Abstract
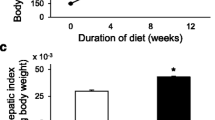
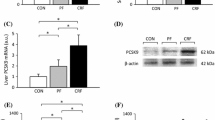
Hypercholesterolemia is a consistent feature of the nephrotic syndrome. However, the mechanisms underlying this perturbation are unclear. In the present work, we have investigated different factors that influence hepatic cholesterol metabolism using the nephrotic rat as a model. The induction of nephrosis resulted in a severe and sustained hypercholesterolemia. However, no effect on the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase, could be detected. Further, plasma lathosterol/cholesterol ratio, a measure of cholesterol synthesis, was not altered. Also, plasma levels of mevalonate, both a substrate for cholesterogenesis beyond the rate-limiting step and a marker for cholesterol synthesis, did not differ between control rats and those with established hypercholesterolemia. There was no detectable change in the expression of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor between the two experimental groups. We conclude that the early increase in cholesterol synthesis reported after the induction of nephrosis is not necessary for the maintenance of hypercholeserolemia. Established hypercholesterolemia of the nephrotic syndrome seems to represent a steady state in which neither enhanced hepatic cholesterol synthesis nor retarded LDL cholesterol clearance is of major importance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GFR:
-
glomerular filtration rate
- HMG-CoA:
-
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA
- LDL:
-
low density lipoprotein
- PAN:
-
puromycin aminonucleoside
References
Baxter, J.H. (1962) Hyperlipoproteinemia in Nephrosis, Arch. Int. Med. 109, 742–757.
Baxter, J.H., Goodman, H.C., and Havel, R.J. (1960) Serum Lipid and Lipoprotein Alterations in Nephrosis. J. Clin. Invest. 39, 455–464.
Marsh, J.B., and Sparks, C.E. (1979) Lipoproteins in Experimental Nephrosis: Plasma Levels and Composition, Metabolism 28, 1040–1045.
Berlyne, G.M., and Mallick, N.P., (1969) Ischaemic Heart Disease as a Complication of Nephrotic Syndrome, Lancet 2, 399–400.
Mallick, N.P., and Short, C.D. (1981) The Nephrotic Syndrome and Ischaemic Heart Disease, Nephron 27, 54–57.
Bernard, D.B. (1988) Extrarenal Complications of the Nephrotic Syndrome, Kidney Int. 33, 1184–1202.
Grundy, S.M. (1990) Management of Hyperlipidemia of Kidney Disease, Kidney Int. 37, 847–853.
Marsh, J.B., and Drabkin, D.L. (1955) Metabolic Channeling in Experimental Nephrosis. II. Lipide Metabolism, J. Biol. Chem. 212, 633–639.
Gherardi, E. and Calandra, S. (1980) Experimental Nephrotic Syndrome Induced in the Rat by Puromycin Aminonucleoside: Hepatic Synthesis of Neutral Lipids and Phospholipids from 3H-Water and 3H-Palmitate Lipids 15, 108–112.
Shafrir, E., and Brenner, T. (1979) Lipoprotein Lipid and Protein Synthesis in Experimental Nephrosis and Plasmapheresis. I: Studies in Rat in vivo. Lipids 14 695–702.
Golper, T.A., Feingold, K.R., Fulford, M.H., and Siperstein, M.-D. (1986) The Role of Circulating Mevalonate in Nephrotic Hypercholesterolemia in the Rat. J. Lipid Res. 27, 1044–1051.
Golper, T.A., and Swartz, S.H. (1982) Impaired Renal Mevalonate Metabolism in Nephrotic Syndrome: A Stimulus for Increased Hepatic Cholesterogenesis Independent of GFR and Hypoalbuminemia, Metabolism 31, 471–476.
Thabet, M.A.E.H., Challa, A., Chan, J.C.M., Pandak, W.M., Heuman, D.M., and Vlahcevic, Z.R. (1993) Studies of Alteration of Hepatic Cholesterol Metabolism in Puromycin-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome in Rats, Kidney Int. 44, 789–794.
Joven, J., Masana, L., Villabona, C., Vilella, E., Bargallo, T., Trias, M., Figueras, M., and Turner, P.R. (1989) Low Density Lipoprotein Metabolism in Rats with Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induced Nephrotic Syndrome, Metabolism 38, 491–495.
Kempen, H.J.M., Glatz, J.F.C., Gevers Leuven, J.A., van der Voort, H.A., and Katan, M.B. (1988) Serum Lathosterol Concentration Is an Indicator of Whole-Body Cholesterol Synthesis in Humans, J. Lipid Res. 29, 1149–1155.
Parker, T.S., McNamara, D.J., Brown, C.D., Kolb, R., Ahrens, E.H., Jr., Alberts, A.W., Tobert, J., Chen, J., and De Schepper, P.J. (1984) Plasma Mevalonate as a Measure of Cholesterol Synthesis in Man. J. Clin. Invest. 74, 795–804.
Goldstein, J.L., and Brown, M.S. (1977) The Low Density Lipoprotein Pathway and Its Relation to Atherosclerosis, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 46, 897–930.
Lund, E., Sisfontes, L., Reihnér, E., and Björkhem, I. (1989) Determination of Serum Levels of Unesterified Lathosterol by Isotope Dilution-Mass Spectrometry, Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 49, 165–171.
Lindenthal, B., and von Bergmann, K. (1994) Determination of Urinary Mevalonic Acid Using Isotope Dilution Technique, Biolog. Mass. Spectrom. 23, 445–450.
Brown, M.S., Goldstein, J.L., and Dietschy, J.M. (1979) Active and Inactive Forms of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase in the Liver of the Rat: Comparison with the Rate of Cholesterol Synthesis in Different Physiological States, J. Biol. Chem. 254, 5144–5149.
Rudling, M., Norstedt, G., Olivecrona, H., Reihnér, E., Gustafsson, J.-A., and Angelin, B. (1992) Importance of Growth Hormone for the Induction of Hepatic Low Density Lipoprotein Receptors, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 6983–6987.
Walker, W.G., and Mitch, W.E. (1988) in The Principles and Practice of Medicine (Harvey, A.M., Johns, R.J., McKusick, V.A., Owens, A.H., and Ross, R.S., eds.), 22nd edn., pp. 723–724. Appelton & Lange, San Mateo.
Björkhem, I., Miettinen, T., Reihnér, E., Ewerth, S., Angelin, B., and Einarsson, K. (1987) Correlation Between Serum Levels of Some Cholesterol Precursors and the Activity of HMG-CoA Reductase in Human Liver, J. Lipid Res. 28, 1137–1143.
Duane, W.C. (1995) Serum Lathosterol Levels in Human Subjects Reflect Changes in Whole Body Cholesterol Synthesis Induced by Lovastatin But Not Dietary Cholesterol, J. Lipid Res. 36, 343–348.
Marsh, J.B. (1984) Lipoprotein Metabolism in Experimental Nephrosis. J. Lipid Res. 25, 1619–1623.
Marsh, J.B., and Sparks, C.E. (1979) Hepatic Secretion of Lipoproteins in the Rat and the Effect of Experimental Nephrosis, J. Clin. Invest. 64, 1229–1237.
Pandak, W.M., Heuman, D.M., Hylemon, P.B., and Vlahcevic, Z.R. (1990) Regulation of Bile Acid Synthesis. IV. Interrelationship Between Cholesterol and Bile Acid Biosynthesis Pathways, J. Lipid Res. 31, 79–90.
Dullaart, R.P.F., Gansevoort, R.T., Sluiter, W.J., de Zeeuw, D., and de Jong, P.E. (1996) The Serum Lathosterol to Cholesterol Ratio, an Index of Cholesterol Synthesis, Is Not Elevated in Patients with Glomerular Proteinuria and Is Not Associated with Improvement of Hyperlipidemia in Response to Antiproteinuric Treatment, Metabolism 45, 723–730.
Vaziri, N.D., and Liang, K.H. (1995) Hepatic HMG-CoA Reductase Gene Expression During the Course of Puromycin-Induced Nephrosis, Kidney Int. 48, 1979–1985.
Edgren, B., and Hellström, K. (1972) In vivo Studies of the Metabolism of Mevalonic Acid in Nephrotic Rats, Nutr. Metab. 14, 331–338.
Subang, M.C., Stewart-Phillips, J.L., Pappu, A.S., Subang, R., and Gagnon, R.F. (1995) Possible Role of Mevalonate in the Hypercholesterolemia Seen in Experimental Chronic Renal Failure, Nephron 69, 151–154.
Rudling, M. (1992) Hepatic mRNA Levels for the LDL Receptor and HMG-CoA Reductase Show Coordinate Regulation in vivo, J. Lipid Res. 33, 493–501.
Vaziri, N.D., and Liang, K.H. (1996) Down-Regulation of Hepatic LDL Receptor Expression in Experimental Nephrosis, Kidney Int. 50, 887–893.
Kaysen, G.A. (1991) Hyperlipidemia of the Nephrotic Syndrome, Kidney Int. 39 (Suppl. 31), S8-S15.
Hirano, T., Furukawa, S., Kurokawa, M., Ebara, T., Dixon, J.L., and Nagano, S. (1995) Intracellular Apoprotein B Degradation Is Suppressed by Decreased Albumin Concentration in Hep G2 cells, Kidney Int. 47, 421–431.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Shurbaji, A., Humble, E., Rudling, M. et al. Hepatic cholesterol metabolism in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Lipids 33, 165–169 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-998-0192-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-998-0192-z