Abstract
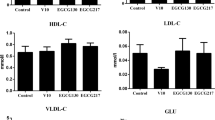
In order to study the mechanism of DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone) in reducing fat in broiler chickens during embryonic development, fertilized eggs were administrated with DHEA before incubation and its effect on lipid metabolism and expression of hepatic lipogenetic genes was investigated. The mRNA levels of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FAS), malic enzyme (ME), apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100) and sterol regulator element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) were determined using real time quantitative PCR. Samples of livers were collected from the chickens on days 9, 14, and 19 of embryonic development as well as at hatching. Blood samples were extracted on days 14, 19 of incubation and at hatching. The results showed that DHEA decreased the concentration of triacyglycerol in the blood and the content in liver, and the mRNA levels of ACC, FAS, ME, SREBP-1c and apoB. This suggested that DHEA decreased the expression of hepatic lipogenetic genes and suppressed triglycerols transport, by which it reduced the deposition of fat in adipose tissue in broiler chickens during embryonic development and hatching.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leveille GA (1969) In vitro hepatic lipogenesis in the hen and chick. Comp Biochem Physiol 28:431–435
Pearce J (1977) Some differences between avian and mammalian biochemistry. Int J Biochem 8:269–275
O’Hea EK, Leveille GA (1969) Lipogenesis in isolated adipose tissue of domestic chick (Gallus domesticus). Comp Biochem Physiol 26:111–120
Noyan M, Lossow WJ, Brot N, Chaikoff IL (1964) Pathway and form of absorption of palmitic acid in the chicken. J Lipid Res 5:538–541
Bensadoun A, Rothfeld A (1972) The form of absorption of lipids in the chicken Gallus domesticus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 141:814–817
Saadoun A, Leclercq B (1983) Comparison of in vivo fatty acid synthesis of the genetically lean and fat chickens. Comp Biochem Physiol B 75:641–644
Hermier D, Chapman MJ (1985) Lipoprotein plasmatiques et engraissement: description d’un modele chez le poulet domestique Gallus domesticus. Reprod Nutr Dev 25:235–241
Leclercq B, Hermier D, Guy G (1990) Metabolism of very low density lipoproteins in genetically lean or fat lines of chicken. Reprod Nutr Dev 30:701–715
Legrand P, Hermier D (1992) Hepatic delta 9 desaturation and plasma VLDL level in genetically lean and fat chickens. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 16:289–294
Douaire M, Le Fur N, el Khadir-Mounier C, Langlois P, Flamant F, Mallard J (1992) Identifying genes involved in the variability of genetic fatness in the growing chicken. Poult Sci 71:1911–1920
Daval S, Lagarrigue S, Douaire M (2000) Messenger RNA levels and transcription rates of hepatic lipogenesis genes in genetically lean and fat chickens. Genet Sel Evol 32:521–531
McGarry JD, Takabayashi Y, Foster DW (1978) The role of malonyl-CoA in the coordination of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 253:8294–8300
Back DW, Goldman MJ, Fisch JE, Ochs RS, Goodridge AG (1986) The fatty acid synthase gene in avian liver: two mRNA are expressed and regulated in parallel by feeding, primarily at the level of transcription. J Biol Chem 261:4190–4197
Hillgartner FB, Salati LM, Goodridge AG (1995) Physiological and molecular mechanisms involved in nutritional regulation of fatty acid synthesis. Physiol Rev 75:47–76
Davis RA, Boogaerts JR, Borchardt RA, Malone-McNeal M, Archambault-Schexnayder J (1985) Intrahepatic assembly of very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem 260:14137–14144
Boren J, Wettesten M, Rustaeus S, Anderson M, Olofsson S0 (1993) The assembly and secretion of apoB-100-containing lipoproteins. Biochem Soc Trans 21:487–493
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1997) The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 89:331–340
Shimano H, Horton JD, Hammer RE, Shimomura I, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1996) Overproduction of cholesterol and fatty acids causes massive liver enlargement in transgenic mice expressing truncated SREBP-1a. J Clin Invest 98:1575–1584
Shimano H, Shimomura I, Hammer RE, Herz J, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, et al (1997) Elevated levels of SREBP-2 and cholesterol synthesis in livers of mice homozygous for a targeted disruption of the SREBP-1 gene. J Clin Invest 100:2115–2124
Magana MM, Lin SS, Dooley KA, Osborne TF (1997) Sterol regulation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase promoter requires two interdependent binding sites for sterol regulatory element binding proteins. J Lipid Res 38:1630–1638
Yin L, Zhuang Y, Hillgartner FB (2002) Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 interacts with the nuclear thyroid hormone receptor to enhance acetyl-CoA carboxylase-alpha transcription in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 277:19554–19565
Zhuang Y, Yin L, Hillgartner FB (2003) SREBP-1 integrates the actions of thyroid hormone, insulin, cAMP, and medium chain fatty acids on ACC alpha transcription in hepatocytes. J Lipid Res 44:356–368
Magana MM, Koo SH, Towle HC, Osborne TF (2000) Different sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 isoforms utilize distinct co-regulatory factors to activate the promoter for fatty acid synthase. J Biol Chem 275:4726–4733
Labrie F, Luu-The V, Belanger A, Lin SX, Simard J, Pelletier G (2005) Is dehydroepiandrosterone a hormone? J Endocrinol 187:169–196
Yen TT, Allen JA, Pearson DV, Acton J, Greenberg MM (1977) Prevention of obesity in mice by dehydroepiandrosterone. Lipids 12:409–413
Tagliaferro A, Davis JR, Truchon S, Van Hamont N (1986) Effect of dehydroepiandrosterone acetate on metabolism, body weight and composition of male and female rats. J Nutr 116:1977–1983
Araghi-Niknam M, Ardestani SK, MOlitor Inserra P, Eskelson Cd, Watson RR (1998) Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) sulfate prevents reduction in tissue vitamin E and increased lipid peroxidation due to murine retrovirus infection of aged mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 218:210–217
Barrou Z, Charru P, Lidy C (1997) Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and aging, arch. Gerontol Geriatr 4:233–241
Khalil A, Lehoux JG, Wagner RJ, Lesur O, Crux S, Dupont E, Jay-Gerin JP, Wallach J, Fulop T (1998) Dehydroepiandrosterone against copper-induced lipid peroxidation in the rat. Free Radic Biol Med 22:1289–1294
Cleary MP, Billheimer J, Finan A, Sartin JL, Schwartz AG (1984) Metabolic consequences of dehydroepiandrosterone in lean and obese adult Zucker rats. Horm Metab Res 16(Suppl 1)43–46
De Pergola G (2000) The adipose tissue metabolism: role of testosterone and Dehydroepiandrosterone. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24(Suppl 2):S59–63
Berdanier CD, McIntosh MK (1989) Further studies on the effects of dehydroepiandrosterone on hepatic metabolism in BHE rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 192:242–247
Valentine B, Nancy K, Monica B, Daniela B, Umberto M, Henry L (1993) Comparative studies of effects of Dehydroepiandrosterone on rat and chicken liver. Comp Biochem Physiol 105B:643–647
Sato Momoka, Tachibana Tetsuya, Furuse Mitsuhiro (2006a) Heat production and lipid metabolism in broiler and layer chickens during embryonic development. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 143:382–388
Folch J, Lee M, Slane-Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J.Bio.Chem 226:497–509
Cleary MP (1991) The antiobesity effect of dehydroepiandrosterone in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 196:8–16
Cleary MP, Zisk JF (1986) Anti-obesity effect of two different levels of dehydroepiandrosterone in lean and obese middle-aged female Zucker rats. Int J Obes 10:193–204
Shepherd A, Cleary MP (1984) Metabolic alterations after dehydroepiandrosterone treatment in Zucker rats. Am J Physiol 246:E123–128
Mohan PF, Cleary MP (1988) Effect of short-term DHEA administration on liver metabolism of lean and obese rats. Am J Physiol 255:E1–8
Margot P, Cleary MP (1990) Effect of dehydroepiandrosterone treatment on liver metabolism in rats. Int J Biochem 22:205–210
McIntosh MK, Berdanier CD (1988) Strain differences in the dose-response curves of adrenalectomized, starved-refed rats to dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 187:216–222
Henry MH, Burke WH (1999) The effects of in ovo administration of testosterone or an antiandrogen on growth of chick embryos and embryonic muscle characteristics. Poul Sci 78:1006–1013
vili Mikheil S, Leila B (2005) Hyperandrogenia and lipid metabolism. Ann Biomed Res Edu 5:39–41
Morris SM Jr, Winberry LK, Fisch JE, Back DW, Goodridge AG (1984) Developmental and nutritional regulation of the messenger RNAs for fatty acid synthase, malic enzyme and albumin in the livers of embryonic and newly-hatched chicks. Mol Cell Biochem 64:63–68
Casazza JP, Schaffer WT, Veech RL (1986) The effect of DHEA on liver metabolites. J Nutr 116:304–310
S. Zhao, Ma H, Zou S, Chen W, Zhao R (2007) Hepatic lipogenesis gene expression in broiler chicken with different fat deposition during embryonic development. J Vet Med.A 54:1–6
Marrero M, Prough RA, Frenkel RA, Milewich L (1990) Dehydroepiandrosterone feeding and protein phosphorylation, phosphatases, and lipogenic enzymes in mouse liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 193:110–117
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program (Project No. 2004CB117505). We are grateful to Ms. Pasha Apontes for editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Ma, H., Zou, S. et al. Effects of In Ovo Administration of DHEA on Lipid Metabolism and Hepatic Lipogenetic Genes Expression in Broiler Chickens During Embryonic Development. Lipids 42, 749–757 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-007-3068-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-007-3068-y