Abstract
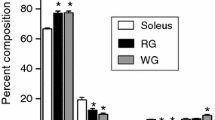
The fatty acid composition of the membrane phospholipids phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine in insulin-sensitive Type I (soleus) and insulin-resistant Type II (EDL) muscle is not known. In the present studies, soleus and EDL muscles were removed from 250–300 g Sprague-Dawley rats, and the fatty acid composition of total and individual phospholipid (PL) species was quantitated. As expected, triglyceride content was increased twofold in soleus muscle. No quantitative differences in the individual PL species or cholesterol content were found between the two muscles. However, a striking difference in PL fatty acid composition was observed in the PC fraction. An increase in 16∶0 with decreases in 18∶0, 18∶1, 22∶5n-3, and 22∶6n-3 (P<0.001 for each) was observed in the PC fraction of EDL compared to that from soleus, consistent with reduced elongation of PC fatty acids. Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation with the carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 inhibitor, etomoxir, did not alter the fatty acid pattern in either muscle. We conclude that an alteration in PL fatty acid composition consistent with reduced elongation of both saturated and unsaturated fatty acids is observed in Type II muscle. The restriction of these alterations to the PC fraction has important implications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
cardiolipin
- DAG:
-
diacylglycerol
- EDL:
-
extensor digitorum longus
- PC:
-
phosphatidylcholine
- PE:
-
phosphatidylethanolamine
- PI:
-
phosphatidylinositol
- PL:
-
phospholipid
- TG:
-
triglycerides
References
James, D.E., Jenkins A.B., and Kraegen E.W. (1985) Heterogeneity of Insulin Action in Individual Muscles in vivo: Euglycemic Clamp Studies in Rats, Am. J. Physiol. 248, E567-E580.
James, D.E., Burleigh, K.M., Storlien, L.H., Bennett, S.P., and Kraegen, E.W. (1986) Heterogeneity of Insulin Action in Muscle: Influence of Blood Flow, Am. J. Physiol. 251, E422-E430.
Sherman, W.M., Katz, A.L., Cutler, C.L., Withers, R.T., and Ivy, J.L. (1988) Glucose Transport: Locus of Muscle Insulin Resistance in Obese Zucker rats, Am. J. Physiol. 255, E374-E382.
Richter, E.A., Garetto, L.P., Goodman, M.N., and Ruderman, N.B. (1984) Enhanced Muscle Glucose Metabolism After Exercise: Modulation by Local Factors, Am. J. Physiol. 246, E476-E482.
Kern, M., Wells, J.A., Stephens, J.M., Elton, C.W., Friedman, J.E., Tapscott, E.B., Pekala, P.H., and Dohm, G.L. (1990) Insulin Responsiveness in Skeletal Muscle Is Determined by Glucose Transporter (Glut 4) Protein Level, Biochem. J. 270, 397–400.
Ploug, T., Galbo, H., Vinten, J., Jorgensen, M., and Richter, E.A. (1987) Kinetics of Glucose Transport in Rat Muscles: Effect of Insulin and Contractions, Am. J. Physiol. 253, E12-E20.
Henriksen, J.E., Bourey, R.E., Rodnick, K.J., Koranyi, L., Permutt, M.A., and Holloszy, J.O. (1990) Glucose Transporter Protein Content and Glucose Transport Capacity in Rat Skeletal muscles, Am. J. Physiol. 259, E593-E598.
Bonen, A., Tan, M.H., Cline, P., and Watson-Wright, W.M. (1981) Insulin Binding and Glucose Uptake Differences in Rodent Skeletal Muscles, Diabetes 30, 702–704.
Webster, B.A., Vigna, S.R., and Paquette, T. (1986) Acute Exercise, Epinephrine and Diabetes Enhance Insulin Binding to Skeletal Muscle, Am. J. Physiol. 250, E186-E197.
James, D.E., Zorzano, A., Boni-Schnetzler, M., Nemenoff, R.A., Powers A., Pilch, P.F., and Ruderman, N.B. (1986) Intrinsic Differences in Insulin Receptor Kinase Activity in Red and White Muscle, J. Biol. Chem. 261, 14939–14944.
Marette, A., Richardson, J.M., Ramlal, T., Babon, T.W., Vranic, M., Pessin, J.E., and Klip, A. (1992) Abundance, Localization and Insulin-Induced Translocation of Glucose Transporters in Red and White Muscle, Am. J. Physiol. 263, C443-C452.
Ginsberg, B.H., Chatterjee, P., and Yorek, M.A. (1991) Insulin Sensitivity Is Increased in Friend Erythroleukemia Cells Enriched in Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid, Receptor 1, 155–166.
Hague, T.A. (1988) Effects of Unsaturated Fatty Acids on Cell Membrane Functions, Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 48, 381–388.
Cullis P.R. and Hope M.J. (1985) Physical Properties and Functional Roles of Lipids in Membranes. Chapter 2 in Biochemistry of Lipids and Membranes (Vance, D.E., and Vance, J.E., eds.), Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co., Inc., Menlo Park.
Ariano, M.A., Armstrong, R.B., and Edgerton, V.R. (1973) Hindlimb Muscle Fiber Populations of Five Mammals, J. Histochem. Cytochem. 21, 51–55.
Barnett, M., Collier, G.R., and O’Dea, K. (1992) The Longitudinal Effect of Inhibiting Fatty Acid Oxidation in Diabetic Rats Fed a High Fat Diet. Horm. Metab. Res. 24, 360–362.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Stanley, H.S. (1957) A Simple Method for the Isolation and Purification of Total Lipids from Animal Tissues, J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509.
Alvarez, J.G., and Ludman, J. (1993) Semi-Automated Multi Sample Analysis of Amniotic Fluid Lipids by High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography—Reflectance Spectrodensitometry, J. Chromatogr. 615, 142–147.
Macala, L.J., Yu, R.K., and Ando, S. (1983) Analysis of Brain Lipids by High Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography and Densitometry, J. Lipid Res. 24, 1243–1250.
Vaysse, J., Pilardeau, P., and Garnier, M. (1985) Rapid Quantitative Analysis of Phospholipids in Biological Fluids After Thin-Layer Chromatography, Clin. Chem. Acta. 147, 183–190.
Storlien, L.H., Jenkins, A.B., Chisholm, D.J., Pascoe, W.S., Khouri, S., and Kraegen, E.W. (1991) Influence of Dietary Fat Composition on Development of Insulin Resistance in Rats: Relationship to Muscle Triglyceride and Omega-8 Fatty Acids in Muscle Phospholipid, Diabetes 40, 280–289.
Horrocks, L.A. (1968) The Alk-1-Enyl Group Content ofMammalian Myelin Phosphoglycerides by Quantitative Two-Dimensional Thin-Layer Chromatography, J. Lipid Research 9, 469–472.
Rawn, J.D. (1989) The Structure of Biological Membranes, in Proteins, Energy and Metabolism, pp. 209–232, Neil Patterson Publishers, Burlington.
Cook, H.W. (1991) Fatty Acid Desaturation and Chain Elongation in Eucaryotes, in Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes (Vance, D.E., and Vance, J., eds.), pp. 141–169, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Holub, B.J. (1978) Differential Utilization of 1-Palmitoyl and 1-Stearoyl Homologues of Various Unsaturated 1,2-Diacyl-sn-Glycerols for Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidyl-Ethanolamine Synthesis in Rat Liver Microsomes, Am. J. Chem. 253, 691–693.
Bordoni, A., Biagi, P.L., Turchetto, E., Rossi, C.A., and Hrelia, S. (1992) Diacylglycerol Fatty Acid Composition Is Related to Activation of Protein Kinase C in Cultured Cardiomyocytes, Cardioscience 3, 251–255.
Wahle, K.W., Milne, L., and McIntosh, G. (1991) Regulation of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Metabolism in Tissue Phospholipids of Obese (fa/fa) and Lean (Fa/-) Zucker Rats 1. Effect of Dietary Lipids on Cardiac Tissue, Lipids 26, 16–22.
Cook, H.W., and Spence, M.W. (1987) Interaction of (n-3) and (n-6) Fatty Acids in Desaturation and Chain Elongation of Essential Fatty Acids in Cultured Glioma Cells, Lipids 22, 613–619.
Vance, D.E. (1990) Phosphatidylcholine Metabolism: Masochistic Enzymology, Metabolic Regulation, and Lipoprotein Assembly, Biochem. Cell. Biol. 68, 1151–1165.
Diez, E., Chilton, F.H., Stroup, G., Mayer, R.J., Winkler, J.D., and Fonteh, A.N. (1994) Fatty Acid and Phospholipid Selectivity of Different Phospholipase A2 Enzymes Studied by Using a Mammalian Membrane as Substrate, Biochem. J. 301, 721–726.
Borkman, M., Storlien, L.H., Pan, D.A., Jenkins, A.B., Chisholm, D.J., and Campbell, L.V. (1993) The Relation Between Insulin Sensitivity and the Fatty Acid Composition of Skeletal Muscle Phospholipids, New Eng. J. Med. 328, 238–244.
Pan, D.A., Lillioja, S., Milner, M.R., Kriketos, A.D., Baur, L.A., Bogardus, C., and Storlien, L.H. (1995) Skeletal Muscle Membrane Lipid Composition Is Related to Adiposity and Insulin Action, J. Clin. Invest. 96, 2802–2808.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deceased (June 28, 1996).
About this article
Cite this article
Blackard, W.G., Li, J., Clore, J.N. et al. Phospholipid fatty acid composition in type I and type II rat muscle. Lipids 32, 193–198 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-997-0024-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-997-0024-1