Abstract
Background
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are involved in the pathogenesis of cancer. This study aimed to elucidate the role and molecular mechanism of circ_0008726 in ESCC.
Methods
The expression levels of circ_0008726, microRNA (miR)-206 and homeobox A13 (HOXA13) were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (QRT-PCR). Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine (EdU) assays were conducted to detect the proliferative ability of ESCC cells. Apoptosis and invasion of ESCC cells were detected by flow cytometry and transwell assays. Tube formation assay was used to detect the angiogenesis of ESCC cells. The expression of related proteins was detected by western blot analysis. Dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay were performed to confirm the interactions among circ_0008726, miR-206 and HOXA13. Xenograft mice model was established to study the in vivo effect of circ_0008726 knockdown.
Results
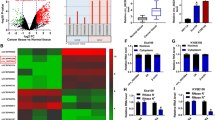
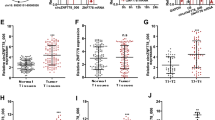
Expression of circ_0008726 was up-regulated in ESCC tissues and cells. Knockdown of circ_0008726 repressed proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and promoted apoptosis of ESCC cells. Circ_0008726 acted as a sponge for miR-206, and HOXA13 was a target of miR-206. The suppressive effects of circ_0008726 knockdown on cell proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis were abated by miR-206 down-regulation. Meanwhile, overexpression of HOXA13 partially reversed the suppressive effects of miR-206 enrichment on ESCC cell malignant behaviors. Knockdown of circ_0008726 inhibited ESCC tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion
In short, circ_0008726 exerted the carcinogenic effects to regulate the proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and apoptosis of ESCC cells by targeting miR-206/HOXA13 axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N, Chen WQ. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: a secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134:783–91.
Abnet CC, Arnold M, Wei WQ. Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:360–73.
Doosti-Irani A, Holakouie-Naieni K, Rahimi-Foroushani A, Mansournia MA, Haddad P. A network meta-analysis of the treatments for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in terms of survival. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018;127:80–90.
Bird-Lieberman EL, Fitzgerald RC. Early diagnosis of oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;101:1–6.
Patop IL, Kadener S. circRNAs in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018;48:121–7.
Xing Y, et al. Circular RNA circ-Foxo3 inhibited esophageal squamous cell cancer progression via the miR-23a/PTEN axis. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121:2595–605.
Song H, et al. up-regulated circ RNA hsa_circ_0000337 promotedd cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:1997–2006.
Ghafouri-Fard S, Honarmand Tamizkar K, Jamali E, Taheri M, Ayatollahi SA. Contribution of circRNAs in gastric cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2021;227:153640.
Lu Y, et al. circRNAs in gastric cancer: current research and potential clinical implications. FEBS Lett. 2021;595:2644–54.
Liu Z, et al. Hsa_circ_0014879 regulates the radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through miR-519–3p/CDC25A axis. Anticancer Drugs. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0000000000001213.
Qu F, et al. Circular RNA circ_0006168 enhances Taxol resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulated miR-194-5p/JMJD1C axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:273.
Zhang Q, et al. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-10b-3p promotedd esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeted TSGA10. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11:10374–84.
Zhu P, et al. Long noncoding RNA FAM225A promotedd esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development and progression via sponging microRNA-197-5p and upregulated NONO. J Cancer. 2021;12:1073–84.
Wang J, Liu L. MiR-149-3p promotedd the cisplatin resistance and EMT in ovarian cancer through downregulated TIMP2 and CDKN1A. J Ovarian Res. 2021;14:165.
Zhang D, Yang XJ, Luo QD, Xue L, Chong T. Transcription factor p53-mediated activation of miR-519d-3p and downregulation of E2F1 attenuates prostate cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-021-00405-6.
Zhang C, et al. Exosomal lncRNA FAM225A accelerates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression and angiogenesis via sponging miR-206 to upregulated NETO2 and FOXP1 expression. Cancer Med. 2020;9:8600–11.
Zhou S, Guo Z, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Wang S. circ_NRIP1 is oncogenic in malignant development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) via miR-595/SEMA4D axis and PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:250.
Tang R, Zhou Q, Xu Q, Lu L, Zhou Y. Circular RNA circ_0006948 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulated microRNA-3612/LASP1 Axis. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-07057-4.
Kong Z, et al. Comprehensive characterization of androgen-responsive circRNAs in prostate cancer. Life (Basel). 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101096.
Fang J, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000700 promotes cell proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by sponging miR-1229. J Cancer. 2021;12:2610–23.
Liang Z, Zhao B, Hou J, Zheng J, Xin G. CircRNA circ-OGDH (hsa_circ_0003340) Acts as a ceRNA to regulated glutamine metabolism and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by the miR-615-5p/PDX1 Axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:3041–53.
Li T, Li S. circ_0023984 Facilitates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulated miR-433–3p/REV3L Axis. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-06916-4.
Huang Y, Jiang L, Wei G. circ_0006168 promotes the migration, invasion and proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via miR-516b-5p-dependent regulation of XBP1. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;14:2475–88.
Qiao C, et al. IGF1-mediated HOXA13 overexpression promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through upregulated ACLY and IGF1R. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:564.
Gu Y, et al. HOXA13 promotes colon cancer progression through beta-catenin-dependent WNT pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2020;395: 112238.
Shi Q, et al. Downregulation of HOXA13 sensitizes human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to chemotherapy. Thorac Cancer. 2018;9:836–46.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: Mingwei Shi and Gong Chen; formal analysis and data curation: Gong Chen and Jiqing Hao; validation and investigation: Tingting Han and Mingwei Shi; writing—original draft preparation and writing—review and editing: Tingting Han, Mingwei Shi and Gong Chen; approval of final manuscript: all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The present study was approved by the ethical review committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. Written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients.
Human and animal rights statement
The animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University.
Consent for publication
Patients agree to participate in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, T., Shi, M., Chen, G. et al. Circ_0008726 promotes malignant progression of ESCC cells through miR-206/HOXA13 pathway. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 71, 33–45 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-022-01874-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-022-01874-8