Abstract
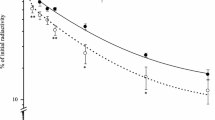
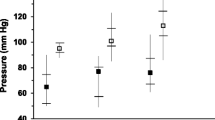
The catabolism and structure of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) may be the determining factor of their atheroprotective properties. To better understand the role of the kidney in HDL catabolism, here we characterized HDL subclasses and the catabolic rates of apo A-I in a rabbit model of proteinuria. Proteinuria was induced by intravenous administration of doxorubicin in New Zealand white rabbits (n = 10). HDL size and HDL subclass lipids were assessed by electrophoresis of the isolated lipoproteins. The catabolic rate of HDL-apo A-I was evaluated by exogenous radiolabelling with iodine-131. Doxorubicin induced significant proteinuria after 4 weeks (4.47 ± 0.55 vs. 0.30 ± 0.02 g/L of protein in urine, P < 0.001) associated with increased uremia, creatininemia, and cardiotoxicity. Large HDL2b augmented significantly during proteinuria, whereas small HDL3b and HDL3c decreased compared to basal conditions. HDL2b, HDL2a, and HDL3a subclasses were enriched with triacylglycerols in proteinuric animals as determined by the triacylglycerol-to-phospholipid ratio; the cholesterol content in HDL subclasses remained unchanged. The fractional catabolic rate (FCR) of [131I]-apo A-I in the proteinuric rabbits was faster (FCR = 0.036 h−1) compared to control rabbits group (FCR = 0.026 h−1, P < 0.05). Apo E increased and apo A-I decreased in HDL, whereas PON-1 activity increased in proteinuric rabbits. Proteinuria was associated with an increased number of large HDL2b particles and a decreased number of small HDL3b and 3c. Proteinuria was also connected to an alteration in HDL subclass lipids, apolipoprotein content of HDL, high paraoxonase-1 activity, and a rise in the fractional catabolic rate of the [131I]-apo A-I.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARE:
-
Arylesterase
- CHD:
-
Coronary heart disease
- FCR:
-
Fractional catabolic rate
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoproteins
- LPL:
-
Lipoprotein lipase
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- PL:
-
Phospholipid
- PON-1:
-
Paraoxonase-1
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerols
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
References
Tran-Dinh A, Diallo D, Delbosc S, Varela-Perez LM, Dang QB, Laupergue B, Burillo E, Michel JB, Levoye A, Martín-Ventura JL, Meilhac O (2013) HDL and endothelial protection. Br J Pharmacol 169:493–511
Lee JY, Lanningham-Foster L, Boudyguina EY, Smith TL, Young ER, Colvin PL, Thomas MJ, Parks JS (2004) Prebeta-high density lipoprotein has two metabolic fates in human apolipoprotein AI transgenic mice. J Lipid Res 45:716–728
Castro GR, Fielding CJ (1988) Early incorporation of cell-derived cholesterol into pre-beta-migrating high density lipoprotein. Biochemistry 12:25–29
Deakin S, Leaviev I, Gomaraschi M, Calabresi I, Franceschini G, James RW (2002) Enzymatically active paraoxonase-1 is located at the external membrane of producing cells and released by a high affinity, saturable, desorption mechanism. J Biol Chem 277:4301–4308
Kontush A, Chantepie S, Chapman MJ (2003) Small, dense HDL particles exert potent protection of atherogenic LDL against oxidative stress. Arterioscler Throm Vasc Biol 23:1881–1888
Pérez-Méndez O, Pacheco HG, Martínez-Sánchez C, Franco M (2014) HDL-cholesterol in coronary artery disease risk: function or structure? Clin Chim Acta 429:111–122
Toledo-Ibelles P, Franco M, Carreón-Torres E, Luc G, Tailleux A, Vargas-Alarcón G, Fragoso JM, Aguilar-Salinas C, Luna-Luna M, Pérez-Méndez O (2013) Normal HDL-apo AI turnover and cholesterol enrichment of HDL subclasses in New Zealand rabbits with partial nephrectomy. Metabolism 62:492–498
Graversen JH, Castro G, Kandoussi A, Nielsen H, Christensen EI, Norden A, Moestrup SK (2008) A pivotal role of the human kidney in catabolism of HDL protein components apolipoprotein AI and A-IV but not of A-II. Lipids 43:467–470
Kaysen GA (2009) Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in chronic kidney disease. J Ren Nutr 19:73–77
Soto-Miranda E, Carreón-Torres E, Lorenzo K, Bazán-Salinas B, García-Sánchez C, Franco M, Posadas-Romero C, Fragoso JM, López-Olmos V, Madero M, Rodríguez-Pérez JM, Vargas-Alarcón G, Pérez-Méndez O (2012) Shift of high-density lipoprotein size distribution toward large particles in patients with proteinuria. Clin Chim Acta 414:241–245
Lamarche B, Uffelman KD, Steiner G, Barrett PH, Lewis GF (1998) Analysis of particle size and lipid composition as determinants of the metabolic clearance of human high density lipoprotein in a rabbits model. J Lipid Res 39:1162–1172
Lewis GF, Lamarche B, Uffelman KD, Heatherigton AC, Honing MA, Szeto LW, Barrett PH (1997) Clearance of postprandial and lipolytically modified human HDL in rabbits and rats. J Lipid Res 38:1771–1778
Kamgang R, Foyet AF, Essame JL, Ngogang JY (2012) Effect of methanolic fraction of Kalanchoe crenata on metabolic parameters in adriamycin-renal induced impairment in rats. Indian J Pharmacol 44:566–570
Khurana S, Bruggeman LA, Kao HY (2012) Nuclear hormone receptors in podocytes. Cell Biosci 2:33
Watanabe N, Kamei S, Ohkubo A, Yamanaka M, Ohsawa S, Makino K, Tokuda K (1986) Urinary protein as measured with a pyrogallol red-molybdate complex, manually and in a Hitachi 726 automated analyzer. Clin Chem 32:1551–1554
Matsuo S, Fukatsu A, Taub ML, Caldwell PR, Brentjens JR, Andres G (1987) Glomerulonephritis induced in the rabbit by antiendothelial antibodies. J Clin Invest 79:1798–1811
Huesca-Gómez C, Franco M, Luc G, Montaño LF, Massó F, Posadas-Romero C, Pérez-Méndez O (2002) Chronic hypothyroidism induces abnormal structure of high-density lipoproteins and impaired kinetics of apolipoprotein A-I in the rat. Metabolism 51:443–450
Toledo-Ibelles P, García-Sánchez C, Ávila-Vazzini N, Carreón-Torres E, Posadas-Romero C, Vargas-Alarcón G, Pérez-Méndez O (2010) Enzymatic assessment of cholesterol on electrophoresis gels for estimating HDL size distribution and plasma concentrations of HDL subclasses. J Lipid Res 51:1610–1617
García-Sánchez C, Torres-Tamayo M, Juárez-Meavepeña M, López-Osorio C, Toledo-Ibelles P, Monter-Garrido M, Cruz-Robles D, Carreón-Torres E, Vargas-Alarcón G, Pérez-Méndez O (2011) Lipid plasma concentrations of HDL subclasses determined by enzymatic staining on polyacrylamide electrophoresis gels in children with metabolic syndrome. Clin Chim Acta 412:292–298
Juárez-Meavepeña M, Carreón-Torres E, López-Osorio C, García-Sánchez C, Gamboa R, Torres-Tamayo M, Fragoso JM, Rodríguez-Pérez JM, Vargas-Alarcón G, Pérez-Méndez O (2012) The Srb1 + 1050T allele is associated with metabolic syndrome concentrations of high-density lipoprotein subclasses. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 10:110–116
Williams PT, Krauss RM, Nichols AV, Vranizan KM, Wood PD (1990) Identifying the predominant peak diameter of high-density and low-density lipoproteins by electrophoresis. J Lipid Res 31:1131–1139
Tailleux A, Torpier G, Caron B, Fruchart JC, Fievet C (1993) Immunological properties of apoB-containing lipoprotein particles in human atherosclerotic arteries. J Lipid Res 34:719–728
Gan KN, Smolen A, Eckerson HW, La Du BN (1991) Purification of human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase. Evidence for one esterase catalyzing both activities. Drug Metab Dispos 19:100–106
Skutelsky E, Hartzan S, Socher R, Gafter U (1995) Modifications in glomerular polyanion distribution in adriamycin nephrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1799–1805
He L, Hao L, Fu X, Huang M, Li R (2015) Severe hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia accelerating renal injury: a novel model of type 1 diabetic hamsters induced by short-term high-fat/high-cholesterol diet and low-dose streptozotocin. BMC Nephrol 16:51
Aizawa K, Takeda S, Tashiro Y, Yorozu K, Hirata M, Kanada H, Moriguchi Y, Endo K (2012) Renoprotection by continuous erythropoietin receptor activator in puromycin aminonucleoside-induced nephrotic syndrome. Am J Nephrol 36:419–426
Bulum T, Kolaric B, Duvnjak L (2013) Lower levels of total HDL and HDL3 cholesterol are associated with albuminuria in normoalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients. J Endocrinol Invest 36:574–578
Kaysen GA, Hoye E, Jones H Jr (1995) Apolipoprotein AI levels are increased in part as a consequence of reduced catabolism in nephrotic rats. Am J Physiol 268:F532–F540
Marsche G, Saemann MD, Heinemman A, Holzer M (2013) Inflammation alters HDL composition and function: implications for HDL-raising therapies. Pharmacol Ther 137:341–351
Festa A, Williams K, Hanley AJ, Otvos JD, Goff DC, Wagenknecht LE, Haffner SM (2005) Nuclear magnetic resonance lipoprotein abnormalities in prediabetic subjects in the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Circulation 111:3465–3472
Van der Steeg WA, Holme I, Boekholdt SM, Larsen ML, Lindahl C, Stroes ES, Tikkanen MJ, Wareham NJ, Faergeman O, Olsson AG, Pedersen TR, Khaw KT, Kastelein JJ (2008) High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein particle size, and apolipoprotein A-I: significance for cardiovascular risk: the IDEAL and EPICNorfolk studies. J Am Coll Cardiol 51:634–642
Keane WF, Tomassini JE, Neff DR (2013) Lipid abnormalities in patients with chronic kidney disease: implications for the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 20:123–133
Scarpioni R, Ricardi M, Albertazzi V, Melfa L (2012) Treatment of dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease: effectiveness and safety of statins. World J Nephrol 1:184–194
Saku K, Mendoza SG, Laver M, Hynd BA, Gartside PS, Kashyap ML (1988) High-density lipoprotein apolipoprotein AI and AII turnover in moderate and severe proteinuria. Nephron 50:112–115
Vaziri ND (2003) Molecular mechanisms of lipid disorders in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 63:1964–1976
Elkhalil L, Majd Z, Bakir R, Perez-Mendez O, Castro G, Poulain P, Lacroix B, Duhal N, Fruchart JC, Luc G (1997) Fish-eye disease: structural and in vivo metabolic abnormalities of high-density lipoproteins. Metabolism 46:474–483
Carreón-Torres E, Rendón-Sauer K, Monter-Garrido M, Toledo-Ibelles P, Gamboa R, Menjivar M, López-Marure R, Luc G, Fievet C, Cruz D, Vargas-Alarcón G, Pérez-Méndez O (2009) Rosiglitazone modifies HDL structure and increases HDL-apo AI synthesis and catabolic rates. Clin Chim Acta 401:37–41
Razavi AE, Ani M, Pourfarzam M, Naderi GA (2012) Associations between high density lipoprotein mean particle size and serum paraoxonase-1 activity. J Res Med Sci 17:1020–1026
Gugliucci A, Caccavello R, Kotani K, Sakane N, Kimura S (2013) Enzymatic assessment of paraoxonase 1 activity on HDL subclasses: a practical zymogram method to assess HDL function. Clin Chim Acta 415:162–168
Kennedy DJ, Tang WH, Fan Y, Wu Y, Mann S, Pepoy M, Hazen SL (2013) Diminished antioxidant activity of high-density lipoprotein-associated proteins in chronic kidney disease. J Am Heart Assoc 2:e000104
Kashyap ML, Srivastava LS, Hynd BA, Brady D, Perisutti G, Glueck CJ, Gartside PS (1980) Apolipoprotein CII and lipoprotein lipase in human nephrotic syndrome. Atherosclerosis 35:29–40
Yamada M, Matsuda I (1970) Lipoprotein lipase in clinical and experimental nephrosis. Clin Chim Acta 30:787–794
Hirano T, Ebara T, Furukawa S, Nagano S, Takahashi T (1994) Mechanism of hypertriglyceridemia in Dahl salt-sensitive rats, an animal model of spontaneous nephrotic syndrome. Metabolism 43:248–256
Pérez-Méndez O, Alvarez-Salcedo P, Carreón-Torres E, Luc G, Arce Fonseca M, de la Peña A, Cruz Robles D, García JJ, Vargas-Alarcón G (2007) Palmitic acid in HDL is associated to low apo A-I fractional catabolic rates in vivo. Clin Chim Acta 78:53–58
Pérez-Méndez O, Carreón-Torres E, Franco M, Juárez-Oropeza MA (2009) HDL physicochemical characteristics as determinants of their plasma concentrations: what we have learned from thiazolidinediones. In: Pagano IS (ed) HDL and LDL cholesterol: physiology and clinical significance. Strait NB Nova Science, New York
Okubo K, Ikewaki K, Sakai S, Tada N, Kawaguchi Y, Mochizuki S (2004) Abnormal HDL apolipoprotein A-I and A-II kinetics in hemodialysis patients: a stable isotope study. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1008–1015
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a CONACYT Grant No. 132473. We are grateful to Rodrigo Velázquez Espejel for his technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
López-Olmos, V., Carreón-Torres, E., Luna-Luna, M. et al. Increased HDL Size and Enhanced Apo A-I Catabolic Rates Are Associated With Doxorubicin-Induced Proteinuria in New Zealand White Rabbits. Lipids 51, 311–320 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4120-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4120-6