Abstract
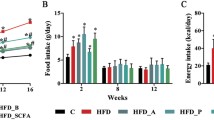
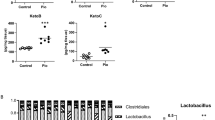
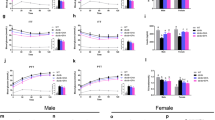
Hydroxy and oxo fatty acids were recently found to be produced as intermediates during gut microbial fatty acid metabolism. Lactobacillus plantarum produces these fatty acids from unsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic acid. In this study, we investigated the effects of these gut microbial fatty acid metabolites on the lipogenesis in liver cells. We screened their effect on sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) expression in HepG2 cells treated with a synthetic liver X receptor α (LXRα) agonist (T0901317). The results showed that 10-hydroxy-12(Z)-octadecenoic acid (18:1) (HYA), 10-hydroxy-6(Z),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid (18:2) (γHYA), 10-oxo-12(Z)-18:1 (KetoA), and 10-oxo-6(Z),12(Z)-18:2 (γKetoA) significantly decreased SREBP-1c mRNA expression induced by T0901317. These fatty acids also downregulated the mRNA expression of lipogenic genes by suppressing LXRα activity and inhibiting SREBP-1 maturation. Oral administration of KetoA, which effectively reduced triacylglycerol accumulation and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (ACC2) expression in HepG2 cells, for 2 weeks significantly decreased Srebp-1c, Scd-1, and Acc2 expression in the liver of mice fed a high-sucrose diet. Our findings suggest that the hypolipidemic effect of the fatty acid metabolites produced by L. plantarum can be exploited in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases or dyslipidemia.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CLA:
-
Conjugated linoleic acids
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified essential medium
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- LA:
-
Linoleic acid
- α-LNA:
-
α-Linolenic acid
- LXRα:
-
Liver X receptor α
- OA:
-
Oleic acid
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- RA:
-
Ricinoleic acid
- SREBP-1c:
-
Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c
References
De Vries MC, Vaughan EE, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM (2006) Lactobacillus plantarum—survival, functional and potential probiotic properties in the human gastrointestinal tract. Int Dairy J 16:1018–1028
Mathara JM, Schillinger U, Kutima PM, Mbugua SK, Guigas C, Franz C, Holzapfel WH (2008) Functional properties of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Maasai traditional fermented milk products in Kenya. Curr Microbiol 56:315–321
Georgieva R, Iliev I, Haertlé T, Chobert JM, Ivanova I, Danova S (2009) Technological properties of candidate probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Int Dairy J 19:696–702
Parvez S, Malik KA, Ah Kang S, Kim HY (2006) Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J Appl Microbiol 100:1171–1185
Candela M, Perna F, Carnevali P, Vitali B, Ciati R, Giochetti P, Rizzello F, Campieri M, Brigidi P (2008) Interaction of probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains with human intestinal epithelial cells: adhesion properties, competition against enteropathogens and modulation of IL-8 production. Int J Food Microbiol 125:286–292
Kishino S, Ogawa J, Omura Y, Matsumura K, Shimizu S (2002) Conjugated linoleic acid by lactic acid bacteria. J Am Oil Chem Soc 79:159–163
Ando A, Ogawa J, Kishino S, Shimizu S (2003) CLA production from ricinoleic acid by lactic acid bacteria. J Am Oil Chem Soc 80:889–894
Ogawa J, Kishino S, Ando A, Sugimoto S, Mihara K, Shimizu S (2005) Production of conjugated fatty acids by lactic acid bacteria. J Biosci Bioeng 100:355–364
Kishino S, Ogawa J, Yokozeki K, Shimizu S (2011) Linoleic acid isomerase in Lactobacillus plantarum AKU1009a proved to be a multi-component enzyme system requiring oxidoreduction cofactors. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:318–322
Kishino S, Takeuchi M, Park S-B, Hirata A, Kitamura N, Kunisawa J, Kiyono H, Iwamoto R, Isobe Y, Arita M, Arai H, Ueda K, Shima J, Takahashi S, Yokozeki K, Shimizu S, Ogawa J (2013) Polyunsaturated fatty acid saturation by gut lactic acid bacteria affecting host lipid composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:17808–17813
Targher G, Bertolini L, Padovani R, Rodella S, Tessari R, Zenari L, Day C, Arcado G (2007) Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with cardiovascular disease among type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 30:1212–1218
Zaima N, Sugawara T, Goto D, Hirata T (2006) Trans geometric isomers of EPA decrease LXRα-induced cellular triacylglycerol via SREBP-1c and PGC-1β. J Lipid Res 47:2712–2717
Nanthirudjanar T, Furumoto H, Hirata T, Sugawara T (2013) Oxidized eicosapentaenoic acids more potently reduce LXRα-induced cellular triacylglycerol via suppression of SREBP-1c, PGC-1β, and GPA than its intact form. Lipids Health Dis 12:73
Curtis RG, Heilbron SI, Jones ERH, Woods GF (1953) The chemistry of the triterpenes. Part XIII. The further characterisation of polyporenic acid A. J Chem Soc 1953:457–464
Takahashi N, Kawada T, Goto T, Yamamoto T, Taimatsu A, Matsui N, Kimura K, Saito M, Hosokawa M, Miyashita K, Fushiki T (2002) Dual action of isoprenols from herbal medicines on both PPARgamma and PPARalpha in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and HepG2 hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 514:315–322
Hannah VC, Ou J, Luong A, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2001) Unsaturated fatty acids down-regulate SREBP isoforms 1a and 1c by two mechanisms in HEK-293 cells. J Biol Chem 276:4365–4372
Caputo M, Zirpoli H, Torino G, Tecce MF (2010) Selective regulation of UGT1A1 and SREBP-1c mRNA expression by docosahexaenoic, eicosapentaenoic, and arachidonic acids. J Cell Physiol 226:187–193
Clarke SD (2001) Nonalcoholic steatosis and steatohepatitis. I. Molecular mechanism for polyunsaturated fatty acid regulation of gene transcription. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G865–G869
Vanden Heuvel JP, Kreder D, Belda B, Hannon DB, Nugent CA, Burns KA, Taylor MJ (2003) Comprehensive analysis of gene expression in rat and human hepatoma cells exposed to the peroxisome proliferator WY14,643. Toxicol Appl Pharm 188:185–198
Tanaka N, Zhang X, Sugiyama E, Kono H, Horiuchi A, Nakajim T, Kanbe H, Tanaka E, Gonzalez FJ, Aoyama T (2010) Eicosapentaenoic acid improves hepatic steatosis independent of PPARgamma and PPARalpha in ion of SREBP-1 maturation in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 80:1601–1612
Barber MC, Price NT, Travers MT (2005) Structure and regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase genes of metazoan. Biochim Biophys Acta 1733:1–28
Wakil SJ, Abu-Elheiga LA (2009) Fatty acid metabolism: target for metabolic syndrome. J Lipid Res 50:S138–S143
Frayn KN, Arner P, Yki-Jarvinen H (2006) Fatty acid metabolism in adipose tissue, muscle and liver in health and disease. Essays Biochem 42:89–103
Abu-Elheiga L, Matzuk MM, Abo-Hashema KAH, Wakil SJ (2001) Continuous fatty acid oxidation and reduced fat storage in mice lacking acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2. Science 291:2613–2616
Haas JT, Miao J, Chanda D, Wang Y, Zhao E, Haas ME, Hirschey M, Vaitheesvaran B, Farese RV Jr, Kurland IJ, Graham M, Crooke R, Foufelle F, Biddinger SB (2012) Hepatic insulin signaling is required for obesity-dependent expression of SREBP-1c mRNA but not for feeding-dependent expression. Cell Metab 15:873–884
Field FJ, Born E, Murthy S, Mathur SN (2002) Poly-unsaturated fatty acids decrease the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 in CaCo-2 cells: effect on fatty acid synthesis and triacylglycerol transport. Biochem J 368:357–363
Castle JC, Hara Y, Raymond CK, Garret-Engee P, Ohwaki K, Kan Z, Kusunoki J, Johnson JM (2009) ACC2 is expressed at high levels human white adipose and has an isoform with a novel N-terminus. PloS One 4:e4369
Acknowledgments
This research was partially supported by the Bio-Oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution of Japan to J. Ogawa. It was also partially supported by the NEDO Innovation Commercialization Venture Support Project with the collaboration of Nitto Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. and J. Ogawa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nanthirudjanar, T., Furumoto, H., Zheng, J. et al. Gut Microbial Fatty Acid Metabolites Reduce Triacylglycerol Levels in Hepatocytes. Lipids 50, 1093–1102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4067-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4067-z