Abstract
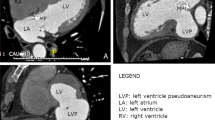
We report a successful surgical ease of giant left ventricular pseudo-false aneurysm in a 63-year-old man. The abnormality of the inferior wall of the left ventricle was discovered incidentally by abdominal ultrasonography for health examination at another hospital. Transthoracic echocardiography and left ventriculography revealed a giant false aneurysm (74×75×40 mm) in the inferior wall of the left ventricle with a large orifice (70×58 mm). Repair of the aneurysm was performed under arrested heart, closing the large orifice with a Hemashield patch. Postoperative pathological examination proved that the wall of the aneurysm had myocardial tissue. The microscopic results strongly suggested that this aneurysm was a pseudo-false aneurysm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Komeda M, David TE. Surgical treatment of postinfarction false aneurysm of the left ventricle. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1993; 106: 1189–91.
Stewart S, Huddle R, Stuard I, Schreiner BF, DeWeese JA. False aneurysm and pseudo-false aneurysm of the left ventricle: Etiology, pathology, diagnosis, and operative management. Ann Thorac Surg 1981; 31: 259–65.
Adachi K, Tanaka J, Satoh T, Tenpaku H, Hirano K, Makino S, et al. Ventricular pseudo-false aneurysm after myocardial infarction; report of a case (Eng abstr). Kyobu Geka 2003; 56: 228–30.
Yamanaka J, Takeuchi Y, Gomi A, Nakatani H, Azuhata K, Namiki S. A case report of pseudo-false aneurysm of the left ventricle perforated into the right ventricle (Eng abstr). Nippon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1996; 44: 58–62.
Yvorra S, Desfossez L, Panagides D, Bonnet JL, Bory M. False pseudoaneurysm of the left ventricle after myocardial infarction. Recognition by transesophageal echocardiography. Arch Mai Coeur Vaiss 1994; 87: 395–8.
Fukuda I, Kohno M, Shigeta O, Saitoh T, Noguchi Y, Tsutsui T. Pseudo-false aneurysm of the left ventricle perforated into the right ventricle: A case report (Eng abstr). Nippon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1993; 41: 332–6.
Evora PR, Moreira Neto FF, Sgarbieri RN, de Freitas JN, Bongiovani HL, Ferez MA, et al. Pseudo-false aneurysm of the left ventricle simulating pulmonary neoplasm. Arq Bras Cardiol 1989; 52: 283–6.
Moreno R, Gordillo E, Zamorano J, Almeria C, Garcia-Rubira JC, Fernandez-Ortiz A, et al. Long term outcome of patients with postinfarction left ventricular pseudoaneurysm. Heart 2003; 89: 1144–6.
Frances C, Romero A, Grady D. Left ventricular pseudoaneurysm. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998; 32: 557–61.
Pretre R, Linka A, Jenni R, Turina MI. Surgical treatment of acquired left ventricular pseudoaneurysms. Ann Thorac Surg 2000; 70: 553–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koizumi, K., Misumi, T., Kudo, M. et al. Giant left ventricular pseudo-false aneurysm following myocardial infarction. Jpn J Thorac Caridovasc Surg 53, 120–123 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-005-0015-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-005-0015-9