Abstract
Purpose
Hypothermic circulatory arrest is considered to be a contraindication in acute traumatic aortic rupture (TAR) because full heparinization and hypothermia may lead to fatal bleeding if concomitant hemorrhagic injuries are present. However, in extremely emergent situations, rapid volume infusion via cardiotomy vacuums and the institution of hypothermic circulatory arrest appears to be the only method for saving patients with uncontrollable bleeding. In this study, we evaluate the feasibility of hypothermic circulatory arrest for treating patients with TAR with hemorrhagic shock.
Methods
Ten patients (nine men and one woman; mean age, 35 ± 18 years), with acute TAR caused by blunt chest trauma and in a shock state, underwent surgery between 1999 and 2007. All ten patients exhibited rupture of the isthmus, and polytraumatism was frequent. Any life-threatening blood loss from other injuries was surgically treated before aortic surgery. All patients were operated on with standard cardiopulmonary bypass under hypothermic circulatory arrest.
Results
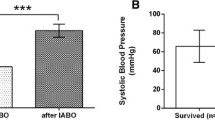
All patients received prosthetic graft replacement. The overall hospital mortality was 10.0% (1/10). One patient died of intraabdominal and pulmonary bleeding during surgery, and the other nine were discharged without complications. There was no evidence of any new or increased hemorrhagic complications during heparinization in the nine surviving patients. Mean operation and circulatory arrest times were 305 ± 44 min and 27 ± 7 min, respectively.
Conclusion
Hypothermic circulatory arrest is feasible for saving TAR patients with unstable hemodynamics resulting from rupture, provided associated injuries are properly treated in advance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parmley LF, Manion WC, Mattingly TW. Nonpenetrating traumatic injury of the heart. Circulation 1958;18:371–396.
Cowley RA, Turney SZ, Hankins JR, Rodriguez A, Attar S, Shankar BS. Rupture of thoracic aorta caused by blunt trauma. A fifteen-year experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1990;100:652–660.
Neschis DG, Moaine S, Gutta R, Charles K, Scalea TM, Flinn WR, et al. Twenty consecutive cases of endograft repair of traumatic aortic disruption: lessons learned. J Vasc Surg 2007;45:487–492.
McPhee JT, Asham EH, Rohrer MJ, Singh MJ, Wong G, Vorhies RW, et al. The midterm results of stent graft treatment of thoracic aortic injuries. J Surg Res 2007;138:181–188.
von Oppell UO, Dunne TT, De Groot MK, Zilla P. Traumatic aortic rupture: twenty-year metaanalysis of mortality and risk of paraplegia. Ann Thorac Surg 1994;58:585–593.
Symbas PN, Sherman AJ, Silver JM, Symbas JD, Lackey JJ. Traumatic rupture of the aorta: immediate or delayed repair? Ann Surg 2002;235:796–802.
Mattox KL, Holzman M, Pickard LR, Beall AC Jr, DeBakey ME. Clamp/repair: a safe technique for treatment of blunt injury to the descending thoracic aorta. Ann Thorac Surg 1985;40:456–463.
Buz S, Zipfel B, Mulahasanovic S, Pasic M, Weng Y, Hetzer R. Conventional surgical repair and endovascular treatment of acute traumatic aortic rupture. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2008;33:143–149.
Xenos ES, Minion DJ, Davenport DL, Hamdallah O, Abedi NN, Sorial EE, et al. Endovascular versus open repair for descending thoracic aortic rupture: institutional experience and meta-analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2009;35:282–286.
Marcheix B, Dambrin C, Bolduc JP, Arnaud C, Hollington L, Cron C, et al. Endovascular repair of traumatic rupture of the aortic isthmus: midterm results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;132:1037–1041.
Akowuah E, Baumbach A, Wilde P, Angelini G, Bryan AJ. Emergency repair of traumatic aortic rupture: endovascular versus conventional open repair. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;134:897–901.
Canaud L, Alric P, Branchereau P, Marty-Ané C, Berthet JP. Lessons learned from midterm follow-up of endovascular repair for traumatic rupture of the aortic isthmus. J Vasc Surg 2008;47:733–738.
Apostolakis E, Koniari I, Dougenis D. Endovascular treatment of acute traumatic aortic rupture: radical solution or postponement of the problem? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2008;34:701.
Marty B. Management of traumatic aortic rupture: endovascular is the winner. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2008;33:149–151.
Ferrari E, Tozzi P, von Segesser L. Thoracic aorta emergencies: is the endovascular treatment the new gold standard? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2006;5:730–734.
Pate JW, Fabian TC, Walker WA. Acute traumatic rupture of the aortic isthmus: repair with cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg 1995;59:90–99.
Gammie JS, Shah AS, Hattler BG, Kormos RL, Peitzman AB, Griffith BP, et al. Traumatic aortic rupture: diagnosis and management. Ann Thorac Surg 1998;66:1295–1300.
Razzouk AJ, Gundry SR, Wang N, del Rio MJ, Varnell D, Bailey LL. Repair of traumatic aortic rupture: a 25-year experience. Arch Surg 2000;135:913–919.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawahito, K., Adachi, H. Hypothermic circulatory arrest for acute traumatic aortic rupture associated with shock. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 59, 472–476 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-011-0783-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-011-0783-3