Abstract
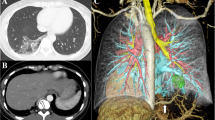
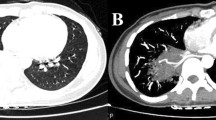
Patients with pulmonary sequestration are at risk of life-threatening bleeding during lung resection. To perform safe and adequate lung resection in patients with pulmonary sequestration, we utilized the following combination of techniques: (1) three-dimensional computed tomographic (3D-CT) imaging for preoperative planning and intraoperative identification of blood vessels, including aberrant arteries, and (2) intraoperative intravenous administration of indocyanine green (ICG). We describe our surgical technique through three cases who underwent lung resection for pulmonary sequestration using 3D-CT and fluorescence navigation with ICG. Intraoperative identification and division of the aberrant arteries, draining veins, and resection margins of the lungs were successfully completed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clements B, Warner J. Pulmonary sequestration and related congenital bronchopulmonary-vascular malformations: Nomenclature and classification based on anatomical and embryological considerations. Thorax. 1987;42:401–8.
Liechty KW, Flake AW. Pulmonary vascular malformations. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2008;17:9–16.
Walker CM, Wu CC, Gilman MD, Godwin JD, Shepard J-AO, Abbott GF. The imaging spectrum of bronchopulmonary sequestration. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2014;43:100–14.
Savic B, Birtel F, Tholen W, Funke H, Knoche R. Lung sequestration: Report of seven cases and review of 540 published cases. Thorax. 1979;34:96–101.
Li R, Li H, Liang T, Wu C. Undiagnosed pulmonary sequestration results in an unexplained hemorrhagic shock in thoracoscopic pulmonary lobectomy. J Clin Anesth. 2016;35:485–7.
Gezer S, Tastepe I, Sirmali M, et al. Pulmonary sequestration: A single-institutional series composed of 27 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133:955–9.
Lin CH, Chuang CY, Hsia JY, et al. Pulmonary sequestration-differences in diagnosis and treatment in a single institution. J Chin Med Assoc. 2013;76:385–9.
Shimizu K, Nakazawa S, Nagashima T, Kuwano H, Mogi A. 3D-CT anatomy for vats segmentectomy. J Vis Surg. 2017;3:88.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuoka, S., Eguchi, T., Takeda, T. et al. Three-dimensional computed tomography and indocyanine green-guided technique for pulmonary sequestration surgery. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 69, 621–624 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-020-01511-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-020-01511-2