Abstract
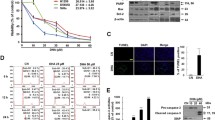
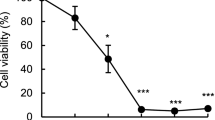
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; 20∶5n−3) may reduce the cell number in cultured leukemia/lymphoma cells owing to reduced cell proliferation, induction of cell death, or a combination of these processes. EPA has been shown to promote apoptosis in Ramos cells, and our present study was focused on a possible cell cycle arrest and the pathways by which the apoptotic process is induced. Apoptosis may proceed along the intrinsic (mitochondrial) or the extrinsic (death receptor) pathway, which are mediated via different caspases. Caspases are a class of homologous cysteine proteases recognized as pivotal mediators of apoptosis. We investigated whether EPA affects progression of the cell cycle or promotes apoptosis directly. By incorporation of [3H]thymidine and [3H]valine, we showed that DNA, as well as protein synthesis, was reduced after incubation of Ramos cells with EPA for 6h. We monitored cell cycle distribution by 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine staining and observed no cell cycle arrest in the EPA-incubated cells. Incubation of cells with EPA caused PS-flipping, as demonstrated by annexin V-binding (flow cytometry), and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase measured by Western blot analysis. Furthermore, we observed increased activity of caspase-3 and-9, but not of caspase-8. Whereas inhibitors of caspase-3 and-9 reduced EPA-induced apoptosis, inhibition of caspase-8 did not. This suggests that EPA may promote apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway in Ramos cells. Thus, the reduction in cell number can be explained by a direct apoptotic effect of EPA rather than via cell cycle arrest.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AnV:
-
annexin V
- BrdU:
-
5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine
- FACS:
-
fluorescence-activated cell sorter
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- HO342:
-
Hoechst 33342
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- PARP:
-
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
References
Albino, A.P., Juan, G., Traganos, F., Reinhart, L., Connolly, J., Rose, D.P., and Darzynkiewicz, Z. (2000) Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis of Melanoma Cells by Docosahexaenoic Acid: Association with Decreased pRb Phosphorylation, Cancer Res. 60, 4139–4145.
Caygill, C.P., Charlett, A., and Hill, M.J. (1996) Fat, Fish, Fish Oil and Cancer, Br. J. Cancer 74, 159–164.
Finstad, H.S., Myhrstad, M.C., Heimli, H., Lomo, J., Blomhoff, H.K., Kolset, S.O., and Drevon, C.A. (1998) Multiplication and Death-type of Leukemia Cell Lines Exposed to Very Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Leukemia 12, 921–929.
Kaizer, L., Boyd, N.F., Kriukov, V., and Tritchler, D. (1989) Fish Consumption and Breast Cancer Risk: An Ecological Study, Nutr. Cancer 12, 61–68.
Petrik, M.B., McEntee, M.F., Johnson, B.T., Obukowicz, M.G., and Whelan, J. (2000) Highly Unsaturated (n−3) Fatty Acids, but Not alpha-Linolenic, Conjugated Linoleic or gamma-Linolenic Acids, Reduce Tumorigenesis in Apc(Min/+) Mice, J. Nutr. 130, 2434–2443.
Rao, C.V., Hirose, Y., Indranie, C., and Reddy, B.S. (2001) Modulation of Experimental Colon Tumorigenesis by Types and Amounts of Dietary Fatty Acids, Cancer Res. 61, 1927–1933.
Heimli, H., Finstad, H.S., and Drevon, C.A. (2001) Necrosis and Apoptosis in Lymphoma Cell Lines Exposed to Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Antioxidants, Lipids 36, 613–621.
Kerr, J.F., Wyllie, A.H., and Currie, A.R. (1972) Apoptosis: A Basic Biological Phenomenon with Wide-Ranging Implications in Tissue Kinetics, Br. J. Cancer 26, 239–257.
Lowe, S.W., and Lin, A.W. (2000) Apoptosis in Cancer, Carcinogenesis 21, 485–495.
Ashkenazi, A., and Dixit, V.M. (1998) Death Receptors: Signaling and Modulation, Science 281, 1305–1308.
Salvesen, G.S., and Dixit, V.M. (1997) Caspases: Intracellular Signaling by Proteolysis, Cell 91, 443–446.
Wallach, D., Boldin, M., Varfolomeev, E., Beyaert, R., Vandenabeele, P., and Fiers, W. (1997) Cell Death Induction by Receptors of the TNF Family: Towards a Molecular Understanding, FEBS Lett. 410, 96–106.
Li, P., Nijhhwan, D., Budihardjo, I., Srinivasula, S.M., Ahmad, M., Alnemri, E.S., and Wang, X. (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-Dependent Formation of Apaf-1/Caspase-9 Complex Initiates an Apoptotic Protease Cascade, Cell 91, 479–489.
Zou, H., Henzel, W.J., Liu, X., Lutschg, A., and Wang, X. (1997) Apaf-1, a Human Protein Homologous to C. elegans CED-4, Participates in Cytochrome c-Dependent Activation of Caspase-3, Cell 90, 405–413.
Adams, J.M., and Cory, S. (1998) The Bcl-2 Protein Family: Arbiters of Cell Survival, Science 281, 1322–1326.
Green, D.R., and Reed, J.C. (1998) Mitochondria and Apoptosis, Science 281, 1309–1312.
Hengartner, M.O. (2000) The Biochemistry of Apoptosis, Nature 407, 770–776.
Kaufmann, S.H., Desnoyers, S., Ottaviano, Y., Davidson, N.E., and Poirier, G.G. (1993) Specific Proteolytic Clevage of Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase: An Early Marker of Chemotherapy-Induced Apoptosis, Cancer Res. 53, 3976–3985.
Lazebnik, Y.A., Kaufmann, S.H., Desnoyers, S., Poirier, G.G., and Earnshaw, W.C. (1994) Cleavage of Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase by a Proteinase with Properties like ICE, Nature 371, 346–347.
Yung, T.M., and Satoh, M.S. (2001) Functional Competition Between Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase and Its 24- kDa Apoptotic Fragment in DNA Repair and Transcription, J. Biol. Chem. 276, 11279–11286.
Gastman, B.R., Yin, X.M., Johnson, D.E., Wieckowski, E., Wang, G.Q., Watkins, G.C., and Rabinowich, H. (2000) Tumor-Induced Apoptosis of T Cells: Amplification by a Mitochondrial Cascade, Cancer Res. 60, 6811–6817.
Schempp, C.M., Simon-Haarhaus, B., Termeer, C.C., and Simon, J.C. (2001) Hypericin Photo-Induced Apoptosis Involves the Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) and Activation of Caspase-8, FEBS Lett. 493, 26–30.
Takahashi, A., Hirata, H., Yonehara, S., Imai, Y., Lee, K.K., Moyer, R.W., Turner, P.C., Mesner, P.W., Okazaki, T., Sawai, H. et al. (1997) Affinity Labeling Displays the Stepwise Activation of ICE-Related Proteases by Fas, Staurosporine, and CrmA-Sensitive Caspase-8, Oncogene 14, 2741–2752.
Bratton, D.L., Fadok, V.A., Richter, D.A., Kailey, J.M., Guthrie, L.A., and Henson, P.M. (1997) Appearance of Phosphatidylserine on Apoptotic Cells Requires Calcium-Mediated Nonspecific Flip-Flop and Is Enhanced by Loss of the Aminophospholipid Translocase, J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26159–26165.
Span, L.F., Pennings, A.H., Vierwinden, G., Boezeman, J.B., Raymakers, R.A., and de Witte, T. (2002) The Dynamic Process of Apoptosis Analyzed by Flow Cytometry Using Annexin-V/Propidium Iodide and a Modified in situ End Labeling Technique, Cytometry 47, 24–31.
Zhuang, J., Ren, Y., Snowden, R.T., Zhu, H., Gogvadze, V., Savill, J.S., and Cohen, G.M. (1998) Dissociation of Phagocyte Recognition of Cells Undergoing Apoptosis from Other Features of the Apoptotic Program, J. Biol. Chem. 273, 15628–15632.
Cain, K., Brown, D.G., Langlais, C., and Cohen, G.M. (1999) Caspase Activation Involves the Formation of the Aposome, a Large (approximately 700 kDa) Caspase-Activating Complex, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 22686–22692.
Antonsson, B., and Martinou, J.C. (2000) The Bcl-2 Protein Family, Exp. Cell Res. 256, 50–57.
Gross, A., McDonnell, J.M., and Korsmeyer, S.J. (1999) BCL-2 Family Members and the Mitochondria in Apoptosis, Genes Dev. 13, 1899–1911.
Reed, J.C. (1997) Double Identity for Proteins of the BCL-2 Family, Nature 387, 773–776.
Glazyrin, A.L., Adsay, V.N., Vaitkevicius, V.K., and Sarkar, F.H. (2001) CD95-Related Apoptotic Machinery Is Functional in Pancreatic Cancer Cells, Pancreas 22, 357–365.
Herrera, B., Fernandez, M., Alvarez, A.M., Roncero, C., Benito, M., Gil, J., and Fabregat, I. (2001) Activation of Caspases Occurs Downstream from Radical Oxygen Species Production, Bcl-xL Down-Regulation, and Early Cytochrome C Release in Apoptosis Induced by Transforming Growth Factor beta in Rat Fetal Hepatocytes, Hepatology 34, 548–556.
Kiyokawa, N., Mori, T., Taguchi, T., Saito, M., Mimori, K., Suzuki, T., Sekino, T., Sato, N., Nakajima, H., Katagiri, Y.U., et al. (2001) Activation of the Caspase Cascade During Stx1-Induced Apoptosis in Burkitt's Lymphoma Cells, J. Cell Biochem. 81, 128–142.
Finstad, H.S., Drevon, C.A., Kulseth, M.A., Synstad, A.V., Knudsen, E., and Kolset, S.O. (1998) Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Accumulation of Lipid Droplets in U937-1 Cells Incubated with Eicosapentaenoic Acid, Biochem. J. 336, 451–459.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Heimli, H., Giske, C., Naderi, S. et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid promotes apoptosis in Ramos cells via activation of caspase-3 and -9. Lipids 37, 797–802 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-002-0963-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-002-0963-6