Abstract
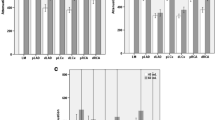
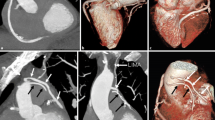
Objective: We assessed the role of multi-detector row computed tomography in cardiovascular surgery. Methods: The efficacy of multi-detector row computed tomography was assessed concerning the graft patency of coronary artery bypass, arterial atheromatous degeneration, small vessel imaging, and left ventricular volume measurement. Images were reconstructed using both the volume-rendering and the maximum-intensity-profile methods. Arterial atherosclerotic degeneration was assessed by aortic wall volume and aortic calcification volume. Results: In the assessment of bypass graft patency, multi-detector row computed tomography showed a 98% correct positive ratio with sensitivity and specificity of 98% and 100%, respectively. Atheromatous degeneration showed matching results in more than 70% of cases compared with intraoperative findings. More than 92% of arterial branches with diameters of 3 mm or greater were detected by preoperative multi-detector row computed tomography images, though only 6% of branches with diameters of 2 mm or less could be visualized. There was a positive linear correlation between left ventricular volumes determined by multi-detector row computed tomography and those calculated from cine angiography. Conclusion: Multi-detector row computed tomography clearly visualized coronary bypass grafts and aortic arterial branches, providing detailed vascular images. Atheromatous degeneration assessed by multi-detector row computed tomography was equivalent with intraoperative findings in more than 70% of cases. Left ventricular volumes measured by multi-detector row computed tomography correlated closely with those determined by cine-angiography. Multi-detector row computed tomography is an efficient and promising modality in cardiovascular surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker CR, Ohnesorge BM, Schoepf UJ, Reiser MF. Current development of cardiac imaging with multidetector-row CT. Eur J Radiol 2000; 36: 97–103.
Treede H, Becker C, Reichenspurner H, Knez A, Detter C, Reiser M, et al. Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) in coronary surgery: first experiences with a new tool for diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Ann Thorac Surg 2002; 74: SI398–402.
Adachi H, Ino T, Ide H, Mizuhara A, Yamaguchi A, Kawahito K, et al. Preoperative diagnosis of the thoracic aortic aneurysm by three-dimensional CT angiography (Eng abstr). Nippon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi l993;41: 1478–86.
Ishikawa M, Morimoto N, Sasajima T, Kubo Y. Three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography in lower extremity revascularization. Surg Today 1999; 29: 243–7.
Takasu J, Mao S, Budoff MJ. Aortic atherosclerosis detected with electron-beam CT as a predictor of obstructive coronary artery disease. Acad Radiol 2003; 10:631–7.
Yamamoto R, Takasu J, Yokoyama K, Watanabe S, Taguchi R, Itani Y, et al. Descending aorta wall volume and coronary artery disease: A comparative study using enhanced computed tomography of the chest and coronary angiography. Jpn Circ J 2000; 64: 842–7.
Yoo KJ, Choi D, Choi BW, Lim SH, Chang BC. The comparison of the graft patency after coronary artery bypass grafting using coronary angiography and multislice computed tomography. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2003; 24: 86–91.
Ropers D, Baum U, Pohle K, Anders K, Ulzheimer S, Ohnesorge B, et al. Detection of coronary artery stenoses with thin-slice multi-detector row spiral computed tomography and multiplanar reconstruction. Circulation 2003; 107: 664–6.
Griepp RB, Ergin MA, Galla JD, Lansman S, Khan N, Quintana C, et al. Looking for the artery of Adamkiewicz: A quest to minimize paraplegia after operations for aneurysms of the descending thoracic and thoracoabdominal aorta. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1996; 112: 1202–15.
Kudo K, Terae S, Asano T, Oka M, Kaneko K, Ushikoshi S, et al. Anterior spinal artery and artery of Adamkiewicz detected by using multi-detector row CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003; 24: 13–7.
Yoshioka K, Niinuma H, Ohira A, Nasu K, Kawakami T, Sasaki M, et al. MR angiography and CT angiography of the artery of Adamkiewicz: Noninvasive preoperative assessment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. Radiographics 2003; 23: 1215–25.
Grossman W, Braunwald E, Mann T, McLaurin LP, Green LH. Contractile state of the left ventricle in man as evaluated from end-systolic pressure-volume relations. Circulation 1977; 56: 845–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Read at the Fifty-sixth Annual Meeting of the Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery, Panel Discussion, Tokyo, November 19–21, 2003.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imagawa, H., Kawachi, K., Takano, S. et al. Impact of multi-detector row computed tomography on the tactics of cardiovascular surgery. Jpn J Thorac Caridovasc Surg 53, 78–83 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-005-0005-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-005-0005-y