Abstract
Purpose
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is associated with allograft dysfunction after lung transplantation (LTX). We attempted to identify outcomes in LTX recipients with clinical evidence of GERD.
Methods
Retrospective review of 162 LTX recipients at our institution between January 1994 and June 2006 was performed. GERD was confirmed in symptomatic patients by esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and/or esophagography. Occurrence of biopsy-proven obliterative bronchiolitis (OB) and bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) were analyzed. Kaplan-Meier analysis of survival and Cox proportional hazard analysis of risk factors were performed.
Results
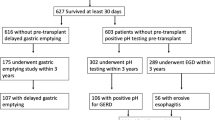
GERD was diagnosed in 21 (13%) of patients, usually following LTX (71%). There was no difference in mean survival (1603 ± 300 vs. 1422 ± 131 days; log rank P > 0.05), or development of OB (5% vs. 6%, respectively; P > 0.05) in patients with GERD compared with patients without GERD. However, there was correlation between GERD and BOS (P = 0.01).
Conclusions
Symptomatic GERD is increased following LTX. Patients with symptomatic GERD demonstrated an increased incidence of BOS, but survival was not affected in this study. More sensitive and specific diagnostic tools should be implemented in all LTX recipients to investigate the impact of symptomatic and silent GERD and thus improve outcomes after LTX.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trulock EP, Christie JD, Edwards LB, Boucek MM, Aurora P, Taylor DO, et al. Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-fourth official adult lung and heart-lung transplantation report—2007. J Heart Lung Transplant 2007;26:782–795.
Verleden GM, Dupont LJ, Van Raemdonck DE. Is it bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome or is it chronic rejection: a reappraisal? Eur Respir J 2005;25:221–224.
Reid KR, McKenzie FN, Menkis AH, Novick RJ, Pflugfelder PW, Kostuk WJ, et al. Importance of chronic aspiration in recipients of heart-lung transplants. Lancet 1990;336:206–208.
Au J, Hawkins T, Venables C, Morritt G, Scott CD, Gascoigne AD, et al. Upper gastrointestinal dysmotility in heart-lung transplant recipients. Ann Thorac Surg 1993;55:94–97.
Rinaldi M, Martinelli L, Volpato G, Pederzolli C, Silvestri M, Pederzolli N, et al. Gastro-esophageal reflux as cause of obliterative bronchiolitis: a case report. Transplant Proc 1995;27:2006–2007.
Cantu E 3rd, Appel JZ 3rd, Hartwig MG, Woreta H, Green C, Messier R, et al. Early fundoplication prevents chronic allograft dysfunction in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Thorac Surg 2004;78:1142–1151.
Davis RD Jr, Lau CL, Eubanks S, Messier RH, Hadjiliadis D, Steele MP, et al. Improved lung allograft function after fundoplication in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease undergoing lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2003;125:533–542.
D’Ovidio F, Mura M, Tsang M, Waddell TK, Hutcheon MA, Singer LG, et al. Bile acid aspiration and the development of bronchiolitis obliterans after lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2005;129:1144–1152.
D’Ovidio F, Mura M, Ridsdale R, Takahashi H, Waddell TK, Hutcheon M, et al. The effect of reflux and bile acid aspiration on the lung allograft and its surfactant and innate immunity molecules SP-A and SP-D. Am J Transplant 2006;6:1930–1938.
Nicod LP. Mechanisms of airway obliteration after lung transplantation. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2006;3:444–449.
Weiss MJ, Madsen JC, Rosengard BR, Allan JS. Mechanisms of chronic rejection in cardiothoracic transplantation. Front Biosci 2008;13:2980–2988.
Hartwig MG, Appel JZ, Li B, Hsieh CC, Yoon YH, Lin SS, et al. Chronic aspiration of gastric fluid accelerates pulmonary allograft dysfunction in a rat model of lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;131:209–217.
Young LR, Hadjiliadis D, Davis RD, Palmer SM. Lung transplantation exacerbates gastroesophageal reflux disease. Chest 2003;124:1689–1693.
Linden PA, Gilbert RJ, Yeap BY, Boyle K, Deykin A, Jaklitsch MT, et al. Laparoscopic fundoplication in patients with end-stage lung disease awaiting transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;131:438–446.
Estenne M, Maurer JR, Boehler A, Egan JJ, Frost A, Hertz M, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome 2001: an update of the diagnostic criteria. J Heart Lung Transplant 2002;21:297–310.
D’Ovidio F, Singer LG, Hadjiliadis D, Pierre A, Waddell TK, de Perrot M, et al. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux in end-stage lung disease candidates for lung transplant. Ann Thorac Surg 2005;80:1254–1260.
Hadjiliadis D, Duane Davis R, Steele MP, Messier RH, Lau CL, Eubanks SS, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in lung transplant recipients. Clin Transplant 2003;17:363–368.
Sweet MP, Herbella FA, Leard L, Hoopes C, Golden J, Hays S, et al. The prevalence of distal and proximal gastroesophageal reflux in patients awaiting lung transplantation. Ann Surg 2006;244:491–497.
Patti MG, Tedesco P, Golden J, Hays S, Hoopes C, Meneghetti A, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: how often is it really idiopathic? J Gastrointest Surg 2005;9:1053–1056.
Tobin RW, Pope CE 2nd, Pellegrini CA, Emond MJ, Sillery J, Raghu G. Increased prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;158:1804–1808.
Sweet MP, Patti MG, Leard LE, Golden JA, Hays SR, Hoopes C, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis referred for lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;133:1078–1084.
Button BM, Roberts S, Kotsimbos TC, Levvey BJ, Williams TJ, Bailey M, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux (symptomatic and silent): a potentially significant problem in patients with cystic fibrosis before and after lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:1522–1529.
Ledson MJ, Tran J, Walshaw MJ. Prevalence and mechanisms of gastro-oesophageal reflux in adult cystic fibrosis patients. J R Soc Med 1998;91:7–9.
Blondeau K, Mertens V, Vanaudenaerde BA, Verleden GM, Van Raemdonck DE, Sifrim D, et al. Gastro-oesophageal reflux and gastric aspiration in lung transplant patients with or without chronic rejection. Eur Respir J 2008;31:707–713.
Moayyedi P, Talley NJ. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet 2006;367:2086–2100.
D’Ovidio F, Keshavjee S. Gastroesophageal reflux and lung transplantation. Dis Esophagus 2006;19:315–320.
Sato M, Keshavjee S. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome: alloimmune-dependent and -independent injury with aberrant tissue remodeling. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2008;20:173–182.
Scott AI, Sharples LD, Stewart S. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome: risk factors and therapeutic strategies. Drugs 2005;65:761–771.
Knoop C, Estenne M. Acute and chronic rejection after lung transplantation. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2006;27:521–533.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina, E.J., Short, S., Monteiro, G. et al. Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease after lung transplantation. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 57, 647–653 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-009-0486-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-009-0486-1