Abstract
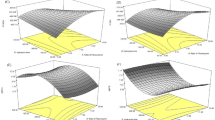
Enzymatic extraction of oil and protein from rice bran, using a commercial protease (Alcalase), was investigated and evaluated by response surface methodology. The effect of enzyme concentration was most significant on oil and protein extraction yields, whereas incubation time and temperature had no significant effect. The maximal extraction yields of oil and protein were 79 and 68%, respectively. Further, the quality of oil recovered from the process in terms of free fatty acid, iodine value, and saponification value was comparable with solvent-extracted oil and commercial rice bran oil, but the peroxide value was higher.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen, F.M., Extraction by Aqueous Enzymatic Processes, inform 1:984–987 (1991).
Dominguez, H., M.J. Nunez, and J.M. Lema, Enzymatic Pretreatment to Enhance Oil Extraction from Fruits and Oilseeds: A Revie, Food Chem. 49:271–286 (1994).
Rosenthal, A., D.L. Pyle, and K. Niranjan, Aqueous and Enzymatic Processes for Edible Oil Extraction, Enzyme Microb. Technol. 19:402–420 (1996).
Buenrostro, M., and C.A. Lopez-Munguia, Enzymatic Extraction of Avocado Oil, Biotechnol. Lett. 8:505–506 (1986).
McGlone, O.C., C.A. Lopez-Munguia, and J.V. Carter, Coconut Oil Extraction by a New Enzymatic Process, J. Food Sci. 51:695–697 (1986).
Barrios, V.A., D.A. Olmos, R.A. Noyola, and C.A. Lopez-Munguia, Optimization of an Enzymatic Process for Coconut Oil Extraction, Oleagineux 45:35–42 (1990).
Che Man, Y.B. Suhardiyono, A.B. Asbi, M.N. Azudin, and L.S. Wei, Aqueous Enzymatic Extraction of Coconut Oil, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 73:683–686 (1996).
Tano-Debrah, K., and Y. Ohta, Aqueous Extraction of Coconut Oil by an Enzyme-Assisted Process, J. Sci. Food Agric. 74:497–502 (1997).
Karlovic, D., M. Bocevska, J. Jakovlevic, and J. Turkulov, Corn Germ Oil Extraction by a New Enzymatic Process, Acta Aliment. 23:389–400 (1994).
Sarker, B.C., B.P.N. Singh, Y.C. Agrawal, and D.K. Gupta, Optimization of Enzyme Pretreatment of Rapeseed for Enhanced Oil Recovery, J. Food Sci. Technol. 35:183–186 (1998).
Dominguez, H., M.J. Nunez, and J.M. Lema, Oil Extractability from Enzymatically Treated Soybean and Sunflower: Range of Operational Variables, Food Chem. 46:277–284 (1993).
Kashyap, M.C., Y.C. Agrawal, B.C. Sarkar, and B.P.N. Singh, Response Surface Analysis of Enzyme Aided Extraction of Soybean, J. Food Sci. Technol. 34:386–390 (1997).
Dominguez, H., M.J. Nunez, and J.M. Lema, Aqueous Processing of Sunflower Kernels with Enzymatic Technology, Food Chem. 53:427–434 (1995).
Sineiro, J., H. Dominguez, M.J. Nunez, and J.M. Lema, Optimization of the Enzymatic Treatment During Aqueous Oil Extraction from Sunflower Seeds, —Ibid. 61:467–474 (1998).
Singh, R.K., B.C. Sarker, B.K. Kumbhar, Y.C. Agrawal, and M.K. Kulshreshtha, Response Surface Analysis of Enzyme Assisted Oil Extraction Factors for Sesame, Groundnut and Sunflowers Seeds, J. Food Sci. Technol. 36:511–514 (1999).
Sengupta, R., and D.K. Bhattacharyya, Enzymatic Extraction of Mustard Seed and Rice Bran, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 73:687–692 (1996).
Hernandez, N., M.E. Rodriguez-Alegria, F. Gonzalez, and A. Lopez-Munguia, Enzymatic Treatment of Rice Bran to Improve Processing, —Ibid. 77:177–180 (2000).
Myers, R.H., and D.C. Montgomery, Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Chichester, 1995, pp. 279–350.
Hanmoungjai, P., L. Pyle, and K. Niranjan, Extraction of Rice Bran Oil Using Aqueous Media, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 75:348–52 (2000).
Association of Official Analytical chemists, Official Methods of Analysis, 16th edn., edited by P. Cunniff, AOAC International, Gaithersburg, 1995.
International Union for Pure and Applied Chemistry, Standard Methods for the Analysis of Oils, Fats and Derivatives, 7th edn., edited by C. Paquot and A. Hautfenne, Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, 1986.
Seetharamaiah, G.S., and J.V. Prabhakar, Oryzanol Content of Indian Rice Bran Oil and Its Extraction from Soap Stock, J. Food Sci. Technol. 23:270–273 (1986).
Long, A.R., S.J. Massie, and W.J. Tyznik, Rapid Direct Extraction Derivatization Method for the Determination of Acylglycerol Lipids in Selected Sample Materials, J. Food Sci. 53:940–959 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hanmoungjai, P., Pyle, D.L. & Niranjan, K. Enzymatic process for extracting oil and protein from rice bran. J Amer Oil Chem Soc 78, 817–821 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-001-0348-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-001-0348-2