Abstract
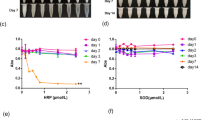
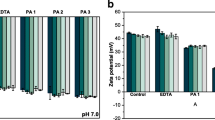
The effect of protein displacement at the interface by a secondary emulsifier on the oxidative stability of sodium caseinate-stabilized tuna oil-in-water emulsion systems was determined. Emulsions were prepared with a selection of anionic and non-ionic emulsifiers and stored at both 25 and 50 °C with no added prooxidant, and at 4 °C in the presence of ferrous sulfate. The progress of oxidation during storage was monitored through solid phase microextraction headspace analysis. Metal ion catalyzed oxidation was enhanced for the emulsions stabilized with an anionic emulsifier in comparison to emulsion systems stabilized with non-ionic emulsifiers and sodium caseinate alone. The increased oxidation observed for the emulsion with the anionic surfactant is due to electrostatic interactions between divalent metal ions and the negatively charged surfactant at the oil-water interface. The sodium caseinate interfacial layer had little prooxidant effect at the droplet surface, most likely due to the ability of free protein molecules in solution to sequester metal ions, which may have provided some protection against oxidative deterioration.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Tween40:
-
Polyoxyethylenesorbitan monopalmitate
- SSL:
-
Sodium stearoyl lactylate
- MGP:
-
Monoglycerol palmitate
- PGE:
-
Polyglycerol ester 55-M
- SPME:
-
Solid phase microextraction
- GC-FID:
-
Gas chromatography-flame ionization detector
- w/w:
-
Weight per weight
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- FA:
-
Fatty acids
- FAMEs:
-
Fatty acid methyl esters
- DHA, 22:6n-3:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- 16:0:
-
Palmitic acid
- EPA, 20:5n-3:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- 18:1n-9:
-
Oleic acid
References
Kellerby SS, McClements DJ, Decker EA (2006) Role of proteins in oil-in-water emulsions on the stability of lipid hydroperoxides. J Agric Food Chem 54:7879–7884
Nawar WW (1996) Lipids. In: Fennema RR (ed) Food chemistry, 3rd edn. Dekker, New York, pp 225–319
Frankel EN (2005) Lipid oxidation, 2nd edn. The Oily Press, Bridgewater, England
Surh J, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2006) Influence of pH and pectin type on properties and stability of sodium-caseinate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids 20:607–618
Hunt JA, Delgleish DG (1995) Heat stability of oil-in-water emulsions containing milk proteins: effect of ionic strength and pH. J Food Sci 60:1120–1123
Srinivasan M, Singh H, Munro PA (2002) Formation and stability of sodium caseinate emulsions: influence of retorting (121 °C for 15 min) before or after emulsification. Food Hydrocolloids 16:153–160
Hu M, McClements DJ, Decker EA (2003) Lipid oxidation in corn oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by casein, whey protein isolate and soy protein isolate. J Agric Food Chem 51:1696–1700
McClements DJ, Decker EA (2000) Impact of molecular environment on chemical reactions in heterogeneous food systems. J Food Sci 65:1270–1282
Tomas A, Paquet D, Courthaudon JL, Lorient D (1994) Effect of fat and protein contents on droplet size and surface protein coverage in dairy emulsions. J Dairy Sci 77(2):413–417
Dickinson E, Semenova M, Antipova AS, Pelan EG (1998) Effect of high-methoxy pectin on properties of casein stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids 12:425–432
Dalgleish DG, Srinivasan M, Singh H (1995) Surface properties of oil-in-water emulsion droplets containing casein and tween60. J Agric Food Chem 43:2351–2355
Dickenson E, Golding M (1998) Influence of calcium ions on creaming and rheology of emulsions containing sodium caseinate. Colloids Surf A 144:167–177
Hindle SA, Povey MJW, Smith KW (2001) Characterizing cocao butterseed crystals by the oil-in-water emulsion crystallization method. J Am Oil Chem Soc 79:993–1002
Dickinson E, Tanai S (1992) Temperature dependence of the competitive displacement of protein from the emulsion droplet surface by surfactants. Food Hydrocolloids 6:163–171
Day L, Xu M, Hoobin P, Burgar I, Augustin MA (2007) Characterization of fish oil emulsions stabilized by sodium caseinate. Food Chem 105:469–479
Vega C, Goff HD, Roos YH (2007) Casein molecular assembly affects the properties of milk fat emulsions encapsulated in lactose or trehalose matrices. Int Dairy J 17:683–695
Antipova AS, Semenova MG, Belyakova LE, Il’in MM (2001) On Relationships between molecular structure, interactions and surface behavior in moxitrues: small-molecule surfactant plus protein. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 21(1–3):217–230
Dimakou CP, Kiokias SN, Tsaprouni IV, Oreopoulou V (2007) Effects of processing and storage parameters on the oxidative deterioration of oil-in-water emulsions. Food Biophys, pp 38–45
Mancuso JR, McClements DJ, Decker EA (1999) The effect of surfactant type, pH and chelators on the oxidation of salmon oil-in-water emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 47:4112–4116
Formusco LB, Corredig M, Akoh CC. Effects of emulsifier on oxidation properties of fish oil-based structured lipid emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 50:2957–2961
Donnelly JL, Decker EA, McClements DJ (1998) Iron-catalysed oxidation of menhaden oil as affected by emulsifiers. J Food Sci 63:997–1000
Klinkersorn U, Sophanodora P, Chinachoti P, McClements DJ, Decker EA (2005) Increasing the oxidative stability of liquid and dried tuna oil-in-water emulsions with electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition technology. J Agric Food Chem 53:4561–4566
Westerbeek JMM, Prins A (1991) Function of α-tending emulsifiers and proteins in whippable emulsions. In: Dickinson E (ed) Food polymers, gels and collioids. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 147–158
Frankel EN (1993) Formation of headspace volatiles by thermal decomposition of oxidized fish oils vs oxidized vegetable oils. J Am Oil Chem Soc 70:767–772
Nuchi CD, McClements DJ, Decker EA (2001) Impact of Tween20 hydroperoxides and iron on the oxidation of methyl linoleate and salmon oil dispersions. J Agric Food Chem 49:2916–4912
Dickinson E (1992) Structure and composition of adsorbed protein layers and the relationship to emulsion stability. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 88:2973–2983
Dickinson E (2001) Milk protein interfacial layers and the relationship to emulsion stability and rheology. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 20:197–210
Ye AQ, Singh H (2001) Interfacial composition and stability of sodium caseinate emulsions as influenced by calcium ions. Food Hydrocolloids 15:195–207
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Claudio Ceccato, Peter Fagan, and Zhiping Shen of CSIRO Food and Nutritional Sciences, Werribee, for their invaluable technical expertise and input with respect to scientific discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Richards, A., Golding, M., Wijesundera, C. et al. The Influence of Secondary Emulsifiers on Lipid Oxidation within Sodium Caseinate-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J Am Oil Chem Soc 88, 65–73 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-010-1642-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-010-1642-6