Abstract
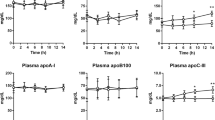
The kinetics of in vivo clearance of apolipoprotein (apo) A-I radioiodinated by the iodine monochloride (ICI) method of McFarlane [McFarlane, A.S. (1958) Efficient Trace-Labelling of Proteins with Iodine, Nature 182, 53] as modified by Bilheimer and co-workers [Bilheimer, D.W., Eisenberg, S., and Levy, R.I. (1972) The Metabolism of Very Low Density Lipoprotein Proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo Observations, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 260, 212–221] and by using the IODO Beads Iodination Reagent were evaluated in rabbits. Both human apoA-I and rabbit HDL radioiodinated by the IODO Beads Iodination Reagent were cleared faster from plasma of rabbits than those radiolabeled by the ICl method. However, the different radiolabeling procedures in the ICl method, i.e., apoA-I radiolabeled either exogenously or in situ as a part of intact HDL, were not associated with a significant difference in the in vivo kinetics of apoA-I in rabbits if apoA-I was prepared by the guanidine HCl method and used fresh. 125I-ApoA-I subjected to delipidation and lyophilization was cleared only slightly faster from the plasma of rabbits than fresh 125I-apoA-I. We also found that apoA-I separated by the guanidine HCl method and used fresh was cleared faster from the plasma of rabbits when it was injected as free apoA-I without adding serum albumin or after in vitro incubation with rabbit HDL than when injected after reassociation with rabbit plasma. We conclude that the ICl method is a more appropriate radioiodination method for studying the in vivo kinetics of HDL than the IODO Beads Iodination Reagent and that the in vitro incubation conditions before injection are important factors that affect the in vivo kinetics of apo A-I.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Apo:
-
apolipoprotein
- CHD:
-
coronary heart disease
- FCR:
-
fractional catabolic rate
- HPCE:
-
high-performance capillary electrophoresis
- LpA-I:
-
human reconstituted HDL
- LPL:
-
lipoprotein lipase
- RMT:
-
relative migration time
- SDS-CGE:
-
SDS-capillary gel electrophoresis
References
Gordon, D.J., and Rifkind, B.M. (1989) High-Density Lipoprotein—The Clinical Implications of Recent Studies, N. Engl. J. Med. 321, 1311–1316.
Gordon, D.J., Probstfield, J.L., Garrison, R.J., Neaton, J.D., Castelli, W.P., Knoke, J.D., Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Bangdiwala, S., and Tyroler, H.A. (1989) High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Disease. Four Prospective American Studies, Circulation 79, 8–15.
Tall, A.R. (1990) Plasma High Density Lipoproteins. Metabolism and Relationship to Atherogenesis, J. Clin. Invest. 86, 379–384.
Tall, A.R., Jiang, X., Luo Y., and Silver, D. (2000) 1999 George Lyman Duff Memorial Lecture: Lipid Transfer Proteins, HDL Metabolism, and Atherogenesis, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20, 1185–1188.
Badimon, J.J., Fuster, V., and Badimon, L. (1992) Role of High Density Lipoproteins in the Regression of Atherosclerosis, Circulation 86, (Suppl.), III86-III94.
van Vlijmen, B.J., and Herz, J. (1999) Gene Targets and Approaches for Raising HDL, Circulation 99, 12–14.
Rubin, E.M., Krauss, R.M., Spangler, E.A., Verstuyft, J.G., and Clift, S.M. (1991) Inhibition of Early Atherogenesis in Transgenic Mice by Human Apolipoprotein AI, Nature 353, 265–267.
Paszty, C., Maeda, N., Verstuyft, J., and Rubin, E.M. (1994) Apolipoprotein AI Transgene Corrects Apolipoprotein E Deficiency-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice, J. Clin. Invest. 94, 899–903.
Plump, A.S., Scott, C.J., and Breslow, J.L. (1994) Human Apolipoprotein A-I Gene Expression Increases High Density Lipoprotein and Suppresses Atherosclerosis in the Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mouse, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 9607–9611.
Plump, A.S., Erickson, S.K., Weng, W., Partin, J.S., Breslow, J.L., and Williams, D.L. (1996) Apolipoprotein A-I Is Required for Cholesteryl Ester Accumulation in Steroidogenic Cells and for Normal Adrenal Steroid Production, J. Clin. Invest. 97, 2660–2671.
Frick, M.H., Elo, O., Haapa, K., Heinonen, O.P., Heinsalmi, P., Helo, P., Huttunen, J.K., Kaitaniemi, P., Koskinen, P., Manninen, V., et al. (1987) Helsinki Heart Study: Primary-Prevention Trial with Gemfibrozil in Middle-Aged Men with Dyslipidemia. Safety of Treatment, Changes in Risk Factors, and Incidence of Coronary Heart Disease, N. Engl. J. Med. 317, 1237–1245.
Saku, K., Gartside, P.S., Hynd, B.A., and Kashyap, M.L. (1985) Mechanism of Action of Gemfibrozil on Lipoprotein Metabolism, J. Clin. Invest. 75, 1702–1712.
Horowitz, B.S., Goldberg, I.J., Merab, J., Vanni, T.M., Ramakrishnan, R., and Ginsberg, H.N. (1993) Increased Plasma and Renal Clearance of an Exchangeable Pool of Apolipoprotein A-I in Subjects with Low Levels of High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol, J. Clin. Invest. 91, 1743–1752.
Goldstein, J.L., Basu, S.K., and Brown, M.S. (1985) Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis of Low-Density Lipoprotein in Cultured Cells, Methods Enzymol. 98, 241–260.
Schaefer, E.J., Zech, L.A., Jenkins, L.L., Bronzert, T.J., Rubalcaba, E.A., Lindgren, F.T., Aamodt, R.L., and Brewer, H.B., Jr. (1982) Human Apolipoprotein A-I and A-II Metabolism, J. Lipid Res. 23, 850–862.
Vega, G.L., Gylling, H., Nichols, A.V., and Grundy, S.M. (1991) Evaluation of a Method for Study of Kinetics of Autologous Apolipoprotein A-I, J. Lipid Res. 32, 867–875.
Saku, K., Yamamoto, K., Sakai, T., Yanagida, T., Hidaka, K., Sasaki, J., and Arakawa, K. (1989) Kinetics of HDL-apo A-I in the Whhl Rabbit, an Animal Model of Familial Hypercholesterolemia, Atherosclerosis 79, 225–230.
Rader, D.J., Castro, G., Zech, L.A., Fruchart, J.C., and Brewer, H.B., Jr. (1991) In vivo Metabolism of Apolipoprotein A-I on High Density Lipoprotein Particles LpA-I and LpA-I, A-II, J. Lipid Res. 32, 1849–1859.
Marsh, J.B., Welty, F.K., and Schaefer, E.J. (2000) Stable Isotope Turnover of Apolipoproteins of High-Density Lipoproteins in Humans, Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 11, 261–266.
Ikewaki, K., Rader, D.J., Schaefer, J.R., Fairwell, T., Zech, L.A., and Brewer, H.B., Jr. (1993) Evaluation of ApoA-I Kinetics in Humans Using Simultaneous Endogenous Stable Isotope and Exogenous Radiotracer Methods, J. Lipid Res. 34, 2207–2215.
Watson, T.D. (1995) New in-vivo Techniques for Measuring Lipoprotein Metabolism, Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 6, 182–186.
Fisher, W.R., Venkatakrishnan, V., Zech, L.A., Hall, C.M., Kilgore, L.L., Stacpoole, P.W., Diffenderfer, M.R., Friday, K.E., Sumner, A.E., and Marsh, J.B. (1995) Kinetic Evidence for Both a Fast and a Slow Secretory Pathway for Apolipoprotein A-I in Humans, J. Lipid Res. 36, 1618–1628.
Foster, D.M., Barrett, P.H., Toffolo G., Beltz, W.F., and Cobelli, C. (1993) Estimating the Fractional Synthetic Rate of Plasma Apolipoproteins and Lipids from Stable Isotope Data, J. Lipid Res. 34, 2193–2205.
Shepherd, J., Packard, C.J., Gotto, A.M., Jr., and Taunton, O.D. (1978) A Comparison of Two Methods to Investigate the Metabolism of Human Apolipoproteins A-I and A-II, J. Lipid Res. 19, 656–661.
Saku, K., Liu, R., Ohkubo, K., Bai, H., Hirata, K., Yamamoto, K., Morimoto, Y., Yamada, K., and Arakawa, K. (1993) In vivo Conversion of Recombinant Human Proapolipoprotein AI (rh-Met-Proapo AI) to Apolipoprotein AI in Rabbits, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1167, 257–263.
Shepherd, J., Gotto, A.M., Jr., Taunton, O.D., Caslake, M.J., and Farish, E. (1977) The in vitro Interaction of Human Apolipoprotein A-I and High Density Lipoproteins, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 489, 486–501.
Osborne, J.C., Jr., Schaefer, E.J., Powell, G.M., Lee, N.S., and Zech, L.A. (1984) Molecular Properties of Radioiodinated Apolipoprotein A-I, J. Biol. Chem. 259, 347–353.
Braschi, S., Neville, T.A., Vohl, M.C., and Sparks, D.L. (1999) Apolipoprotein A-I Charge and Conformation Regulate the Clearance of Reconstituted High Density Lipoprotein in vivo, J. Lipid Res. 40, 522–532.
Braschi, S., Neville, T.A., Maugeais, C., Ramsamy, T.A., Seymour, R., and Sparks, D.L. (2000) Role of the Kidney in Regulating the Metabolism of HDL in Rabbits: Evidence That Iodination Alters the Catabolism of Apolipoprotein A-I by the Kidney, Biochemistry 39, 5441–5449.
Patterson, B.W., and Lee, A.M. (1986) Self-Association and Phospholipid Binding Properties of Iodinated Apolipoprotein A-I, Biochemistry 25, 4953–4957.
McFarlane, A.S. (1958) Efficient Trace-Labelling of Proteins with Iodine, Nature 182, 53.
Bilheimer, D.W., Eisenberg, S., and Levy, R.I. (1972) The Metabolism of Very Low Density Lipoprotein Proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo Observations, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 260, 212–221.
Zhang, B., Saku, K., Hirata, K., Liu, R., Tateishi, K., Shiomi, M., and Arakawa, K. (1994) Quantitative Characterization of Insulin-Glucose Response in Watanabe Heritable Hyperlipidemic and Cholesterol-Fed Rabbits and the Effect of Cilazapril, Metabolism 43, 360–366.
Nichols, A.V., Gong, E.L., Blanche, P.J., Forte, T.M., and Anderson, D.W. (1976) Effects of Guanidine Hydrochloride on Human Plasma High Density Lipoproteins, Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 446, 226–239.
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of Structural Proteins During the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4, Nature 227, 680–685.
Stocks, J., Nanjee, M.N., Miller, N.E. (1998) Analysis of High Density Lipoprotein Apolipoproteins by Capillary Zone and Capillary SDS Gel Electrophoresis, J. Lipid. Res. 39, 218–227.
Goux, A., Athias, A., Persegol, L., Lagrost, L., Gambert, P., and Lallemant, C. (1994) Capillary Gel Electrophoresis Analysis of Apolipoproteins A-I and A-II in Human High-Density Lipoproteins, Anal. Biochem. 218, 320–324.
Saku, K., von Eckardstein, A., Zhang, B., Liu, R., Jimi, S., Ou, J., Ohta, T., Assmann, G., and Arakawa, K. (1999) In vivo Kinetics of Human Apolipoprotein A-I Variants in Rabbits, Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 29, 196–203.
Brousseau, M.E., Santamarina-Fojo, S., Zech, L.A., Berard, A.M., Vaisman, B.L., Meyn, S.M., Powell, D., Brewer, H.B., Jr., and Hoeg, J.M. (1996) Hyperalphalipoproteinemia in Human Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase Transgenic Rabbits. In vivo Apolipoprotein A-I Catabolism Is Delayed in a Gene Dose-Dependent Manner, J. Clin. Invest. 97, 1844–1851.
Saku, K., Liu, R., Jimi, S., Matsuo, K., Yamamoto, K., Yanagita, T., and Arakawa, K. (1995) Combined Effects of Pravastatin and Probucol on High-Density Lipoprotein Apolipoprotein A-I Kinetics in Cholesterol-Fed Rabbits, Jpn. Circ. J. 59, 292–298.
SAS (1990) SAS/STAT User's Guide, v. 6, 4th edn., Vol. 2, pp. 891–1456, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC.
Borresen, A.L., and Kindt, T.J. (1978) Purification and Partial Characterization of the ApoA-I of Rabbit High Density Lipoprotein, J. Immunogenet. 5, 5–12.
Schaefer, E.J., Eisenberg, S., and Levy, R.I. (1978) Lipoprotein Apoprotein Metabolism, J. Lipid Res. 19, 667–687.
Schonfeld, G. and Pfleger, B. (1974) The Structure of Human High Density Lipoprotein and the Levels of Apolipoprotein A-I in Plasma as Determined by Radioimmunoassay, J. Clin. Invest. 54, 236–246.
Osborne, J.C., Jr., Powell, G.M., and Brewer, H.B. Jr. (1980) Analysis of the Mixed Association Between Human Apolipoproteins A-I and A-II in Aqueous Solution, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 619, 559–571.
Kunitake, S.T., and Kane, J.P. (1982) Factors Affecting the Integrity of High Density Lipoproteins in the Ultracentrifuge, J. Lipid Res. 23, 936–940.
Malmendier, C.L., Delcroix, C., and Ameryckx, J.P. (1983) In vivo Metabolism of Human Apoprotein A-I-Phospholipid Complexes. Comparison with Human High Density Lipoprotein-Apoprotein A-I Metabolism, Clin. Chim. Acta 131, 201–210.
Akazawa, S., Ikeda, Y., Kuriya, N., Nakanishi, T., Toyama, K., Miyake, S. and Nagataki, S. (1985) Radioimmunoassay of Human Plasma Apolipoprotein A-1: Pretreatment of Plasma with Guanidine Hydrochloride, Artery 12, 388–398.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Shimoji, E., Tanaka, H. et al. Evaluation of apolipoprotein A-I kinetics in rabbits in vivo using in situ and exogenous radioiodination methods. Lipids 38, 209–218 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-003-1053-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-003-1053-5