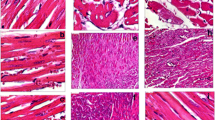
Abstract
Dolichol (D) levels increase dramatically in older tissue. An understanding of the exchangeability of D between tissues may be essential in order to understand the mechanism of the abnormal accumulation associated with aging. The question was investigated by the use of organ transplantation. D-poor hearts donated by 3-mon-old and D-rich by 22-mon-old male Lewis rats were transplanted heterotopically in 3-mon-old syngenic recipients, whose peripheral tissues and liver were poor in D. Native and transplanted hearts were taken 7 and 21 d after surgery. Native hearts of 3-mon- and 22-mon-old male Lewis rats served as control. D concentration and quantity were higher in older than in younger native hearts as expected. In the transplanted hearts, the quantity of D was unchanged, irrespective of the age of the donor and of the time of transplantation, whereas D concentration increased because of the remarkable disuse atrophy. No changes in D were observed in recipients’ tissues. It is concluded that dolichol is not redistributed via circulation from the transplanted heart to the tissues and liver of the younger recipient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HHTx:
-
heterotopic heart transplantation
References
Hemming, F.W. (1992) Dolichol: A Curriculum Cognitionis, Biochem. Cell. Biol. 70, 377–381.
Rip, J.W., Rupar, A., Ravi, K., and Carroll, K.K. (1985) Distribution, Metabolism and Function of Dolichol and Polyprenols, Prog. Lipid Res. 24, 269–309.
Choinacki, T., and Dallner, G. (1988) The Biological Role of Dolichol, Biochem. J. 251, 1–9.
Carroll, K.K., Githrie, N., and Ravi, K. (1992) Dolichol: Function, Metabolism and Accumulation in Human Tissue, Biochem. Cell. Biol. 70, 382–384.
Elmberger, P.G., Kalèn, A., Brunk, U.T. and Dallner, G. (1989) Discharge of Newly Synthetized Dolichol and Ubiquinone with Lipoprotein to Rat Perfusate and to the Bile, Lipids 24, 919–930.
Kutiyama, M., Yashidone, H., Nakahara, K., Nakagawa, H., Fujiyama, J., Take, H., and Osame, M. (1999) Blood Dolichols in a Patient with Abetalipoproteinaemia, Ann. Clin. Biochem. 36, 176–179.
Pullarkat, R.K., and Reha, H. (1982) Accumulation of Dolichols in Brain of Elderly, J. Biol. Chem. 257, 5991–5993.
Kalèn, A., Appelkvist, A.L., and Dallner, G. (1989) Age-Related Changes in the Lipid Composition of Rat and Human Tissues, Lipids 24, 579–584.
Daniels, I., and Hemming, F.W. (1990) Changes in Murine Tissue Concentrations of Dolichol and Dolichyl Derivatives Associated with Age, Lipids 25, 586–593.
Marino, M., Dolfi, C., Paradiso, C., Cavallini, G., Masini, M., Gori, Z., Pollera, M., Trentalance, A., and Bergamini, E. (1998) Age-Dependent Accumulation of Dolichol in Rat Liver: Is Tissue Dolichol a Biomarker of Aging? J. Gerontol. Biol. Sci. 53A, B87-B93.
Page, E., McCallister, L.P., and Power, B. (1971) Stereological Measurements of Cardiac Ultrastructures Implicated in Excitation-Contraction Coupling, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 68, 1465–1466.
Ono, K., and Lindsey, E.S. (1969) Improved Technique of Heart Transplantation in Rats, J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 57, 225–229.
Maltese, W.A., and Erdman, R.A. (1989) Characterization of Isoprenoid Involved in the Post-translational Modification of Mammalian Cell Proteins, J. Biol. Chem. 264, 18168–18172.
Dini, B., Dolfi, C., Santucci, V., Cavallini, G., Donati, A., Gori, Z., Maccheroni, M., and Bergamini, E. (2001) Effects of Ageing and Increased Haemolysis on the Levels of Dolichol in Rat Spleen, Exp. Gerontol. 37, 99–105.
Asfour, B., Hare, J.M., Kohl, T., Baba, H.A., Kass, D.A., Chen, K., Tjan, T.D., Hammel, D., Weyand, M., Hruban, R.H., et al. (1999) A Simple New Model of Physiologically Working Heterotopic Heart Transplantation Provides Hemodynamic Performance Equivalent to That of an Orthotopic Heart, J. Heart Lung Transplant. 18, 927–936.
Rakusan, K., Cicutti, N., Spatenka, J., and Samanek, M. (1997) Geometry of the Capillary Net in Human Hearts, Int. J. Microcir. Clin. Exp. 17, 29–32.
Marino, M., Pallottini, V., D’Eramo, C., Cavallini, G., Bergamini, E., and Trentalance, A. (2002) Age-Related Changes of Cholesterol and Dolichol Biosynthesis in Rat Liver, Mech. Ageing Dev. 123, 1183–1189.
Stevens, A., and Lowe, J. (2000) Pathology, 2nd edn., p. 13, Mosby, London.
Cutran, R.S., Kumar, V., and Collins, T. (1999) Robbins Pathologic Basis of Diseases, 6th edn., pp. 35–36, Saunders, Philadelphia.
Simons, K., and Ikonen, E. (2000) How Cells Handle Cholesterol, Science 290, 1721–1726.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Cavallini, G., Parentini, I., Di Stefano, R. et al. Dolichol levels in younger and older rat hearts heterotopically transplanted in younger recipients. Lipids 37, 913–916 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-002-0979-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-002-0979-y