Abstract
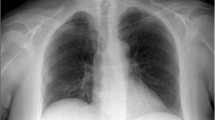
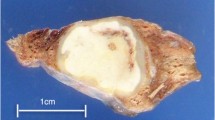
Pulmonary dirofilariasis is a rare disease. We have experienced a case which developed pleural effusion while being followed, rendering it difficult to establish the diagnosis. The patient, a 53-year-old woman, had previously undergone two operations; one for uterine cancer and another for breast cancer. She developed a cough in February 2002, and chest computed tomography (CT) scans disclosed a nodular mass in the right lung. A biopsy revealed a fibrous nodule with macrophage aggregation. Pleural effusion was demonstrated on chest CT scans performed in May. As the possibility of malignant tumor could not be ruled out, an operation was undertaken. The nodular lesion showed marked coagulation necrosis, and dead parasites were noted in the vascular lumen. The parasites had the characteristic morphological features of Dirofilaria immitis. Immunological studies produced a positive test result for the anti-dirofilaria immitis antibody; hence a diagnosis of pulmonary dirofilariasis was made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima T, Kataoka K, Kataoka M, Shibuya Y, Aji T, Fujiwara T, et al. A Case of Pulmonary dirofilariasis (Eng abstr). Kyobu Geka 2001; 54: 889–91.
Echeverri A, Long RF, Check W, Burnett CM. Pulmonary dirofilariasis. Ann Thorac Surg 1999; 67: 201–2.
Asimacopoulos PJ, Katras A, Christie B. Pulmonary dirofilariasis: The largest single—hospital experience. Chest 1992; 102: 851–5.
Malanez de Campos JR, Barbas CS, Filomeno LT, Fernandez A, Minamoto H, Filho JV, et al. Human pulmonary dirofilariasis: Analysis of 24 cases from S ão Paulo, Brazil. Chest 1997; 112: 729–33.
Kido A, Ishida, T, Oka T, Tateishi M, Mitsudomi T, Sugimachi K. Pulmonary dirofilariasis causing a solitary lung mass and pleural effusion. Thorax 1991; 46: 608–9.
Sano A, Mukae H, Iiboshi H, Matsumoto K, Matsumoto N, Hiratsuka T, et al. Pulmonary dirofilariasis with cavity formation and pleural effusion (Eng abstr). Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi 2000; 38: 490–3.
Yamakami Y, Mizunoe S, Yamagata E, Hiramatsu K, Yamasaki T, Nagai H, et al. Pulmonary, dirofilariasis associated with pleural effusion (Eng abstr). Nihon Kokyuki, Gakkai Zasshi 1998; 36: 560–3.
Kahn FW, Wester SM, Agger WA. Pulmonary dirofilariasis and transitional cell carcinoma: Benign lung nodules mimicking metastatic malignant neoplasms. Arch Intern Med 1983; 143: 1259–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshino, N., Hisayoshi, T., Sasaki, T. et al. Human pulmonary dirofilariasis in a patient whose clinical condition altered during follow-up. Jpn J Thorac Caridovasc Surg 51, 211–213 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-003-0035-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-003-0035-2