Abstract
Objective
We developed an effective hemostatic method using Hydrofit® and a hemostatic gelatin sponge (Spongel®). We evaluated the hemostatic effect in comparison to the conventional silicone sheet method.
Methods
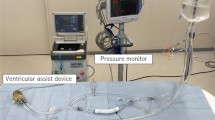
A simulated circuit was created using the pump of a Nipro ventricular assist system and a prosthetic graft. A hole was made in the graft by a needle and three hemostatic methods were applied: the silicone sheet method (SS) using Hydrofit® and a silicone sheet, the bread and butter method (BB) using Hydrofit® and a gelatin sponge instead of a silicone sheet, and French toast method (FT) using Hydrofit® and a gelatin sponge over which water was poured before compression. The amount of leakage before and after the application each of the methods was measured according to the compression time.
Results
In the 60 s compression, the amount of leakage after SS, BB, and FT was 0.4 ± 0.8, 0.2 ± 0.6, and 0 ± 0.0 ml, respectively, and FT showed no leakage. In the 30 s compression, the amount of leakage after SS, BB, and FT was 14.2 ± 27.9, 1.0 ± 3.2, and 7.8 ± 22.6 ml, respectively, and did not differ to a statistically significant extent.
Conclusions
The method of combining Hydrofit® and Spongel® could obtain reliable hemostasis in 60 s.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams JB, Phillips-Bute B, Bhattacharya SD, Shah AA, Andersen ND, Altintas B, Lima B, et al. Predictors of massive transfusion with thoracic aortic procedures involving deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;141:1283–8.
Malfait F, De Paepe A. Bleeding in the heritable connective tissue disorders: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Blood Rev. 2009;23:191–7.
Guan XL, Wang XL, Liu YY, Lan F, Gong M, Li HY, Liu O, et al. Changes in the hemostatic system of patients with acute aortic dissection undergoing aortic arch surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101:945–51.
Rosou J, Levitsky S, Ganzalez-Lavin L, Cosgrove D, Magilligan D, Weldon C, Hiebert C et al. Randomized crinical trial of fibrin sealant in patients undergoing resternotomy or reoperation after cardiac operations. A multicenter study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1989; 97:194–203.
Glickman M, Gheissari A, Money S, Martin J, Ballard JL. A polymeric sealant inhibits anatomic suture hole bleeding more rapidly than gelform/thrombin: results of a randomized controlled trial. Arch Surg. 2002;137:326–31.
Passage J, Jalali H, Tam RK, Harrocks S, O’Brien MF. BioGlue surgical adhesive—an appraisal of its indications in cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;74:432–7.
Eto M, Morita S, Sugiura M, Yoshimura T, Tominaga R, Matsuda T. Elastomeric surgical sealant for hemostasis of cardiovascular anastomosis under full heparinization. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007;32:730–4.
Jenkins HP, Janda R, Clarke J. Clinical and experimental observations on the use of gelatin sponge or form. Surgery. 1946;20:124–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest in association with present study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawashima, T., Hatori, K., Mizoguchi, T. et al. In vitro evaluation of the hemostatic effect of method involving the combined use of Hydrofit® and Spongel®. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 68, 932–937 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-019-01282-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-019-01282-5