Objective
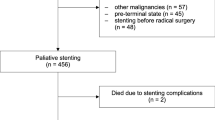
Self-expandable metallic stent (EMS) placement has been the first choice for dysphagia because of the certainty over its safety, low invasiveness, and immediate efficacy. However, there still remain some problems in relation to the EMS placement site and anticancer therapies before and after EMS placement. Methods: Consecutive 78 patients in whom EMS was placed due to the unresectable malignant stricture in the esophagus or cardia from July 1995 to August 2003 in our department were studied. Results: Gastroesophageal reflux was found in 5 of 8 patients after placement of conventional EMS for the stricture in the gastroesophageal junction. Meanwhile, acid and bile reflux into the esophagus were not detected by pH and bilirubin monitoring, respectively, in 6 patients after placement of the EMS with an anti-reflux mechanism for the stricture in the gastroesophageal junction. The median survival period of all patients after EMS placement was 123 days. The median survival period of 7 patients with radiotherapy only after EMS placement was 138 days and that of 17 patients with radiotherapy before EMS placement was 60 days, which was shorter than that of the former (p<0.05). On the other hand, the median survival period after hospital admission due to dysphagia of these 7 patients was longer than that of 17 patients with radiotherapy only before EMS placement, although, the difference was not significant. Conclusion: EMS with an antireflux mechanism is not commercially available in Japan and approval is urgently required. The indication of radiotherapy associated with EMS placement is to be studied further.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knyrim K, Wagner HJ, Bethge N, Keymling M, Vakil N. A controlled trial of an expansil metal stent for palliation of esophageal obstruction due to inoperable cancer. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 1302–7.
De Palma GD, di Matteo E, Romano G, Fimmano A, Rondinone G, Catanzano C. Plastic prosthesis versus expandable metal stents for palliation of inoperable esophageal thoracic carcinoma: A controlled prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 1996; 43: 478–82.
Adam A, Ellul J, Watkinson AF, Tan BS, Morgan RA, Saunders MP, et al. Palliation of inoperable esophageal carcinoma: A prospective randomized trial of laser therapy and stent placement. Radiology 1997; 202: 344–8.
Mizumoto Y, Matsuda K, Itoh Y. Trial use of a gore-tex covered Ultraflex stent with reflux preventive action for cardioesophageal cancer (Eng abstr). Gastrointest Endosc 1997; 45: AB35.
Neuhaus H, Hoffmann W, Dittler HJ, Niedermeyer HP, Classen M. Implantation of self-expanding esophageal metal stents for palliation of malignant dysphagia. Endoscopy 1992; 24: 405–10.
Bechi P, Pucciani F, Baldini F, Cosi F, Falciai R, Mazzanti R, et al. Long-term ambulatory enterogastric reflux monitoring. Validation of a new fiberoptic technique. Dig Dis Sci 1993; 38: 1297–306.
Lee S, Osugi H, Tokuhara T, Kaseno S, Takada N, Takemura M, et al. Self-expandable metallic stents with an anti-reflux mechanism for malignant strictures of gastroesophageal junction. Scand J Gastroenterol 2002; 37: 990–1.
Osugi H, Lee S, Higashino M, Tokuhara T, Kaseno S, Takada N, et al. Usefulness of self-expandable metallic stent with an antireflux mechanism as a palliation for malignant strictures at the gastroesophageal junction. Surg Endosc 2002; 16: 1478–82.
Laasch HU, Marriott A, Wilbraham L, Tunnah S, England RE, Martin DF. Effectiveness of open versus antireflux stents for palliation of distal esophageal carcinoma and prevention of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux. Radiology 2002; 225: 359–65.
Dua KS. Antireflux stents in tumors of the cardia. Am J Med 2001; HlSuppl8A: 190S-6S.
Bethge N, Sommer A, von Kleist D, Vakil N. A prospective trial of self-expanding metal stents in the palliation of malignant esophageal obstruction after failure of primary curative therapy. Gastrointest Endosc 1996; 44: 283–6.
Nishimura Y, Nagata K, Katano S, Hirota S, Nakamura K, Higuchi F, et al. Severe complications in advanced esophageal cancer treated with radiotherapy after intubation of esophageal stents: A questionnaire survey of the Japanese Society for Esophageal Diseases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003; 56: 1327–32.
Ludwig D, Dehne A, Burmester E, Wiedemann GJ, Stange EF. Treatment of unresectable carcinoma of the esophagus or the gastroesophageal junction by mesh stents with or without radiochemotherapy. Int J Oncol 1998; 13: 583–8.
Zhong J, Wu Y, Xu Z, Liu X, Xu B, Zhai Z. Treatment of medium and late stage esophageal carcinoma with combined endoscopie metal stenting and radiotherapy. Chin Med J 2003; 116:24–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Osugi, H., Tokuhara, T. et al. Self-expandable metallic stent for unresectable malignant strictures in the esophagus and cardia. Jpn J Thorac Caridovasc Surg 53, 470–476 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-005-0089-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-005-0089-4