Abstract
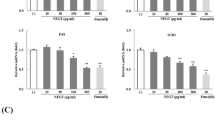
The (−)-gallocatechin gallate (GCG) concentration in some tea beverages can account for as much as 50% of the total catechins, as a result of sterilization. The present study aims to examine the effects of GCG-rich tea catechins on hyperlipidemic rats and the mechanisms associated with regulating cholesterol metabolism in the liver. By performing heat epimerization of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), we manufactured a mixture of catechins that had a GCG content of approximately 50% (w/w). In sucrose-rich diet-induced hyperlipidemic rats, the GCG-rich tea catechins exhibited strong activity in reducing plasma cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations. Furthermore, the hepatic cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations that had increased as a result of the sucrose-rich diet were reduced due to GCG-rich tea catechins consumption. In order to investigate the hyperlipidemic mechanism of GCG-rich tea catechins, we examined the hepatic expressions of LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase in hyperlipidemic rats. We further evaluated the action of purified GCG on LDL receptor activity, which is a key contributor to the regulation of cholesterol concentrations. We found that purified GCG increased LDL receptor protein level and activity to a greater extent than EGCG. In conclusion, our study indicates that GCG-rich tea catechins in tea beverages may be effective in preventing hyperlipidemia by lowering plasma and hepatic cholesterol concentrations.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGCG:
-
(−)-Epigallocatechin gallate
- GCG:
-
(−)-Gallocatechin gallate
- HDL:
-
High density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- VLDL:
-
Very low density lipoprotein
- LDLR:
-
Low density lipoprotein receptor
- HMG-CoA:
-
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A
References
Imai K, Nakachi K (1995) Cross sectional study of effects of drinking green tea on cardiovascular and liver diseases. Br Med J 310(6981):693–696 (PubMed: 7711535)
Kono S, Shinchi K, Wakabayashi K, Honjo S, Todoroki I, Sakurai Y, Imanishi K, Nishikawa H, Ogawa S, Katsurada M (1996) Relation of green tea consumption to serum lipids and lipoproteins in Japanese men. J Epidemiol 6(3):128–133 (PubMed: 8952216)
Yang CS, Landau JM (2000) Effects of tea consumption on nutrition and health. J Nutr 130(10):2409–2412 (PubMed: 11015465)
Zaveri NT (2006) Green tea and its polyphenolic catechins: medicinal uses in cancer and noncancer applications. Life Sci 78(18):2073–2080 (PubMed: 16445946)
Wang S, Noh SK, Koo SI (2006) Epigallocatechin gallate and caffeine differentially inhibit the intestinal absorption of cholesterol and fat in ovariectomized rats. J Nutr 136(11):2791–2796 (PubMed: 11015465)
Raederstorff DG, Schlachter MF, Elste V, Weber P (2003) Effect of EGCG on lipid absorption and plasma lipid levels in rats. J Nutr Biochem 14(6):326–332 (PubMed: 12873714)
Chisaka T, Matsuda H, Kubomura Y, Mochizuki M, Yamahara J, Fujimura H (1988) The effect of crude drugs on experimental hypercholesteremia: mode of action of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate in tea leaves. Chem Pharm Bull 36(1):227–233 (PubMed: 3378286)
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1986) A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 232(4746):34–47 (PubMed: 3513311)
Kuhn DJ, Burns AC, Kazi A, Dou QP (2004) Direct inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway by ester bond-containing green tea polyphenols is associated with increased expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 and LDL receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1682(1–3):1–10 (PubMed: 15158750)
Bursill CA, Roach PD (2006) Modulation of cholesterol metabolism by the green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin gallate in cultured human liver (HepG2) cells. J Agric Food Chem 54(5):1621–1626 (PubMed: 16506810)
Chen Z, Zhu QY, Tsang D, Huang Y (2001) Degradation of green tea catechins in tea drinks. J Agric Food Chem 49(1):477–482 (PubMed: 11170614)
Ikeda I, Kobayashi M, Hamada T, Tsuda K, Goto H, Imaizumi K, Nozawa A, Sugimoto A, Kakuda T (2003) Heat-epimerized tea catechins rich in gallocatechin gallate and catechin gallate are more effective to inhibit cholesterol absorption than tea catechins rich in epigallocatechin gallate and epicatechin gallate. J Agric Food Chem 51(25):7303–7307 (PubMed: 14640575)
Kobayashi M, Unno T, Suzuki Y, Nozawa A, Sagesaka Y, Kakuda T, Ikeda I (2005) Heat-epimerized tea catechins have the same cholesterol-lowering activity as green tea catechins in cholesterol-fed rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69(12):2455–2458 (PubMed: 16377909)
Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1984) Progress in understanding the LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase, two membrane proteins that regulate the plasma cholesterol. J Lipid Res 25(13):1450–1461 (PubMed: 6397553)
Bisgaier CL, Essenburg AD, Auerbach BJ, Pape ME, Sekerke CS, Gee A, Wolle S, Newton RS (1997) Attenuation of plasma low density lipoprotein cholesterol by select 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors in mice devoid of low density lipoprotein receptors. J Lipid Res 38(12):2502–2515 (PubMed: 9458274)
Yang M, Wang C, Chen H (2001) Green, oolong and black tea extracts modulate lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemia rats fed high-sucrose diet. J Nutr Biochem 12(1):14–20 (PubMed: 11179857)
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18(6):499–502 (PubMed: 4337382)
Folch J, Lees M, Slovan Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226(1):497–509 (PubMed: 13428781)
Wassmann S, Faul A, Hennen B, Scheller B, Bohm M, Nickenig G (2003) Rapid effect of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibition on coronary endothelial function. Circ Res 93(9):e98–e103 (PubMed: 14551237)
Munoz S, Merlos M, Zambon D, Rodriguez C, Sabate J, Ros E, Laguna JC (2001) Walnut-enriched diet increases the association of LDL from hypercholesterolemic men with human HepG2 cells. J Lipid Res 42(12):2069–2076 (PubMed: 11734580)
Klaus S, Pultz S, Thone-Reineke C, Wolfram S (2005) Epigallocatechin gallate attenuates diet-induced obesity in mice by decreasing energy absorption and increasing fat oxidation. Int J Obes (Lond) 29(6):615–623 (PubMed: 15738931)
Jiang J, Nilsson-Ehle P, Xu N (2006) Influence of liver cancer on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Lipids Health Dis 5:4 (PubMed: 16515689)
Lombardo YB, Drago S, Chicco A, Fainstein-Day P, Gutman R, Gagliardino JJ, Gomez Dumm CL (1996) Long-term administration of a sucrose-rich diet to normal rats: relationship between metabolic and hormonal profiles and morphological changes in the endocrine pancreas. Metabolism 45(12):1527–1532 (PubMed: 8969287)
Park HJ, Shin DH, Chung WJ, Leem K, Yoon SH, Hong MS, Chung JH, Bae JH, Hwang JS (2006) Epigallocatechin gallate reduces hypoxia-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. Life Sci 78(24):2826–2832 (PubMed: 16445947)
Moon HS, Lee HG, Choi YJ, Kim TG, Cho CS (2007) Proposed mechanisms of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate for anti-obesity. Chem Biol Interact 167(2):85–98 (PubMed: 17368440)
Bursill CA, Roach PD (2007) A green tea catechin extract upregulates the hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptor in rats. Lipids 42(7):621–627 (PubMed: 17582541)
Spady DK, Turley SD, Dietschy JM (1985) Rates of low density lipoprotein uptake and cholesterol synthesis are regulated independently in the liver. J Lipid Res 26(4):465–472. (PubMed: 4009063)
Strobl W, Gorder NL, Fienup GA, Lin-Lee YC, Gotto AM Jr, Patsch W (1989) Effect of sucrose diet on apolipoprotein biosynthesis in rat liver. Increase in apolipoprotein E gene transcription. J Biol Chem 264(2):1190–1194 (PubMed: 2463248)
Radosavljevic M, Lin-Lee YC, Soyal SM, Strobl W, Seelos C, Gotto AM Jr, Patsch W (1992) Effect of sucrose diet on expression of apolipoprotein genes A-I, C-III and A-IV in rat liver. Atherosclerosis 95(2–3):147–156 (PubMed: 1418089)
Yang TT, Koo MW (2000) Chinese green tea lowers cholesterol level through an increase in fecal lipid excretion. Life Sci 66(5):411–423 (PubMed: 10670829)
Zhong L, Furne JK, Levitt MD (2006) An extract of black, green, and mulberry teas causes malabsorption of carbohydrate but not of triacylglycerol in healthy volunteers. Am J Clin Nutr 84(3):551–555 (PubMed: 16960168)
Zhang J, Kashket S (1998) Inhibition of salivary amylase by black and green teas and their effects on the intraoral hydrolysis of starch. Caries Res 32(3):233–238 (PubMed: 9577990)
Oki T, Matsui T, Matsumoto K (2000) Evaluation of alpha-glucosidase inhibition by using an immobilized assay system. Biol Pharm Bull 23(9):1084–1087 (PubMed: 10993209)
Witztum JL, Steinberg D (1991) Role of oxidized low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J Clin Invest 88(6):1785–1792 (PubMed: 1752940)
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (2004) Lowering plasma cholesterol by raising LDL receptors. Atheroscler Suppl 5(3):57–59 (PubMed: 15531276)
Pal S, Thomson AM, Bottema CD, Roach PD (2002) Polyunsaturated fatty acids downregulate the low density lipoprotein receptor of human HepG2 cells. J Nutr Biochem 13(1):55–63 (PubMed: 11834220)
Wilcox LJ, Borradaile NM, de Dreu LE, Huff MW (2001) Secretion of hepatocyte apoB is inhibited by the flavonoids, naringenin and hesperetin, via reduced activity and expression of ACAT2 and MTP. J Lipid Res 42(5):725–734 (PubMed: 11352979)
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1997) The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 89(3):331–340 (PubMed: 9150132)
Sanae F, Miyaichi Y, Kizu H, Hayashi H (2002) Effects of catechins on vascular tone in rat thoracic aorta with endothelium. Life Sci 71(21):2553–2562 (PubMed: 12270760)
Satoh K, Sakamoto Y, Ogata A, Nagai F, Mikuriya H, Numazawa M, Yamada K, Aoki N (2002) Inhibition of aromatase activity by green tea extract catechins and their endocrinological effects of oral administration in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 40(7):925–933 (PubMed: 12065214)
Kajiya K, Kumazawa S, Nakayama T (2001) Steric effects on interaction of tea catechins with lipid bilayers. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65(12):2638–2643 (PubMed: 11826958)
No JK, Soung DY, Kim YJ, Shim KH, Jun YS, Rhee SH, Yokozawa T, Chung HY (1999) Inhibition of tyrosinase by green tea components. Life Sci 65(21):PL241–PL246 (PubMed: 10576599)
Guo Q, Zhao B, Shen S, Hou J, Hu J, Xin W (1999) ESR study on the structure-antioxidant activity relationship of tea catechins and their epimers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1427(1):13–23 (PubMed: 10082983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.M., Kim, C.W., Kim, J.K. et al. GCG-Rich Tea Catechins are Effective in Lowering Cholesterol and Triglyceride Concentrations in Hyperlipidemic Rats. Lipids 43, 419–429 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-008-3167-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-008-3167-4