Abstract
Objectives
The treatment of patients with brain metastases associated with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is frequently challenging. Starting in 2003, we conducted a phase II study of surgery for patients with clinical T1-2N0-1 NSCLC with oligometastasis. The aim of this subset study was to assess the clinical significance of bifocal treatment for synchronous brain metastases in T1-2N0-1 NSCLC using prospectively collected data.
Methods
In this phase II study of clinical T1-2N0-1 NSCLC patients with oligometastasis, 47 patients were enrolled from December 2003 to December 2016. Among them, 18 NSCLC patients with synchronous brain metastases were investigated in this subset analysis.
Results
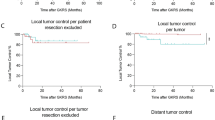
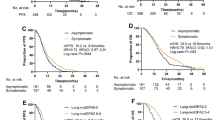
Fourteen patients underwent complete resection, and 4 underwent incomplete resection of the primary lung cancer. The number of synchronous brain metastases was one in 14 and multiple in 4 patients. After surgery for the primary lung cancer, 12 of 18 patients underwent treatment for their brain lesions, including stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in 10, surgical resection in 1, and SRS followed by surgical resection in 1. In 5 of the 18 patients (28%), the brain lesion was diagnosed as benign on follow-up radiological imaging. The 5-year overall survival rate after enrollment was 31.8% for all 18 patients and 35.2% for the 13 patients with brain metastases. Univariate analysis showed that having multiple brain lesions was a significant factor related to a worse prognosis.
Conclusion
For patients with suspected brain metastases associated with NSCLC, bifocal local treatment could be an acceptable therapeutic strategy, especially for solitary brain metastasis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung cancer
- BM:
-
Brain metastasis
- SBM:
-
Synchronous brain metastasis
- PET:
-
Positron-emission tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- SRS:
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery
- JNETS:
-
Japan North-East Thoracic Surgical Study Group
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;1:1–131.
Detterbeck FC, Jones DR, Kernstine KH, Naunheim KS. Special treatment issues. Chest. 2003;123:244S-258S.
Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Eberhardt WE, et al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:39–51.
Mussi A, Pistolesi M, Lucchi M, Janni A, Chella A, Parenti G, et al. Resection of single brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer: prognostic factors. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996;112:146–53.
Billing PS, Miller DL, Allen MS, Deschamps C, Trastek VF, Pairolero PC. Surgical treatment of primary lung cancer with synchronous brain metastases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001;122:548–53.
Bonnette P, Puyo P, Gabriel C, Giudicelli R, Regnard JF, Riquet M, et al. Surgical management of non-small cell lung cancer with synchronous brain metastases. Chest. 2001;119:1469–75.
Getman V, Devyatko E, Dunkler D, Eckersberger F, End A, Klepetko W, et al. Prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer with isolated brain metastases undergoing combined surgicall treatment. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;25:1107–13.
Furák J, Troján I, Szöke T, Agócs L, Csekeö A, Kas J, et al. Lung cancer and its operable brain metastasis: survival rate and staging problems. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79:241–7.
Girard N, Cottin V, Tronc F, Etienne-Mastroianni B, Thivolet-Bejui F, Honnorat J, et al. Chemotherapy is the cornerstone of the combined surgical treatment of lung cancer with synchronous brain metastases. Lung Cancer. 2006;53:51–8.
Griffioen GH, Toguri D, Dahele M, Warner A, de Haan PF, Rodrigues GB, et al. Radical treatment of synchronous oligometastatic non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Patient outcomes and prognostic factors. Lung cancer. 2013;82:95–102.
Loi M, Mazzella A, Mansuet-Lupo A, Bobbio A, Canny E, Magdeleinat P, et al. Synchronous oligometastatic lung cancer deserves a dedicated management. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;107:1053–9.
Penel N, Brichet A, Prevost B, Duhamel A, Assaker R, Dubois F, et al. Prognostic factors of synchronoud brain metastases from lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2001;33:143–54.
Hellman S, Weischselbaum RR. Oligometastasis. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:8–10.
Giaj-Levra N, Giaj-Levra M, Durieux V, Novello S, Besse B, Hasan B, et al. Defining synchronous oligomertastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14:2053–61.
Gomez DR, Tang C, Zhang J, Blumenshein GR, Hernandez M, Lee JJ, et al. Therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:1558–65.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2020) Guidelines for surveillance following therapy for non-small cell lung cancer Ver 3.2020. Available at: www.nccn.com.
Downey RJ, Ng NK, Kris MG, Bains MS, Miller VA, Heelan R, et al. A phase II trial of chemotherapy and surgery for non-small cell lung cancer patients with a synchronous solitary metastasis. Lung Cancer. 2002;38:193–7.
De Ruysscher D, Wanders R, van Baardwijk A, Dingemans AM, Reymen B, Houben R, et al. Radical treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer patients with synchronous oligometastases: long-term results of a prospective phase II trial (Nct01282450). J Thorac Oncol. 2012;10:1547–55.
Collen C, Christian N, Schallier D, Meysman M, Duchateau M, Storme G, et al. Phase II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy to primary tumor and metastatic locations in oligometastatic nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1954–9.
Endo C, Hasumi T, Matsumura Y, Sato N, Deguchi H, Oizumi H, et al. A prospective study of surgical procedures for patients with oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;98:258–64.
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, et al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:706–14.
Mordant P, Arame A, De Dominicis F, Pricopi C, Foucault C, Dujon A, et al. Which metastasis management allows long-term survival of synchronous solitary M1b non-small cell lung cancer? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;41:617–22.
Congedo MT, Cesario A, Lococo F, De Waure C, Apolone G, Meacci E, et al. Surgery for oligometastatic non–small cell lung cancer: Long-term results from a single center experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;144:444–52.
Modi A, Vohra HA, Weeden DF. Does surgery for primary non-small cell lung cancer and cerebral metastasis have any impact on survival? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009;8:467–73.
Sato J, Horinouchi H, Goto Y, Kanda S, Fujiwara Y, Nokihara H, et al. Long-term survival without surgery in NSCLC patients with synchronous brain oligometastasis: systemic chemotherapy revisited. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10:1696–702.
Hu C, Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ 3rd, Allen PK, Woo SY, Mahajan A, et al. Nonsmall cell lung cancer presenting with synchronous solitary brain metastasis. Cancer. 2006;106:1998–2004.
Flannery TW, Suntharalingam M, Regine WF, Chin LS, Krasna MJ, Shehata MK, et al. Long-term survival in patients with synchronous, solitary brain metastasis from non-small-cell lung cancer treated with radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;72:19–23.
Kamath SD, Kumthekar PU. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) metastatic disease. Front Oncol. 2018;8:414. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00414.
Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Han JY, Katakami N, Kim HR, et al. CNS efficacy of Osimertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Data from a randomized phase III tiral (AURA3). J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2702–9.
Schellinger PD, Meinck HM, Thron A. Diagnostic accuracy of MRI compared to CCT in patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol. 1999;44:275–81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, K., Shiono, S., Hasumi, T. et al. Clinical significance of bifocal treatment for synchronous brain metastasis in T1-2 non-small-cell lung cancers: JNETS0301. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 69, 967–975 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-020-01568-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-020-01568-z