Abstract
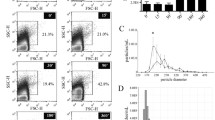
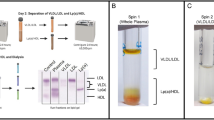
Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] represents a class of lipoprotein particles having as a protein moiety apoB-100 linked by a single disulfide bond to apolipoprotein(a) [apo(a)], a multikringle structure with a high degree of homology with plasminogen. A recognized feature of Lp(a) is its instability on storage caused by attendant protein and lipid modifications that affect the structural, functional, and immunological properties of this lipoprotein. Here we present data showing that, under appropriate conditions of cryopreservation, Lp(a) retains the properties of the freshly isolated product, and we provide examples supporting the stability of this cryopreserved product as a primary standard in immunoassay settings and in cell culture systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APMSF:
-
(4-amidinophenyl)-methanesulfonyl fluoride
- apo(a):
-
apolipoprotein(a)
- apoB-100:
-
apolipoprotein B-100
- G3PDH:
-
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase
- KI:
-
kallikrein inactivator
- IL-8:
-
interleukin 8
- Lp(a):
-
lipoprotein(a)
- lyo-Lp(a):
-
lyophilized Lp(a)
- ox:
-
oxidized
References
Fless, G.M., ZumMallen, M.E., and Scanu, A.M. (1986) Physicochemical Properties of Apolipoprotein(a) and Lipoprotein(a) Derived from the Dissociation of Human Plasma Lipoprotein(a), J. Biol. Chem. 261, 8712–8718.
Marcovina, S.M., Albers, J.J., Scanu, A.M., Kennedy, H., Giaculli, F., Berg, K., Couderc, R., Dati, F., Rifai, N., Sakurabayashi, I. etal. (2000) Use of a Reference Material Proposed by the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine to Evaluate Analytical Methods for the Determination of Plasma Lipoprotein(a), Clin. Chem. 46, 1956–1967.
Scanu, A.M. (2003) Lipoprotein(a) and the Atherothrombotic Process: Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Implications, Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 5, 106–113.
Edelstein, C., Italia, J.A., Klezovitch, O., and Scanu, A.M. (1996) Functional and Metabolic Differences Between Elastase-Generated Fragments of Human Lipoprotein(a) and Apolipoprotein(a), J. Lipid Res. 37, 1786–1801.
Edelstein, C., Hinman, J., Marcovina, S.M., and Scanu, A.M. (2001) Preservation of the Properties of Free-and Lipoprotein-Bound Apolipoprotein(a) After Lyophilization in the Presence of Cryopreservatives, Anal. Biochem. 288, 201–208.
Kearney, J.F., Barletta, R., Quan, Z.S., and Quintans, J. (1981) Monoclonal vs. Heterogeneous Anti-H-8 Antibodies in the Analysis of the Antiphosphorylcholine Response in BALB/c Mice, Eur. J. Immunol. 11, 877–883.
Edelstein, C., Pfaffinger, D., Hinman, J., Miller, E., Lipkind, G., Tsimikas, S., Bergmark, C., Getz, G.S., Witztum, J.L., and Scanu, A.M. (2003) Lysine-Phosphatidylcholine Adducts in Kringle V Impart Unique Immunological and Potential Proinflammatory Properties to Human Apolipoprotein(a), J. Biol. Chem. 278, 52841–52847.
Klezovitch, O., Edelstein, C., and Scanu, A.M. (2001) Stimulation of Interleukin-8 Production in Human THP-1 Macrophages by Apolipoprotein(a): Evidence for a Critical Involvement of Elements of Its C-Terminal Domain, J. Biol. Chem. 276, 46864–46869.
Marcovina, S.M., Koschinsky, M.L., Albers, J.J., and Skarlatos, S. (2003) Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Workshop on Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Disease: Recent Advances and Future Directions, Clin. Chem. 49, 1785–1796.
Fless, G.M., Snyder, M.L., and Scanu, A.M. (1989) Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay for Lp(a), J. Lipid Res. 30, 651–662.
Shaw, P.X., Hörkkö, S., Chang-Kyung, M., Curtiss, L.K., Palinski, W., Silverman, G.J., and Witztum, J.L. (2000) Natural Antibodies with the T15 Idiotype May Act in Atherosclerosis, Apopotic Clearance, and Protective Immunity, J. Clin. Invest. 105 1731–1740.
Fless, G.M., ZumMallen, M.E., and Scanu, A.M. (1985) Isolation of Apolipoprotein(a) from Lipoprotein(a), J. Lipid Res. 26, 1224–1229.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T. (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Scanu, A.M., Hinman, J., Pfaffinger, D. et al. Successful utilization of lyophilized lipoprotein(a) as a biological reagent. Lipids 39, 589–593 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-004-1268-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-004-1268-5