since time immemorial. In: Agronomic Crops. Springer, Berlin, pp 507–531
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R (2009) Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. 2009. The Sequence alignment/map (SAM) format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 1000:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Sen S, Rai M, Das D, Chandra S, Acharya K (2020) Blister blight a threatened problem in tea industry: A review. J King Saud Univ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2020.09.008
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Luca Denti, for the guidance to run the docker version of ASGAL., The authors are also thankful to Secretariat, National Tea Research Foundation, Kolkata for administrative support. Authors are also thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their enormous support toward improvement of the earlier version of manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
Authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahadani, P., Hazra, A. Expression and splicing dynamics of WRKY family genes along physiological exigencies of tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Biologia 76, 2491–2499 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00784-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00784-z