Abstract
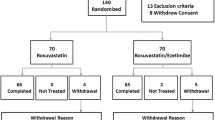
The aim of the study was to compare the efficacy of high-dose rosuvastatin, low-dose rosuvastatin plus fenofibrate and low-dose rosuvastatin plus omega-3 fatty acids with regard to the lipid profile in patients with mixed hyperlipidemia. The primary endpoint was changes in non-high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (non-HDL-C) levels. Study participants were randomly allocated to receive rosuvastatin 40 mg (n = 30, R group), rosuvastatin 10 mg plus fenofibrate 200 mg (n = 30, RF group) or rosuvastatin 10 mg plus n-3 fatty acids 2 g (n = 30, RN group). Non-HDL-C levels were reduced in all groups: in R group by 54%, in RF group by 42% and in RN group by 42%. Significant reductions in total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein (LDL)-C and triglyceride levels were observed in all groups. The reductions in total and LDL-C were greatest in the R group while a more pronounced reduction of triglycerides in the RF group compared with that in the R and the RN group was observed. HDL-C levels were significantly increased only in the RF group. In conclusion, high doses of rosuvastatin and small doses of rosuvastatin plus either fenofibrate or n-3 fatty acids exhibit favorable effects on both LDL-C and non-HDL-C levels. However, rosuvastatin monotherapy more potently reduces these parameters. The combination of rosuvastatin plus fenofibrate leads to a greater decrease in triglyceride levels and a greater increase in HDL-C levels compared with the other two treatments. While awaiting the results of ongoing trials high doses of rosuvastatin may represent the treatment of choice in individuals with mixed dyslipidemia.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ApoA-1:
-
Apolipoprotein A-1
- apoB:
-
Apolipoprotein B
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- HDL:
-
High density lipoprotein
- HOMA:
-
Homeostasis model assessment
- IDL:
-
Intermediate density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- R group:
-
Rosuvastatin group
- RF group:
-
Rosuvastatin-fenofibrate combination group
- RN group:
-
Rosuvastatin-n-3 fatty acids combination group
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- TSH:
-
Thyroid stimulating protein
References
Durrington P (2003) Dyslipidaemia. Lancet 362:717–731
Fruchart JC, Sacks F, Hermans MP, Assmann G, Brown WV, Ceska R, Chapman MJ, Dodson PM, Fioretto P, Ginsberg HN, Kadowaki T, Lablanche JM, Marx N, Plutzky J, Reiner Z, Rosenson RS, Staels B, Stock JK, Sy R, Wanner C, Zambon A, Zimmet P (2008) The residual risk reduction initiative: a call to action to reduce residual vascular risk in patients with dyslipidemia. Am J Cardiol 102:1K–34K
McKenney JM, Jones PH, Adamczyk MA, Cain VA, Bryzinski BS, Blasetto JW (2003) Comparison of the efficacy of rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin, simvastatin, and pravastatin in achieving lipid goals: results from the STELLAR trial. Curr Med Res Opin 19:689–698
Nissen SE, Nicholls SJ, Sipahi I, Libby P, Raichlen JS, Ballantyne CM, Davignon J, Erbel R, Fruchart JC, Tardif JC, Schoenhagen P, Crowe T, Cain V, Wolski K, Goormastic M, Tuzcu EM (2006) Effect of very high-intensity statin therapy on regression of coronary atherosclerosis: the ASTEROID trial. JAMA 295:1556–1565
Milionis HJ, Rizos E, Kostapanos M, Filippatos TD, Gazi IF, Ganotakis ES, Goudevenos J, Mikhailidis DP, Elisaf MS (2006) Treating to target patients with primary hyperlipidaemia: comparison of the effects of ATOrvastatin and ROSuvastatin (the ATOROS study). Cur Med Res Opin 22:1123–1131
Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM Jr, Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, MacFadyen JG, Nordestgaard BG, Shepherd J, Willerson JT, Glynn RJ (2008) Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med 359:2195–2207
Elisaf M (2002) Effects of fibrates on serum metabolic parameters. Curr Med Res Opin 18:269–276
Ginsberg HN, Elam MB, Lovato LC, Crouse JR, Leiter LA, Linz P, Friedewald WT, Buse JB, Gerstein HC, Probstfield J, Grimm RH, Ismail-Beigi F, Bigger JT, Goff DC Jr, Cushman WC, Simons-Morton DG, Byington RP (2010) Effects of combination lipid therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 362:1563–1574
Wierzbicki AS, Mikhailidis DP, Wray R, Schacter M, Cramb R, Simpson WG, Byrne CB (2003) Statin-fibrate combination: therapy for hyperlipidemia: a review. Curr Med Res Opin 19:155–168
Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Mehra MR, Ventura HO (2009) Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular diseases. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:585–594
Gazi I, Liberopoulos EN, Saougos VG, Elisaf M (2006) Beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acids: the current evidence. Hellenic J Cardiol 47:223–231
Davidson MH, Stein EA, Bays HE, Maki KC, Doyle RT, Shalwitz RA, Ballantyne CM, Ginsberg HN (2007) Efficacy and tolerability of adding prescription omega-3 fatty acids 4 g/dl to simvastatin 40 mg/dL in hypertriglyceridemic patients: an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Ther 29:1354–1367
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC Jr, Stone NJ (2004) Implications of recent clinical trials for the national cholesterol education program adult treatment panel III guidelines. Circulation 110:227–239
Pocock SJ (1983) Clinical trials. A practical approach. Wiley, New York
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Grundy SM, Brewer HB Jr, Cleeman JI, Smith SC Jr, Lenfant C, American Heart Association, National Heart, Lung, Blood Institute (2004) Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation 109:433–438
Castelli WP, Garrison RJ, Wilson PW, Abbott RD, Kannel WB, Kalousdian S (1986) Incidence of coronary heart disease and lipoprotein cholesterol levels. The Framingham study. JAMA 256:2835–2838
Bairaktari ET, Seferiadis KI, Elisaf MS (2005) Evaluation of methods for the measurement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 10:45–54
Pischon T, Girman CJ, Sacks FM, Rifai N, Stampfer MJ, Rimm EB (2005) Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apolipoprotein B in the prediction of coronary heart disease in men. Circulation 112:3375–3383
Robinson JG, Wang S, Smith BJ, Jacobson TA (2009) Meta-analysis of the relationship between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction and coronary heart disease risk. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:316–322
Robins SJ, Collins D, Wittes JT, Papademetriou V, Deedwania PC, Schaefer EJ, McNamara JR, Kashyap ML, Hershman JM, Wexler LF, Rubins HB, VA-HIT Study Group, Veterans Affairs High-Density Lipoprotein Intervention Trial (2001) Relation of gemfibrozil treatment and lipid levels with major coronary events: VA-HIT: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 285:1585–1591
Rubenfire M, Brook RD, Rosenson RS (2010) Treating mixed hyperlipidemia and the atherogenic lipid phenotype for prevention of cardiovascular events. Am J Med 123:892–898
Cannon CP, Steinberg BA, Murphy SA, Mega JL, Braunwald E (2006) Meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcomes trials comparing intensive versus moderate statin therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:438–445
ACCORD Study Group, Ginsberg HN, Elam MB, Lovato LC, Crouse JR 3rd, Leiter LA, Linz P, Friedewald WT, Buse JB, Gerstein HC, Probstfield J, Grimm RH, Ismail-Beigi F, Bigger JT, Goff DC Jr, Cushman WC, Simons-Morton DG, Byington RP (2010) Effects of combination lipid therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 362:1563–1574
Keech A, Simes RJ, Barter P, Best J, Scott R, Taskinen MR, Forder P, Pillai A, Davis T, Glasziou P, Drury P, Kesaniemi YA, Sullivan D, Hunt D, Colman P, d’Emden M, Whiting M, Ehnholm C, Laakso M (2005) Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in 9795 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): randomised controlled trial. Lancet 366:1849–1861
Tsimihodimos V, Miltiadous G, Daskalopoulou SS, Mikhailidis DP, Elisaf MS (2005) Fenofibrate: metabolic and pleiotropic effects. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 3:87–98
Kostapanos MS, Milionis HJ, Agouridis AD, Rizos CV, Elisaf MS (2009) Rosuvastatin treatment is associated with an increase in insulin resistance in hyperlipidaemic patients with impaired fasting glucose. Int J Clin Pract 63:1308–1313
Baker WL, Talati R, White CM, Coleman CI (2010) Differing effect of statins on insulin sensitivity in non-diabetics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87:98–107
Lankinen M, Schwab U, Erkkila A, Seppanen-Laakso T, Hannila ML, Mussalo H, Lehto S, Uusitupa M, Gylling H, Oresic M (2009) Fatty fish intake decreases lipids related to inflammation and insulin signaling—a lipidomics approach. PLoS One 4:e5258
Kuda O, Jelenik T, Jilkova Z, Flachs P, Rossmeisl M, Hensler M, Kazdova L, Ogston N, Baranowski M, Gorski J, Janovska P, Kus V, Polak J, Mohamed-Ali V, Burcelin R, Cinti S, Bryhn M, Kopecky J (2009) n-3 fatty acids and rosiglitazone improve insulin sensitivity through additive stimulatory effects on muscle glycogen synthesis in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 52:941–951
Mostad IL, Bjerve KS, Bjorgaas MR, Lydersen S, Grill V (2006) Effects of n-3 fatty acids in subjects with type 2 diabetes: reduction of insulin sensitivity and time-dependent alteration from carbohydrate to fat oxidation. Am J Clin Nutr 84:540–550
Tenenbaum H, Behar S, Boyko V, Adler Y, Fisman EZ, Tanne D, Lapidot M, Schwammenthal E, Feinberg M, Matas Z, Motro M, Tenenbaum A (2007) Long-term effect of bezafibrate on pancreatic beta-cell function and insulin resistance in patients with diabetes. Atherosclerosis 194:265–271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Agouridis, A.P., Tsimihodimos, V., Filippatos, T.D. et al. High Doses of Rosuvastatin are Superior to Low Doses of Rosuvastatin Plus Fenofibrate or n-3 Fatty Acids in Mixed Dyslipidemia. Lipids 46, 521–528 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-011-3538-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-011-3538-0