Abstract
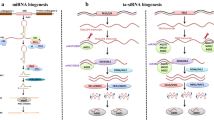
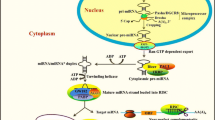
Numerous types of small RNAs play an important role in sustainable agricultural plant productivity. The micro RNAs (miRNAs) are tiny, 20–24 nt (nucleotides) long, endogenous RNA derived from double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and their complex biogenesis process will finally yield mature functional miRNAs after multiple events. Among different small RNAs, miRNAs have been mainly studied in plants for their applications that begin from transcriptional regulation of photosynthesis, nutritional homeostasis, growth, and development, yield along with tolerance to various types of stresses including a/biotic stresses. Tissue and stress-specific expression of miRNAs ultimately indicate spatial and temporal regulation of miRNA accumulation and target expression. The approaches of functional genomics studies using gene knock-out and knock-in approaches have been implicated that miRNAs are participated in the developmental process, adaptation to various stresses, enhanced utilization of micronutrients. In this review, we discussed the details on the mechanism and biogenesis of miRNA. Besides, their potential role in phytohormone crosstalk, homeostasis of nutrients, plant growth and development as well as their response to various abiotic stresses. Therefore, elucidation of the detailed molecular mechanism of the regulation of miRNAs with the response to various biotic and abiotic stresses along with spatial/temporal types facilitates the augmentation of improved agronomic traits in crop plants.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- miRNAs:
-
Micro RNAs
- dsRNA:
-
Double-stranded RNA
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- Nt:
-
Nucleotides
- DCL1:
-
Dicer like 1
- HYL1 :
-
Hyponastic leaves 1
- HEN1:
-
HUA Enhancer 1
- AGO1:
-
Argonaute 1
- ESTs:
-
Expressed sequence tags
- RISC:
-
RNA-induced silencing complex
- DDL:
-
Dawdle protein
- MEL1:
-
Meiosis Arrested at Leptotene 1
- HESO1:
-
HEN1 suppressor1
- SLIM1:
-
Sulfur Limitation1
- RAM:
-
Root apical meristem
- SAM:
-
Shoot apical meristem
- siRNAs:
-
Short interfering RNAs
- hpRNAs:
-
Hairpin RNAs
- CUC1:
-
Cup-shaped cotyledon1
References
Abdel-Ghany SE, Pilon M (2008) microRNA-mediated systemic down-regulation of copper protein expression in response to low copper availability in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 283:15932–15945. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M801406200
Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC (2005) microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.004
Ardito F, Giuliani M, Perrone D, Troiano G, Lo Muzio L (2017) The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling and its use as targeted therapy. Int J Mol Med 40(2):271–280. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.3036
Baek D, Chun HJ, Yun DJ, Kim MC (2017) Crosstalk between phosphate starvation and other environmental stress signaling pathways in plants. Mol Cells 40:697–705. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.0192
Baek D, Kim MC, Chun HJ, Kang S, Park HC, Shin G, Park J, Shen M, Hong H, Kim WJ, Kim DH, Lee SY, Bressan RA, Bohnert HJ, Yun DJ (2013) Regulation of miR399f transcription by AtMYB2 affects phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 161:362–373. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.205922
Bajczyk M, Bhat SS, Szewc L, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Jarmolowski A, Dolata J (2019) Novel nuclear functions of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1: Beyond RNA interference. Plant Physiol 179(3):1030–1039. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01351
Bakhshi B, MohseniFard E, Nikpay N, Ebrahimi MA, Bihamta MR, Mardi M, Salekdeh GH (2016) microRNA signatures of drought signaling in rice root. PloS One 11(6):e0156814. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156814
Barrera-Figueroa BE, Gao L, Wu Z, Zhou X, Zhu J, Jin H, Liu R, Zhu JK (2012) High throughput sequencing reveals novel and abiotic stress-regulated microRNAs in the inflorescences of rice. BMC Plant Biol 12:132. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-132
Basu S, Ramegowda V, Kumar A, Pereira A (2016) Plant adaptation to drought stress. F1000Res 5:F1000 Faculty Rev-1554. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.7678.1
Beauclair L, Yu A, Bouché N (2010) microRNA-directed cleavage and translational repression of the copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase mRNA in Arabidopsis. Plant J 62:454–462. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04162.x
Bouzid M, He F, Schmitz G, Häusler RE, Weber A, Mettler-Altmann T, De Meaux J (2019) Arabidopsis species deploy distinct strategies to cope with drought stress. Annals Bot 124(1):27–40. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcy237
Branscheid A, Sieh D, Pant BD, May P, Devers EA, Elkrog A, Schauser L, Scheible W, Krajinski F (2010) Expression pattern suggests a role of MiR399 in the regulation of the cellular response to local Pi increase during arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 23:915–926. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-23-7-0915
Budak H, Akpinar A (2011) Dehydration stress-responsive miRNA in Brachypodium distachyon: evident by genome‐wide screening of microRNAs expression. Omics 15:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2011.0073
Carrió-Seguí À, Ruiz-Rivero O, Villamayor-Belinchón L, Puig S, Perea-García A, Peñarrubia L (2019) The altered expression of microRNA408 influences the Arabidopsis response to iron deficiency. Front Plant Sci 10:324. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00324
Cedillo-Jiménez CA, Hernández–Salazar M, Escobar-Feregrino T, Caballero-Pérez J, Arteaga-Vázquez M, Cruz-Ramírez A, Torres-Pacheco I, Guevara-González R, Cruz-Hernández A (2016) microRNAs sequencing for understanding the genetic regulation of plant genomes. Plant Genomics, Ibrokhim Y. Abdurakhmonov, IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/62203
Cheah BH, Nadarajah K, Divate MD, Wickneswari R (2015) Identification of four functionally important microRNA families with contrasting differential expression profiles between drought-tolerant and susceptible rice leaf at vegetative stage. BMC Genom 16(1):692. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1851-3
Chen J, Qi T, Hu Z, Fan X, Zhu L, Iqbal MF, Yin X, Xu G, Fan X (2019) OsNAR2.1 positively regulates drought tolerance and grain yield under drought stress conditions in rice. Front Plant Sci 10:197. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00197
Chen ZH, Bao ML, Sun YZ, Yang YJ, Xu XH, Wang JH, Han N, Bian HW, Zhu MY (2011) Regulation of auxin response bymiR393-targeted transport inhibitor response protein 1 is involved in normal development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 77:619–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9838-1
Choudhary A, Kumar A, Kaur H, Kaur N (2021) MiRNA: the taskmaster of plant world. Biologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00720-1
Cui J, You C, Chen X (2016) The evolution of microRNAs in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 35:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2016.11.006
Curaba J, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (2014) miRNAs in the crosstalk between phytohormone signalling pathways. J Exp Bot 65(6):1425–1438. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru002
D’Ario M, Griffiths-Jones S, Kim M (2017) Small RNAs: big impact on plant development. Trends Plant Sci 22(12):1056–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.09.009
Dangol SD, Yel I, Caliskan ME, Bakhsh A (2020) Manipulating genome of diploid potato inbred line Solanum chacoense M6 using selectable marker gene. Turk J Agric For 44:399–407. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1910-13
Das PR, Sherif SM (2020) Application of exogenous dsRNAs-induced RNAi in agriculture: Challenges and triumphs. Front Plant Sci 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00946
Dastidar MG, Scarpa A, Magele I, Ruiz-Duarte P, Born P, Bald L, Jouannet V, Maizel A (2019) ARF5/MONOPTEROS directly regulates miR390 expression in Arabidopsis thaliana primary root meristem. Plant Direct 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/pld3.116
Din M, Barozai MYK, Baloch IA (2014) Identification and functional analysis of new conserved microRNAs and their targets in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Turk J Bot 38:1199–1213. https://doi.org/10.3906/bot-1405-105
Ding B, Wang GL (2015) Chromatin versus pathogens: the function of epigenetics in plant immunity. Front Plant Sci 6:675. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00675
Ding Y, Tao Y, Zhu C (2013) Emerging roles of microRNAs in the mediation of drought stress response in plants. J Exp Bot 64:3077–3086. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert164
Dong Z, Han MH, Fedoroff N (2008) The RNA-binding proteinsHYL1 and SE promote accurate in vitro processing of pri-miRNA byDCL1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9970–9975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803356105
Drisch RC, Stahl Y (2015) Function and regulation of transcription factors involved in root apical meristem and stem cell maintenance. Front Plant Sci 6:505. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00505
Du Q, Wang H (2015) The role of HD-ZIP III transcription factors and miR165/166 in vascular development and secondary cell wall formation. Plant Signal Behav 10(10):e1078955. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2015.1078955
Du Q, Wang K, Zou C, Xu C, Li WX (2018) The PILNCR1-miR399 regulatory module is important for low phosphate tolerance in maize. Plant Physiol 177:1743–1753. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00034
Eamens AL, Smith NA, Curtin SJ, Wang MB, Waterhouse PM (2009) The Arabidopsis thaliana double-stranded RNA binding protein DRB1 directs guide strand selection from microRNA duplexes. RNA 15:2219–2235. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.1646909
Ferreira TH, Gentile A, Vilela RD, Costa GGL, Dias LI, Endres L, Menossi M (2012) microRNAs associated with drought response in the bioenergy crop sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). PLoS One 7:e46703. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046703
Formey D, Iñiguez LP, Peláez P, Li YF, Sunkar R, o Sánchez F, Reyes JL, Hernández G (2015) Genome-wide identification of the Phaseolus vulgariss RNAome using small RNA and degradome sequencing. BMC Genom 16:423. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1639-5
Fu Y, Yang Y, Chen S, Ning N, Hu H (2019a) Arabidopsis IAR4 modulates primary root growth under salt stress through ROS-mediated modulation of auxin distribution. Front Plant Sci 10:522. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00522
Fu XZ, Zhang XY, Qiu JY, Zhou X, Yuan M, He YZ, Chun CP, Cao L, Ling LL, Peng LZ (2019b) Whole transcriptome RNA sequencingreveals the global molecular responses and ceRNA regulatory network of mRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs and circRNAs in response to copper toxicity in Ziyang Xiangcheng (Citrus junos Sieb. Ex Tanaka). BMC Plant Biol 19:509. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2087-1
Gao P, Bai X, Yang L, Lv D, Pan X, Li Y, Cai H, Ji W, Chen Q, Zhu Y (2011) Osa-MIR393: a salinity- and alkaline stress-related microRNA gene. Mol Biol Rep 38:237–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0100-8
Gao P, Bai X, Yang L, Lv DK, Li Y, Cai H, Ji W, Guo D, Zhu Y (2010) Over-expression of osa-MIR396c decreases salt and alkali stress tolerance. Planta 231:991–1001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1104-2
Gifford ML, Dean A, Gutieerez RA, Coruzzi GM, Birnbaum KD (2008) Cell-specific nitrogen responses mediate developmental Arabidopsis plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:803–808. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709559105
Gonzalez-Carranza ZH, Zhang X, Peters JL, Boltz V, Szecsi J, Bendahmane M, Roberts JA (2017) HAWAIIAN SKIRT controls size and floral organ number by modulating CUC1 and CUC2 expression. PLos One 12(9):e0185106. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185106
Gu M, Xu K, Chen A, Zhu Y, Tang G, Xu G (2010) Expression analysis suggests potential roles of microRNAs for phosphate and arbuscular mycorrhizal signaling in Solanum lycopersicum. Physiol Plant 138:226–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2009.01320.x
Guo Q, Liu Q, Smith NA, Liang G, Wang MB (2016) RNA silencing in plants: Mechanisms, technologies and applications in horticultural crops. Curr Genomics 17(6):476–489. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202917666160520103117
Gutierrez L, Mongelard G, Floková K, Pacurar DI, Novák O, Staswick P, Kowalczyk M, Pacurar M, Demailly H, Geiss G, Bellini C (2012) Auxin controls Arabidopsis adventitious root initiation by regulating jasmonic acid homeostasis. Plant Cell 24(6):2515–2527. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.099119
Haak DC, Fukao T, Grene R, Hua Z, Ivanov R, Perrella G, Li S (2017) Multilevel regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. Front Plant Sci 8:1564. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01564
Hackenberg M, Huang PJ, Huang CY, Shi BJ, Gustafson P, Langridge P (2012) A comprehensive expression profile of microRNAs and other classes of non-coding small RNAs in barley under phosphorous deficient and -sufficient conditions. DNA Res 20:109–125. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095800
He H, Liang G, Li Y, Wang F, Yu D (2014) Two young MicroRNAs originating from target duplication mediate nitrogen starvation adaptation via regulation of glucosinolate synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 164(2):853–865. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.228635
Hou J, Lu D, Mason AS, Li B, Xiao M, An S, Fu D (2019) Non-coding RNAs and transposable elements in plant genomes: emergence, regulatory mechanisms and roles in plant development and stress responses. Planta 250(1):23–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03166-7
Hrtyan M, Šliková E, Hejátko J, Růžička K (2015) RNA processing in auxin and cytokinin pathways. J Exp Bot 66(16):4897–4912. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv189
Hsieh LC, Lin SI, Shih ACC, Chen JW, Lin WY, Tseng CY, Li WH, Chiou TJ (2009) Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing. Plant Physiol 151:2120–2132. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.147280
Hu B, Wang W, Deng K, Li H, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Chu C (2015) MicroRNA399 is involved in multiple nutrient starvation responses in rice. Front Plant Sci 6:188. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00188
Hu JY, Zhou Y, He F, Dong X, Liu LY, Coupland G, Turck F, de Meaux J (2014) miR824-regulated AGAMOUS-LIKE16 contributes to flowering time repression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:2024–2037. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.124685
Huang D, Koh C, Feurtado JA, Tsang EW, Cutler AJ (2013) MicroRNAs and their putative targets in Brassica napus seed maturation. BMC Genom 14:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-140
Huang J, Li Z, Zhao D (2016) Deregulation of the OsmiR160 target gene OsARF18 causes growth and developmental defects with an alteration of auxin signaling in rice. Sci Rep 6:29938. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29938
Jagadeeswaran G, Li YF, Sunkar R (2014) Redox signaling mediates the expression of a sulfate-deprivation inducible miR395 in Arabidopsis. Plant J 77:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12364
Jatan R, Lata C (2019) Role of MicroRNAs in abiotic and biotic stress resistance in plants. Proc Ind Nat Sci Acad 85:553–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0914-2
Jeong DH, Park S, Zhai J, Gurazada SG, De Paoli E, Meyers BC, Green PJ (2011) Massive analysis of rice small RNAs: mechanistic implications of regulated microRNAs and variants for differential target RNA cleavage. Plant Cell 23:4185–4207. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.089045
Jeong DH, Thatcher SR, Brown RS, Zhai J, Park S, Rymarquis LA, Meyers BC, Green PJ (2013) Comprehensive investigation of microRNAs enhanced by analysis of sequence variants, expression patterns, ARGONAUTE loading, and target cleavage. Plant Physiol 162:1225–1245. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.219873
Jerome Jeyakumar JM, Ali A, Wang WM, Thiruvengadam M (2020) Characterizing the role of the miR156-SPL network in plant development and stress response. Plants 9(9):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091206
Jin Q, Xue Z, Dong C, Wang Y, Chu L, Xu Y (2015) Identification and characterization of micrornas from treepeony (Paeoniaostii) and their response to copper stress. PLoS One 10:e0117584. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117584
Jover-Gil S, Candela H, Robles P, Aguilera V, Barrero JM, Micol JL, Ponce MR (2012) The microRNA pathway genes AGO1, HEN1 and HYL1 participate in leaf proximal–distal, venation and stomatal patterning in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 53:1322–1333. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcs077
Kamthan A, Chaudhuri A, Kamthan M, Datta A (2015) Small RNAs in plants: recent development and application for crop improvement. Front Plant Sci 6:208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00208
Kant S, Peng M, Rothstein SJ (2011) Genetic regulation by NLA and microRNA827 for maintaining nitrate-dependent phosphate homeostasis in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 7:e1002021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002021
Kantar M, Lucas S, Budak H (2011) miRNA expression patterns of Triticum dicoccoides in response to shock drought stress. Planta 233:471–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1309-4
Katiyar A, Smita S, Chinnusamy V, Pandey DM, Bansal KC (2012) Identification of miRNAs in Sorghum by using a bioinformatics approach. Plant Signal Behav 7:246–259. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.18914
Khraiwesh B, Zhu JK, Zhu J (2012) Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1819(2):137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.05.001
Kidner CA, Martienssen RA (2004) Spatially restricted microRNA directs leaf polarity through ARGONAUTE1. Nature 428(6978):81–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02366
Kim JA, Bhatnagar N, Kwon SJ, Min MK, Moon SJ, Yoon IS, Kwon TR, Kim ST, Kim BG (2018) Transcriptome analysis of ABA/JA-dual responsive genes in rice shoot and root. Curr Genomics 19(1):4–11. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202918666170228134205
Kim JY, Lee HJ, Jung HJ, Maruyama K, Suzuki N, Kang H (2010) Overexpression of microRNA395c or 395e affects differently the seed germination of Arabidopsis thaliana under stress conditions. Planta 232:1447–1454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1267-x
Koc I, Filiz E, Tombuloglu H (2015) Assessment of miRNA expression profile and differential expression pattern of target genes in cold-tolerant and cold-sensitive tomato cultivars. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 29:851–860. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2015.1061447
Komiya R, Ohyanagi H, Niihama M, Watanabe T, Nakano M, Kurata N, Nonomura K (2014) Rice germline-specific Argonaute MEL1 protein binds to phasiRNAs generated from more than 700 lincRNAs. Plant J 78(3):385–397. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12483
Kong X, Zhang M, Xu X, Li X, Li C, Ding Z (2014) System analysis of microRNAs in the development and aluminium stress responses of the maize root system. Plant Biotechnol J 12:1108–1121. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12218
Koroban NV, Kudryavtseva AV, Krasnov GS, Sadritdinova AF, Fedorova MS, Snezhkina AV, Bolsheva NL, Muravenko OV, Dmitriev AA, Melnikova NV (2016) The role of microRNA in abiotic stress response in plants. Mol Biol 50:337–343. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0026898416020105
Kouhi F, Sorkheh K, Ercisli S (2020) MicroRNA expression patterns unveil differential expression of conserved miRNAs and target genes against abiotic stress in safflower. PLoS One 15(2):e0228850. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228850
Koyama T, Sato F, Ohme-Takagi M (2017) Roles of miR319 and TCP transcription factors in leaf development. Plant Physiol 175(2):874–885. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00732
Kulcheski FR, Côrrea R, Gomes IA, de Lima JC, Margis R (2015) NPK macronutrients and microRNA homeostasis. Front Plant Sci 6:451. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00451
Kumar N, Iyer-Pascuzzi AS (2020) Shedding the last layer: Mechanisms of root cap cell release. Plants 9:308. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9030308
Kumar S, Verma S, Trivedi PK (2017) Involvement of small RNAs in phosphorus and sulfur sensing, signaling and stress: Current update. Front Plant Sci 8:285. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00285
Kuo HF, Chiou TJ (2011) The role of microRNAs in phosphorus deficiency signaling. Plant Physiol 156(3):1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175265
Lantzouni O, Alkofer A, Falter-Braun P, Schwechheimer C (2020) Growth-regulating factors interact with DELLAs and regulate growth in cold stress. Plant Cell 32(4):1018–1034. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00784
Lau S, Jürgens G, De Smet I (2008) The evolving complexity of the auxin pathway. Plant Cell 20(7):1738–1746. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.060418
Leyser O (2018) Auxin signaling. Plant Physiol 176:465–479. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00765
Li B, Duan H, Li J, Deng XW, Yin W, Xia X (2013) Global identification of miRNAs and targets in Populus euphratica under salt stress. Plant Mol Biol 81(6):525–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0010-y
Li XJ, Li M, Zhou Y, Hu S, Hu R, Chen Y, Li XB (2015) Overexpression of cotton RAV1 gene in Arabidopsis confers transgenic plants high salinity and drought sensitivity. PloS One 10(2):e0118056. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118056
Li Y, Wan L, Bi S, Wan X, Li Z, Cao J, Tong Z, Xu H, He F, Li X (2017) Identification of drought-responsive microRNAs from roots and leaves of Alfalfa by high-throughput sequencing. Genes 8(4):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8040119
Lian C, Yao K, Duan H, Li Q, Liu C, Yin W, Xia X (2018) Exploration of ABA responsive miRNAs reveals a new hormone signaling crosstalk pathway regulating root growth of Populus euphratica. Int J Mol Sci 19(5):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051481
Liang G, Ai Q, Yu D (2015) Uncovering miRNAs involved in crosstalk between nutrient deficiencies in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep 5:11813. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11813
Liang G, He H, Yu D (2012) Identification of nitrogen starvation-responsive microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One 7:e48951. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048951
Liang G, Yang FX, Yu DQ (2010) MicroRNA395 mediates regulation of sulfate accumulation and allocation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 62:1046–1057. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04216.x
Lin Y, Lai Z, Tian Q, Lin L, Lai R, Yang M, Zhang D, Chen Y, Zhang Z (2015) Endogenous target mimics down-regulate miR160 mediation of ARF10, -16, and – 17 cleavage during somatic embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan Lour. Front Plant Sci 6:956. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00956
Liu C, Xin Y, Xu L, Cai ZK, Xue YC, Liu Y, Qi Y (2018) Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE 1 binds chromatin to promote gene transcription in response to hormones and stresses. Dev Cell 44:348–361.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.12.002
Liu Y, ElKassaby YA (2017) Regulatory crosstalk between microRNAs and hormone signalling cascades controls the variation on seed dormancy phenotype at Arabidopsis thaliana seed set. Plant Cell Rep 36:705–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2111-6
Liu Z, Jia L, Wang H, He Y (2011) HYL1 regulates the balance between adaxial and abaxial identity for leaf flattening via miRNA-mediated pathways. J Exp Bot 62:4367–4381. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err167
Lu SF, Sun YH, Shi R, Clark C, Li LG, Chiang VL (2005) Novel and mechanical stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus trichocarpa that are absent from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:2186–2203. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.033456
Lu Y, Feng Z, Liu X, Bian L, Xie H, Zhang C, Mysore KS, Liang J (2018) MiR393 and miR390 synergistically regulate lateral root growth in rice under different conditions. BMC Plant Biol 18(1):261. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1488-x
Luo J, Zhou JJ, Zhang JZ (2018) Aux/IAA gene family in plants: Molecular structure, regulation, and function. Int J Mol Sci 19(1):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010259
Ma CL, Qi YP, Liang WW, Yang LT, Lu YB, Guo P, Ye X, Chen LS (2016) MicroRNA regulatory mechanisms on Citrus sinensis leaves to magnesium deficiency. Front Plant Sci 7:201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00201
Manavella PA, Yang SW, Palatnik J (2019) Keep calm and carry on: miRNA biogenesis under stress. Plant J 99:832–843. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14369
Marin E, Jouannet V, Herz A, Lokerse AS, Weijers D, Vaucheret H, Nussaume L, Crespi MD, Maizel A (2010) miR390, Arabidopsis TAS3 tasiRNAs, and their AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR targets define an auto regulatory network quantitatively regulating lateral root growth. Plant Cell 22:1104–1117. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.072553
Massah J, Vakilian K, Torktaz S (2019) Supervised machine learning algorithms can predict penetration resistance in mineral-fertilized soils. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 50(17):2169–2177. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2019.1654505
Medina CR, Atkins CA, Mann AJ, Jordan ME, Smith PMC (2011) Macromolecular composition of phloem exudate from white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). BMC Plant Biol 11:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-36
Michlewski G, Cáceres JF (2019) Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis. RNA J 25(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.068692.118
Millar AA, Lohe A, Wong G (2019) Biology and function of miR159 in plants. Plants 8:255. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8080255
Miyashima S, Honda M, Hashimoto K, Tatematsu K, Hashimoto T, Sato-Nara K, Okada K, Nakajima K (2013) A comprehensive expression analysis of the ArabidopsisMICRORNA165/6gene family during embryogenesis reveals a conserved role in meristem specification and a non-cell-autonomous function. Plant Cell Physiol 54:375–384. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcs188
Morris KV, Mattick JS (2014) The rise of regulatory RNA. Nat Rev Genet 15(6):423–437. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3722
Nadarajah K, Kumar IS (2019) Drought response in rice: The miRNA story. Int J Mol Sci 20(15):3766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153766
Naya L, Paul S, Valde ́s-Lo ́pez O, Mendoza-Soto AB, Nova-Franco B, Sosa-Valencia G, Reyes JL, Hernández G (2014) Regulation of copper homeostasis and biotic interactions by MicroRNA398b in common bean. PLoS One 9(1):e84416. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084416
Nguyen TCT, Obermeier C, Friedt W, Abrams SR, Snowdon RJ (2016) Disruption of germination and seedling development in Brassica napus by mutations causing severe seed hormonal imbalance. Front Plant Sci 7:322. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00322
Nizampatnam NR, Schreier SJ, Damodaran S, Adhikari S, Subramanian S (2015) microRNA160 dictates stage-specific auxin and cytokinin sensitivities and directs soybean nodule development. Plant J 84:140–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12965
Noman A, Aqeel M (2017) miRNA-based heavy metal homeostasis and plant growth. Env Sci Pollu Res 24:10068–10082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8593-5
Oliver C, Pradillo M, Jover-Gil S, Cuñado N, Ponce MR, Santos JL (2017) Loss of function of Arabidopsis microRNA-machinery genes impairs fertility and has effects on homologous recombination and meiotic chromatin dynamics. Sci Rep 7(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07702-x
Olmedo-Monfil V, Durán-Figueroa N, Arteaga-Vázquez M, Demesa-Arévalo E, Autran D, Grimanelli D, Slotkin RK, Martienssen RA, Vielle-Calzada JA (2010) Control of female gamete formation by a small RNA pathway in Arabidopsis. Nature 464:628–632. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08828
Omidvar V, Mohorianu I, Dalmay T, Fellner M (2015) Identification of miRNAs with potential roles in the regulation of anther development and male-sterility in 7B-1 male-sterile tomato mutant. BMC Genom 16:878. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2077-0
Ozhuner E, Eldem V, Ipek A, Okay S, Sakcali S, Zhang B, Boke H, Unver T (2013) Boron stress-responsive microRNAs and their targets in barley. PloS One 8(3):e59543. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059543
Panda SK, Sunkar R (2015) Nutrient- and other stress-responsive microRNAs in plants: Role for thiol-based redox signaling. Plant Signal Behav 10(4):e1010916. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2015.1010916
Pant BD, Musialak-Lange M, Nuc P, May P, Buhtz A, Kehr J, Walther D, Scheible WR (2009) Identification of nutrient-responsive Arabidopsis and rapeseed microRNAs by comprehensive real-time polymerase chain reaction profiling and small RNA sequencing. Plant Physiol 150(3):1541–1555. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.139139
Paolo SD, Gaudio L, Aceto S (2015) Analysis of the TCP genes expressed in the inflorescence of the orchid Orchisitalica. Sci Rep 5:16265. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16265
Parmer S, Shaw BP (2018) Salt stress tolerance in plants: the role of miRNAs. Adv Plants Agric Res 8(6):411–415. https://doi.org/10.15406/apar.2018.08.00360
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Müller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408(6808):86–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/35040556
Paul S, Datta SK, Datta K (2015) miRNA regulation of nutrient homeostasis in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:232. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00232
Penfield S, MacGregor DR (2017) Effects of environmental variation during seed production on seed dormancy and germination. J Exp Bot 68(4):819–825. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw436
Peng T, Sun HZ, Du Y, Zhang J, Li JZ, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Zhao Q (2013) Characterization and expression patterns of micro RNAs involved in rice grain filling. PLoS One 8(1):e54148. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054148
Pilon M (2017) The copper microRNAs. New Phytol 213:1030–1035. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14244
Pomeranz MC, Hah C, Lin PC, Kang SG, Finer JJ, Blackshear PJ, Jang JC (2010) The Arabidopsis tandem zinc finger protein AtTZF1 traffics between the nucleus and cytoplasmic foci and binds both DNA and RNA. Plant Physiol 152(1):151–165. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.145656
Prigge MJ, Platre M, Kadakia N, Zhang Y, Greenham K, Szutu W, Pandey BK, Bhosale RA, Bennett MJ, Busch W, Estelle M (2020) Genetic analysis of the Arabidopsis TIR1/AFB auxin receptors reveals both overlapping and specialized functions. Dev Biol Plant Biol 9:e54740. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.54740
Rhoades J, Bartel DP, Bartel B (2006) MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:19–53. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105218
Rosas Cárdenas FDF, Suárez YR, Cano Rangel RM, Garcia VL, González Aguilera KL, Martínez NM, Folter SD (2017) Effect of constitutive miR164 expression on plant morphology and fruit development in Arabidopsis and tomato. Agronomy 7:48. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy7030048
Roychoudhry S, Kieffer M, Bianco MD, Liao CY, Weijers D, Kepinski S (2017) The developmental and environmental regulation of gravitropic setpoint angle in Arabidopsis and bean. Sci Rep 7:42664. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42664
Samad AFA, Sajad M, Nazaruddin N, Fauzi IA, Murad AMA, Zainal Z, Ismail I (2017) MicroRNA and transcription factor: Key players in plant regulatory network. Front Plant Sci 8:565. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00565
Sanz-Carbonell A, Marques MC, Bustamante A, Fares MA, Rodrigo G, Gomez G (2019) Inferring the regulatory network of the miRNA-mediated response to biotic and abiotic stress in melon. BMC Plant Biol 19:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1679-0
Schommer C, Palatnik JF, Aggarwal P, Chételat A, Cubas P, Farmer EE, Nath U, Weigel D (2008) Control of jasmonate biosynthesis and senescence by miR319 targets. PLoS Biol 6(9):e230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060230
Schulten A, Bytomski L, Quintana J, Bernal M, Krämer U (2019) Do Arabidopsis Squamosapromoter binding protein-like genes act together in plant acclimation to copper or zinc deficiency? Plant Direct 3(7):e00150. https://doi.org/10.1002/pld3.150
Sharma N, Tripathi A, Sanan-Mishra N (2015) Profiling the expression domains of a rice-specific microRNA under stress. Front Plant Sci 6:333. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00333
Shriram V, Kumar V, Devarumath RM, Khare TS, Wani SH (2016) MicroRNAs as potential targets for abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Front Plant Sci 7:817. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00817
Shuai P, Liang D, Zhang Z, Yin W, Xia X (2013) Identification of drought-responsive and novel Populus trichocarpa microRNAs by high throughput sequencing and their targets using degradome analysis. BMC Genom 14:233. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-233
Si-Ammour A, Windels D, Arn-Bouldoires E, Kutter C, Ailhas J, Meins F (2011) miR393 and secondary siRNAs regulate expression of the TIR1/AFB2 auxin receptor clade and auxin-related development of Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol 157:683–691. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.180083
Singh M, Goel S, Meeley RB, Dantec C, Parrinello H, Michaud C, Leblanc O, Grimanelli D (2011) Production of viable gametes without meiosis in maize deficient for an ARGONAUTE protein. Plant Cell 23(2):443–458. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.079020
Skubacz A, Daszkowska-Golec A, Szarejko I (2016) The role and regulation of ABI5 (ABA-Insensitive 5) in plant development, abiotic stress responses and phytohormone crosstalk. Front Plant Sci 7:1884. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01884
Speth C, Willing EM, Rausch S, Schneeberger K, Laubinger S (2013) RACK1 scaffold proteins influence miRNA abundance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 76(3):433–445. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12308
Srivastava S, Srivastava AK, Suprasanna P, D'souza SF (2013) Identification and profiling of arsenic stress-induced microRNAs in Brassica juncea. J Exp Bot 64:303–315. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers333
Sun F, Guo G, Du J, Guo W, Peng H, Ni Z, Sun Q, Yao Y (2014) Whole-genome discovery of miRNAs and their targets in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol 14:142. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-142
Sunkar R, Li YF, Jagadeeswaran G (2012) Functions of microRNAs in plant stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 17:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.01.010
Swapna M, Kumar S (2017) MicroRNAs and their regulatory role in sugarcane. Front Plant Sci 8:997. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00997
Takatsuka H, Umeda M (2014) Hormonal control of cell division and elongation along differentiation trajectories in roots. J Exp Bot 65(10):2633–2643. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert485
Tian H, Lv B, Ding T, Bai M, Ding Z (2018) Auxin-BR interaction regulates plant growth and development. Front Plant Sci 18:2256. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02256
Vakilian KA (2020) Machine learning improves our knowledge about miRNA functions towards plant abiotic stresses. Sci Rep 10:3041. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59981-6
Vanstraelen M, Benkova E (2012) Hormonal interactions in the regulation of plant development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28:463–487. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101011-155741
Varallyay E, Havelda Z (2013) Unrelated viral suppressors of RNA silencing mediate the control of ARGONAUTE1 level. Mol Plant Pathol 14(6):567–575. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12029
Vives-Peris V, Ollas CD, Gómez-Cadenas A, Pérez-Clemente RM (2020) Root exudates: from plant to rhizosphere and beyond. Plant Cell Rep 39:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02447-5
Voinnet O (2009) Origin, biogenesis, and activity of plant microRNAs. Cell 136:669–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.046
Waheed S, Zeng L (2020) The critical role of miRNAs in regulation of flowering time and flower development. Genes 11(3):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030319
Wang Y, Chen R (2014) Regulation of compound leaf development. Plants 3:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010867
Wang T, Chen L, Zhao M, Tian Q, Zhang WH (2011a) Identification of drought-responsive microRNAs in Medicago truncatula by genome-wide high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genom 12:367. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-367
Wang L, Gu X, Xu D, Wang W, Wang H, Zeng M, Cui X (2011b) MiR396-targeted AtGRF transcription factors are required for coordination of cell division and differentiation during leaf development in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 62:761–773. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq307
Wang C, Huang W, Ying Y, Li S, Secco D, Tyerman S (2012) Functional characterization of the rice SPX-MFS family reveals a key role of OsSPX‐MFS1 in controlling phosphate homeostasis in leaves. New Phytol 196:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04227.x
Wang Y, Li K, Chen L, Zou Y, Liu H, Tian Y, Li D, Wang R, Zhao F, Ferguson BJ, Gresshoff PM, Li X (2015) MicroRNA167-directed regulation of the auxin response factors GmARF8a and GmARF8b is required for soybean nodulation and lateral root development. Plant Physiol 168(3):984–999. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00265
Wang J, Meng X, Dobrovolskaya OB, Orlov YL, Chen M (2017) Non-coding RNAs and their roles in stress response in plants. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 15:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2017.01.007
Wang J, Mei J, Ren G (2019) Plant microRNAs: Biogenesis, homeostasis, and degradation. Front Plant Sci 10:360. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00360
Wani SH, Kumar V, Khare T, Tripathi P, Shah T, Ramakrishna C, Aglawe S, Mangrauthia SK (2020) miRNA applications for engineering abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Biologia 75:1063–1081. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00397-7
Wójcik AM, Nodine MD, Gaj MD (2017) miR160 and miR166/165 contribute to the LEC2-mediated auxin response involved in the somatic embryogenesis induction in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 8:2024. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02024
Wollmann H, Mica E, Todesco M, Long JA, Weigel D (2010) On reconciling the interactions between APETALA2,miR172and AGAMOUS with the ABC model of flower development. Development 137:3633–3642. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.036673
Wu L, Tian Z, Zhang J (2018) Functional dissection of auxin response factors in regulating tomato leaf shape development. Front Plant Sci 9:957. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00957
Xia K, Wang R, Ou X, Fang Z, Tian C, Duan J, Wang Y, Zhang M (2012) OsTIR1 and OsAFB2 downregulation via OsmiR393 overexpression leads to more tillers, early flowering and less tolerance to salt and drought in rice. PLoS One 7:e30039. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030039
Xie F, Zhang B (2015) microRNA evolution and expression analysis in polyploidized cotton genome. Plant Biotechnol J 13:421–434. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12295
Xie J, Yang X, Song Y, Du Q, Li Y, Chen J, Zhang D (2017) Adaptive evolution and functional innovation of Populus-specific recently evolved microRNAs. New Phytol 213(1):470. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14046
Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2003) Negative feedback regulation of Dicer-like1 in Arabidopsis by microRNA-guided mRNA degradation. Current Biol 13:784–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00281-1
Xu MY, Zhang L, Li WW, Hu XL, Wang MB, Fan YL, Zhang CY, Wang L (2014) Stress-induced early flowering is mediated by miR169 in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 65:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert353
Yamasaki H, Hayashi M, Fukazawa M, Kobayashi Y, Shikanai T (2009) SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein-like7 is a central regulator for copper homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21(1):347–361. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.060137
Yang C, Li D, Mao D, Liu X, Ji C, Li X, Zhao X, Cheng Z, Chen C, Zhu L (2013) Overexpression of microRNA319 impacts leaf morphogenesis and leads to enhanced cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Env 36:2207–2218. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12130
Yang Y, Zhang X, Su Y, Zou J, Wang Z, Xu L, Que Y (2017) miRNA alteration is an important mechanism in sugarcane response to low-temperature environment. BMC Genom 18:833. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4231-3
Yao X, Chen J, Zhou J, Yu H, Ge C, Zhang M, Gao X, Dai X, Yang ZN, Zhao Y (2019) An essential role for miRNA167 in maternal control of embryonic and seed development. Plant Physiol 180(1):453–464. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00127
You C, Cui J, Wang H, Qi X, Kuo LY, Ma H, Gao L, Mo B, Chen X (2017) Conservation and divergence of small RNA pathways and microRNAs in land plants. Genome Biol 18(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1291-2
Zeng Q, Yang C, Ma Q, Li X, Dong W, Nian H (2012) Identification of wild soybean miRNAs and their target genes responsive to aluminum stress. BMC Plant Biol 12:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-182
Zhang B (2015) MicroRNA: a new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 66(7):1749–1761. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv013
Zhang H, Liu X, Yang X, Wu H, Zhu J, Zhang H (2020) miRNA-mRNA integrated analysis reveals roles for miRNAs in a typical halophyte, Reaumuria soongorica, during seed germination under salt stress. Plants 9(3):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9030351
Zhang H, Xia R, Meyers BC, Walbot V (2015) Evolution, functions, and mysteries of plant ARGONAUTE proteins. Curr Opin Plant Biol 27:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2015.06.011
Zhang L, Yao L, Zhang N, Yang J, Zhu X, Tang X, Calderón-Urrea A, Si H (2018) Lateral root development in potato is mediated by Stu-mi164 regulation of NAC transcription factor. Front Plant Sci 9:383. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00383
Zhang N, Yang J, Wang Z, Wen Y, Wang J, He W, Liu B, Si H, Wang D (2014) Identification of novel and conserved microRNAs related to drought stress in potato by deep sequencing. PLoS One 9:e95489. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095489
Zhang T, Huang L, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhao X, Zhang S, Zhang J, Hu F, Fu B, Li Z (2017) Differential transcriptome profiling of chilling stress response between shoots and rhizomes of Oryza longistaminata using RNA sequencing. PLoS One 12(11):e0188625. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188625
Zhang X, Liu L, Chen B, Qin Z, Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Yao R, Liu H, Yang H (2019) Progress in understanding the physiological and molecular responses of Populus to salt stress. Int J Mol Sci 20(6):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061312
Zhang X, Zou Z, Gong P, Zhang J, Ziaf K, Li H, Xiao F, Ye Z (2011) Over-expression of microRNA169 confers enhanced drought tolerance to tomato. Biotechnol Lett 33:403–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2012.05.007
Zhang Z, Zhang X (2012) Argonautes compete for miR165/166 to regulate shoot apical meristem development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15(6):652–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2012.05.007
Zhao L, Liu F, Crawford NM, Wang Y (2018) Molecular regulation of nitrate responses in plants. Int J Mol Sci 19(7):2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072039
Zhao M, Ding H, Zhu JK, Zhang F, Li WX (2011) Involvement of miR169 in the nitrogen-starvation responses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 190:906–915. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03647.x
Zhao W, Li Z, Fan J, Hu C, Yang R, Qi X, Chen H, Zhao F, Wang S (2015) Identification of jasmonic acid-associated microRNAs and characterization of the regulatory roles of the miR319/TCP4 module under root-knot nematode stress in tomato. J Exp Bot 66(15):4653–4667. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv238
Zheng C, Ye M, Sang M, Wu R (2019) A regulatory network for miR156-SPL module in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci 20(24):6166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246166
Zheng Y, Hivrale V, Zhang X, Valliyodan B, Lelandais-Brière C, Farmer AD, May GD, Crespi M, Nguyen HT, Sunkar R (2016) Small RNA profiles in soybean primary root tips under water deficit. BMC Syst Biol 10(S5):126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12918-016-0374-0
Zhou L, Liu Y, Liu Z, Kong D, Duan M, Luo L (2010) Genome-wide identification and analysis of drought-responsive microRNAs in Oryza sativa. J Exp Bot 61:4157–4168. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq237
Zhou M, Li D, Li Z, Hu Q, Yang C, Zhu L, Luo H (2013) Constitutive expression of a miR319 gene alters plant development and enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic creeping bentgrass. Plant Physiol 161:1375–1391. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.208702
Zhu YY, Zeng HQ, Dong CX, Yin XM, Shen QR, Yang ZM (2010) microRNA expression profiles associated with phosphorus deficiency in white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Sci 178:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.09.011
Funding
This paper was supported by the KU Research Professor Program of Konkuk University, Seoul, South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BHG, BV, RK and MT searched the literature, wrote, and revised the manuscript. BS and IMC searched the literature and participated in a discussion of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gangadhar, B.H., Venkidasamy, B., Samynathan, R. et al. Overview of miRNA biogenesis and applications in plants. Biologia 76, 2309–2327 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00763-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00763-4