Abstract
Background
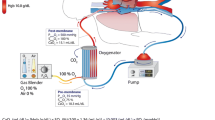
Acute respiratory failure is a serious issue that occasionally occurs after weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) after heart surgery. This condition can be refractory to mechanical ventilation and the mortality rate is high. Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO) is applied to treat acute lung failure after CPB at our institution. This report describes the use of VV-ECMO after cardiac surgery at a single institution.
Methods
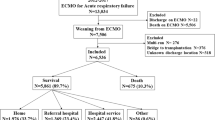
We analyzed the outcomes of 11 patients who developed severe acute respiratory failure requiring VV-ECMO after undergoing heart surgery with a cardiopulmonary bypass.
Results
Four (36.4 %) patients died in hospital. One patient required conversion from VV- to venoarterial (VA-) ECMO because of circulatory instability. One patient each died of respiratory failure and heart failure and two died of ischemic colitis. Lung damage secondarily developed in these four patients to other disabled organs. Seven (63.6 %) patients whose lungs were primarily disabled were weaned from VV-ECMO upon recovery from respiratory failure and were ambulatory at the time of discharge from hospital. The ratio of PaO2/FIO2 (P/F) at 24 h after starting VV-ECMO did not significantly differ between survivors and non-survivors (187.9 ± 57.7 vs. 135.5 ± 20.5, p = 0.10), but tended to be higher in survivors. Non-survivors were significantly older than survivors.
Conclusion
Patients who develop severe acute respiratory failure after undergoing heart surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass derive a survival benefit from VV-ECMO.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsushima K, King LS, Aggarwal NR, De Gorordo A, D’Alessio FR, Kubo K. Acute lung injury review. Intern Med. 2009;48(9):621–30.
Wheeler AP, Bernard GR. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a clinical review. Lancet. 2007;369(9572):1553–64.
Hammermeister KE, Burchfiel C, Johnson R, Grover FL. Identification of patients at greatest risk for developing major complications at cardiac surgery. Circulation 1990;82(5 Suppl):IV380–9.
Hemmila MR, Napolitano LM. Severe respiratory failure: advanced treatment options. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(9 Suppl):S278–90.
Bartlett RH, Roloff DW, Cornell RG, Andrews AF, Dillon PW, Zwischenberger JB. Extracorporeal circulation in neonatal respiratory failure: a prospective randomized study. Pediatrics. 1985;76(4):479–87.
UK collaborative randomised trial of neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. UK Collaborative ECMO Trail Group. Lancet 1996;348(9020):75–82.
Lindén V, Palmér K, Reinhard J, Westman R, Ehrén H, Granholm T, Frenckner B. High survival in adult patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome treated by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, minimal sedation, and pressure supported ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26(11):1630–7.
Hemmila MR, Rowe SA, Boules TN, Miskulin J, McGillicuddy JW, Schuerer DJ, Haft JW, Swaniker F, Arbabi S, Hirschl RB, Bartlett RH. Extracorporeal life support for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults. Ann Surg. 2004;240(4):595–607.
Oshima K, Kunimoto F, Hinohara H, Ohkawa M, Mita N, Tajima Y, Saito S. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory failure: comparison of venovenous versus venoarterial bypass. Surg Today 2010;40(3):216–22. (Epub 2010 Feb 24).
Bohn D. Pushing the boundaries for the use of ECMO in acute hypoxic respiratory failure. Intensive Care Med. 2005;31(7):896–7.
Zapol WM, Snider MT, Hill JD, Fallat RJ, Bartlett RH, Edmunds LH, Morris AH, Peirce EC 2nd, Thomas AN, Proctor HJ, Drinker PA, Pratt PC, Bagniewski A, Miller RG Jr. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe acute respiratory failure. A randomized prospective study. JAMA. 1979;242(20):2193–6.
Morris AH, Wallace CJ, Menlove RL, Clemmer TP, Orme JF Jr, Weaver LK, Dean NC, Thomas F, East TD, Pace NL, Suchyta MR, Beck E, Bombino M, Sittig DF, Böhm S, Hoffmann B, Becks H, Butler S, Pearl J, Rasmusson B. Randomized clinical trial of pressure-controlled inverse ratio ventilation and extracorporeal CO2 removal for adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149(2 Pt 1):295–305.
Oto T, Rosenfeldt F, Rowland M, Pick A, Rabinov M, Preovolos A, Snell G, Williams T, Esmore D. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation after lung transplantation: evolving technique improves outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78(4):1230–5.
Schmid C, Philipp A, Mueller T, Hilker M. Extracorporeal life support—systems, indications, and limitations. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;57(8):449–54.
Kolla S, Awad SS, Rich PB, Schreiner RJ, Hirschl RB, Bartlett RH. Extracorporeal life support for 100 adult patients with severe respiratory failure. Ann Surg. 1997;226(4):544–64.
Anderson HL 3rd, Delius RE, Sinard JM, McCurry KR, Shanley CJ, Chapman RA, Shapiro MB, Rodriguez JL, Bartlett RH. Early experience with adult extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the modern era. Ann Thorac Surg. 1992;53(4):553–63.
Schmid C, Philipp A, Hilker M, Rupprecht L, Arlt M, Keyser A, Lubnow M, Müller T. Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute lung failure in adults. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2012;31(1):9–15. (Epub 2011 Sep 1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, H., Yamaguchi, H., Amano, A. et al. Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is effective against post-cardiotomy acute respiratory failure in adults. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 61, 402–408 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-013-0226-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-013-0226-4