Abstract
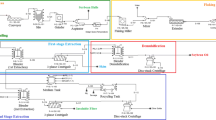
Simple, low-capital-investment oil refining techniques, which may also meet the needs of natural or organic food industries, were explored to process extruded-expelled (E-E) soybean oils with various fatty acid compositions. Most settled E-E oils are naturally low in phosphatides (<100 ppm phosphorus) and were easily water degummed to low phosphorus levels (<55 ppm). Free fatty acids were reduced to 0.04% by adsorption with 3% Magnesol®. Magnesol reduced residual phosphorus contents to negligible levels. This material also adsorbed primary and secondary oil oxidation products. Our adsorption refining procedure was much milder than conventional refining, as indicated by little formation of primary and secondary lipid oxidation products and less loss of tocopherol. The remaining challenge to effective natural refining is the removal of off-flavor components. Our adsorption treatment reduced the natural flavor of soybean oil but flavor was still present, probably too strong for many consumers. Polyunsaturated oils oxidized more easily than did the other types of oils; therefore, precautions should be taken when refining such oils. High-oleic soybean oil, on the other hand, had excellent oxidative stability and better flavor characteristics after degumming and adsorption with Magnesol compared with other oils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson, A.I., W.B. Wijeratne, S.W. Yeh, T.M. Wei, and L.S. Wei, Dry Extrusion as an Aid to Mechanical Expelling of Oil from Soybeans J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 64:1341–1347 (1987).
Bargale, P.C., R.J. Ford, F.W. Sosulski, D. Wulfsohn, and J. Irudayaraj, Mechanical Oil Expression from Extruded Soybean Samples, ——Ibid. 76:223–229 (1999).
Hill, S., Characterization and Oxidative Stability of Mechanically Expelled Soybean Oil, M.Sc. Thesis, University of Illinois, Champaign, 1990.
Hill, S., Studies on the Qualities of Soybean Oil: Extraction Method, Soybean Type, and Soybean Stability, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois, Champaign, 1992.
Wang, T., and L.A. Johnson, Survey of Soybean Oil and Meal Qualities Produced by Different Processes, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 78:311–318 (2001).
Wang, T., and L.A. Johnson, Refining High-Free Fatty Acid Wheat Germ Oil, ——Ibid. 78:71–76 (2001).
Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 4th edn., AOCS Press, Champaign, 1994.
SAS, SAS User's Guide: Statistics, SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, 1984.
Hernandez, E., and L. Yu, Adsorption Technology for Refining of Specialty Oils, Abstract of the 91st AOCS Annual Meeting and Expo, a Special Supplement to inform 11:s54 (2000).
Nicolosi, R.J., T.A. Wilson, C.W. Lawton, and F. Orthoefer, Crude vs., Refined Oils-Function, Application, and Nutrition, Ibid. Abstract of the 91st AOCS Annual Meeting and Expo, a Special Supplement to inform 11(5):s6 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Johnson, L.A. Natural refining of extruded-expelled soybean oils having various fatty acid compositions. J Amer Oil Chem Soc 78, 461–466 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-001-0286-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-001-0286-z