Abstract
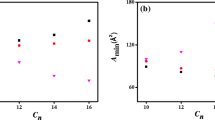
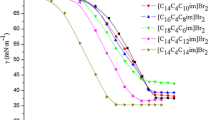
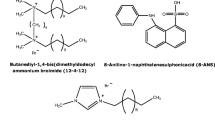
Tuning physicochemical properties of aqueous surfactant solutions comprised of normal or reverse micelles by external additives is of utmost importance due to the enormous application potential of surfactant-based systems. Unusual and interesting properties of environmentally benign ionic liquids (IL) make them suitable candidates for this purpose. To understand and establish the role of IL in modifying properties of aqueous gemini surfactants, we studied the effect of the IL, 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ([Hmim][Br]) and 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ([Omim][Br]) on the properties of the aqueous cationic gemini surfactant 1,6-hexanediyl-α,ω-bis(dimethyltetradecyl)ammonium bromide (14-6-14,2Br−). The behavioral changes were investigated by measuring the critical micelle concentration (CMC ) using electrical conductance, surface tension, dye solubilization and fluorescence probe measurements at 298.15 K. It was observed that the CMC of 14-6-14,2Br− gemini surfactant decreases with addition of IL, thus favoring the micellization process. An increase in micellar size was observed at lower IL concentration using dynamic light scattering, with a decrease in aggregation number (N agg) determined from fluorescence probe quenching measurements. It is noteworthy that the extent of modulation of the micellar properties is different for both the IL due to their structural differences. IL behave like electrolytes at lower concentrations and cosurfactants at higher concentrations and form mixed micelles with the cationic gemini surfactant showing an increase in N agg.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANS:
-
8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
- CMC:
-
Critical micelle concentration
- CPC:
-
Cetylpyridinium chloride
- DLS:
-
Dynamic light scattering measurements
- EG:
-
Ethylene glycol
- [Hmim][Br]:
-
1-Hexyl 3-methyl imidazolium bromide
- IL:
-
Ionic liquids
- Nagg :
-
Aggregation numbers
- [Omim][Br]:
-
1-Octyl 3-methyl imidazolium bromide
- SANS:
-
Small angle neutron scattering
- 14-6-14,2Br− :
-
1,6-Hexanediyl-α,ω-bis(dimethyltetradecyl)ammonium bromide
- PIL:
-
Protic ionic liquids
- β :
-
Counter ion binding
- \(\varDelta G_{\text{m}}^{0}\) :
-
Standard free energy of micelle formation
- γ :
-
Surface tension
- A min :
-
Area per molecule at the air–water interface
- Γmax :
-
Maximum surface excess concentration
- R :
-
Universal gas constant
- N A :
-
Avogadro’s number
- ΠCMC :
-
Surface pressure at the CMC
References
Zana R (2002) Alkanediyl-α,ω-bis(dimethylalkylammonium bromide) surfactants: 10. Behavior in aqueous solution at concentrations below the critical micellization concentration: an electrical conductivity study. J Colloid Interface Sci 246:182–190
Menger FM, Keiper JS, Mbadugha BNA, Caran KL, Romsted LS (2000) Interfacial composition of gemini surfactant micelles determined by chemical trapping. Langmuir 16:9095–9098
Menger FM, Mbadugha BNA (2001) Gemini surfactants with a disaccharide spacer. J Am Chem Soc 123:875–885
Rosen MJ, Mathias JH, Davenport L (1999) Aberrant aggregation behavior in cationic gemini surfactants investigated by surface tension, interfacial tension, and fluorescence methods. Langmuir 15:7340–7346
Eastoe J, Nave S, Downer A, Paul A, Rankin A, Tribe K (2000) Adsorption of ionic surfactants at the air–solution interface. Langmuir 16:4511–4518
Brown P, Butts CP, Eastoe J, Grillo I, James G, Khan A (2013) New catanionic surfactants with ionic liquid properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 395:185–189
Bai G, Wang J, Yan H, Li Z, Thomas RK (2001) Thermodynamics of molecular self-assembly of cationic gemini and related double chain surfactants in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 105:3105–3108
Moulik S, Dutta P, Chattoraj DK, Moulik SP (1998) Biopolymer–surfactant interactions: 5: equilibrium studies on the binding of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide and sodium dodecyl sulfate with bovine serum albumin, β-lactoglobulin, hemoglobin, gelatin, lysozyme and deoxyribonucleic acid. Colloids Surf B 11:1–8
Zana R, Xiao JD (2004) Gemini surfactants. Marcel Dekker, New York
Kirby AJ, Camilleri P, Engberts JBFN, Feiters MC, Nolte RJM, Soderman O, Bergsma M, Bell PC, Fielden ML, Rodrıguez CLG, Guedat P, Kremer A, McGregor C, Perrin C, Ronsin G, van Eijk MCP (2003) Gemini surfactants: new synthetic vectors for gene transfection. Angew Chem Int Ed 42:1448–1457
Bombelli C, Caracciolo G, Di Profio P, Diociaiuti M, Luciani P, Mancini G, Mazzuca C, Marra M, Molinari A, Monti D, Toccacieli L, Venanzi M (2005) Inclusion of a photosensitizer in liposomes formed by DMPC/gemini surfactant: correlation between physicochemical and biological features of the complexes. J Med Chem 48:4882–4891
Borde C, Nardello V, Wattebled L, Laschewsky A, Aubry JM (2008) A gemini amphiphilic phase transfer catalyst for dark singlet oxygenation. J Phys Org Chem 21:652–658
Bernheim-Groswasser A, Zana R, Talmon Y (2000) Sphere-to-cylinder transition in aqueous micellar solution of a dimeric (gemini) surfactant. J Phys Chem B 104:4005–4009
Cl Oelschlaeger, Waton G, Candau SJ, Cates ME (2002) Structural, kinetics, and rheological properties of low ionic strength dilute solutions of a dimeric (gemini) surfactant. Langmuir 18:7265–7271
Kabir-ud-Din, Siddiqui US, Ghosh G (2009) Growth of gemini surfactant micelles under the influence of additives: DLS studies. J Dispers Sci Technol 30:1310–1319
Alargova RG, Kochijashky II, Sierra ML, Kwetkat KJ, Zana R (2001) Mixed micellization of dimeric (gemini) surfactants and conventional surfactants: II. CMC and micelle aggregation numbers for various mixtures. J Colloid Interface Sci 235:119–129
Wattebled L, Laschewsky A (2007) Effects of organic salt additives on the behavior of dimeric (“gemini”) surfactants in aqueous solution. Langmuir 23:10044–10052
Rodriguez A, Graciani MDM, Angulo M, Moya ML (2007) Effects of organic solvent addition on the aggregation and micellar growth of cationic dimeric surfactant 12-3-12,2Br−. Langmuir 23:11496–11505
Lu T, Huang J, Li Z, Jia S, Fu H (2008) Effect of hydrotropic salt on the assembly transitions and rheological responses of cationic gemini surfactant solutions. J Phys Chem B 112:2909–2914
Sajid MA, Suhail M, Ghosh G, Kamil M, Kabir-ud-Din (2009) Interactions between cationic gemini/conventional surfactants with polyvinylpyrrolidone: specific conductivity and dynamic light scattering studies. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 350:51–56
Ukrikova D, Zajac I, Dubnickova M, Pisarcik M, Funari SS, Rapp G, Balgavy P (2005) Interaction of gemini surfactants butane-1,4-diyl-bis(alkyldimethyl ammonium bromide) with DNA. Colloids Surf B 42:59–68
Ajmal KP, Kabir-ud-Din, Ismail K (2012) Micellization and thermodynamic parameters of butanediyl-1,4-bis(tetradecyldimethylammonium bromide) gemini surfactant at different temperatures: effect of the addition of 2-methoxyethanol. J Solut Chem 41:1271–1281
Brown P, Bushmelev A, Butts CP, Cheng J, Eastoe J, Grillo I, Heenan RK, Schmidt AM (2012) Magnetic control over liquid surface properties with responsive surfactants. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:2414–2416
Kabir-ud-Din, Ajmal PK (2010) Effects of solvent media and temperature on the self-aggregation of cationic dimeric surfactant 14-6-14, 2Br− studied by conductometric and fluorescence techniques. Langmuir 26:7905–7914
Vanyur R, Biczok L, Miskolczy Z (2007) Micelle formation of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ionic liquids in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 299:256–261
Wang JJ, Wang HJ, Zhang SL, Zhang HC, Zhao Y (2007) Conductivities, volumes, fluorescence, and aggregation behavior of ionic liquids [C4mim][BF4] and [C n mim]Br (n = 4, 6, 8, 10, 12) in aqueous solutions. J Phys Chem B 111:6181–6188
Dong B, Li N, Zheng LQ, Yu L, Inoue T (2007) Surface adsorption and micelle formation of surface active ionic liquids in aqueous solution. Langmuir 23:4178–4182
Mukherjee I, Mukherjee S, Naskar B, Ghosh S, Moulik SP (2013) Amphiphilic behavior of two phosphonium based ionic liquids. J Colloid Interface Sci 395:135–144
Shanshan Z, Jing Yu, Jianzhou Wu, Wei T, Qunfang L, Wenjun F (2014) Micellization parameters of six gemini quaternary ammonium surfactants from measurements of conductivity and surface tension. J Chem Eng Data 59:2891–2900
El Seoud OA, Pires PAR, Abdel-Moghny T, Bastos EL (2007) Synthesis and micellar properties of surface-active ionic liquids: 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chlorides. J Colloid Interface Sci 313:296–304
Naved A, Andleeb ZN, Mohd A, Kabir-ud-Din (2009) Properties of mixed aqueous micellar solutions formed by cationic alkanediyl-α,ω-bis(tetradecyldimethylammonium bromide) and alkyltrimethylammonium bromides: fluorescence and conductivity studies. J Chem Eng Data 54:1518–1523
Scamehorn JF (1986) Phenomena in mixed surfactant systems, ACS symposium series. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC
Yang X, Wang J, Wang Y, Ye J, Yan H, Thomas RK (2005) Properties of mixed micelles of cationic gemini surfactants and nonionic surfactant triton X-100: effects of the surfactant composition and the spacer length. J Colloid Interface Sci 286:739–746
Attwood D, Florence AT (1983) Surfactant systems: their chemistry, pharmacy and biology. Chapman and Hall, London
Behera K, Malek NI, Pandey S (2009) Visual evidence for formation of water-in-ionic liquid microemulsions. ChemPhysChem 10:3204–3208
Trivedi S, Malek NI, Behera K, Pandey S (2010) Temperature-dependent solvatochromic probe behavior within ionic liquids and (ionic liquid + water) mixtures. J Phys Chem B 114:8118–8125
Behera K, Om H, Pandey S (2009) Modifying properties of aqueous cetyltrimethylammonium bromide with external additives: ionic liquid 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide versus cosurfactant n-hexyltrimethyl ammonium bromide. J Phys Chem B 113:786–793
Behera K, Kumar V, Pandey S (2010) Role of the surfactant structure in the behavior of hydrophobic ionic liquids within aqueous micellar solutions. ChemPhysChem 11:1044–1052
Armstrong DW, Anderson JL, Pino V, Hagberg EC, Sheares VV (2003) Surfactant salvation effects and micelle formation in ionic liquids. Chem Commun 19:2444–2445
Evans DF, Yamauchi A, Jason Wei G, Bloomfield VA (1983) Micelle formation in ethylammonium nitrate, a low-melting fused salt. J Phys Chem 87:3537–3541
Beyaz A, Oh WS, Reddy VP (2004) Ionic liquids as modulators of the critical micelle concentration of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 35:119–124
Pal A, Chaudhary S (2014) Ionic liquids effect on critical micelle concentration of SDS: conductivity, fluorescence and NMR studies. Fluid Phase Equilib 372:100–104
Pal A, Pillania A (2014) Effect of trisubstituted imidazolium based ionic liquid 1-butyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium chloride on the aggregation behaviour of sodium dodecylsulphate in aqueous media. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 452:18–24
Javadian S, Nasiri F, Heydari A, Yousefi A, Asadzadeh Shahir A (2014) Modifying effect of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on surface activity and self-assembled nanostructures of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Phys Chem B 118:4140–4150
Shi L, Jing X, Gao H, Gu Y, Zheng L (2013) Ionic liquid-induced changes in the properties of aqueous sodium dodecyl sulfate solution: effect of acidic/basic functional groups. Colloid Polym Sci 291:1601–1612
Zhang S, Gao Y, Dong B, Zheng L (2010) Interaction between the added long-chain ionic liquid 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate and Triton X-100 in aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 372:182–189
Chai J, Zhang H, Liu N, Liu N, Chai H, Liu Z (2015) Comparison between phase behavior of gemini imidazoliums and monomeric ionic liquid surfactants in W/O microemulsion systems. J Dispers Sci Technol 36:129–135
Li Q, Wang X, Yue X, Chen X (2014) Phase transition of a quaternary ammonium gemini surfactant induced by minor structural changes of protic ionic liquids. Langmuir 30:1522–1530
Wang X, Li Q, Chen X, Li Z (2012) Effects of structure dissymmetry on aggregation behaviors of quaternary ammonium gemini surfactants in a protic ionic liquid EAN. Langmuir 28:16547–16554
Shang Y, Wang T, Han X, Peng C, Liu H (2010) Effect of ionic liquids C n mimBr on properties of gemini surfactant 12-3-12 aqueous solution. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:8852–8857
Sharma R, Mahajan S, Mahajan RK (2013) Surface adsorption and mixed micelle formation of surface active ionic liquid in cationic surfactants: conductivity, surface tension, fluorescence and NMR studies. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 427:62–75
Azum N, Naqvi AZ, Akram M, Kabir-ud-Din (2008) Mixing behavior of conventional and gemini cationic surfactants. J Dispers Sci Technol 29:711–717
De S, Aswal VK, Goyal PS, Bhattacharya S (1996) Role of spacer chain length in dimeric micellar organization. Small angle neutron scattering and fluorescence studies. J Phys Chem 100:11664–11671
Malek NI, Ijardar SP, Oswal SL (2014) Excess molar properties for binary systems of C n MIM-BF4 ionic liquids with alkylamines in the temperature range (298.15 to 318.15) K. Experimental results and theoretical model calculations. J Chem Eng Data 59:540–553
Malek NI, Singh A, Surati R, Ijardar SP (2014) Study on thermo physical and excess molar properties of binary systems of ionic liquids. I: [C n mim][PF6] (n = 6, 8) and alkyl acetates. J Chem Thermodyn 74:103–118
Ijardar SP, Malek NI (2014) Experimental and theoretical excess molar properties of imidazolium based ionic liquids with molecular organic solvents—I. 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate and 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate with cyclic ethers. J Chem Thermodyn 71:236–248
Jones MJ, Chapman D (1995) Micelles, monolayers, and biomembranes. Wiley-LISS, New York
Holmberg K, Johnsson B, Kronberg B, Lindman B (2003) Surfactants and polymers in aqueous solution, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Kabir-ud-Din, Ajmal Koya P (2010) Micellar properties and related thermodynamic parameters of the 14-6-14, 2Br− gemini surfactant in water + organic solvent mixed media. J Chem Eng Data 55:1921–1929
Farah K, Umme SS, Malik AR, Iqrar AK, Kabir-ud-Din (2015) Micellization behavior of butanediyl-1,4-bis(dimethyldodecylammonium bromide) gemini surfactant in presence of organic additives. J Dispers Sci Technol 36:83–93
Yu D, Huang X, Deng M, Lin Y, Jiang L, Huang J, Wang Y (2010) Effects of inorganic and organic salts on aggregation behavior of cationic gemini surfactants. J Phys Chem B 114:14955–14964
Tiwari AK, Subit KS (2013) Aggregation behaviour and thermodynamics of mixed micellization of gemini surfactants with a room temperature ionic liquid in water and water–organic solvent mixed media. J Chem Thermodyn 60:29–40
Khan F, Siddiqui US, Khan IA, Kabir-ud-Din (2012) Physicochemical study of cationic gemini surfactant butanediyl-1,4-bis(dimethyldodecylammonium bromide) with various counterions in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 394:46–56
Iqrar AK, Riyaj M, Md. Sayem A, Kabir-ud-Din (2009) Effect of alkylamine chain length on the critical micelle concentration of cationic gemini butanediyl-α,ω-bis(dimethylcetylammonium bromide) surfactant. J Dispers Sci Technol 30:1486–1493
Zana R (1996) Critical micellization concentration of surfactants in aqueous solution and free energy of micellization. Langmuir 12:1208–1211
Rosen MJ (2004) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena. Wiley, New York
Rodrıguez A, Graciani M, Munoz M, Robina I, Moya ML (2006) Effects of ethylene glycol addition on the aggregation and micellar growth of gemini surfactants. Langmuir 22:9519–9525
Li ZX, Dong CC, Thomas RK (1999) Neutron reflectivity studies of the surface excess of gemini surfactants at the air–water interface. Langmuir 15:4392–4396
Bae S, Haage K, Wantke K, Motschmann HJ (1999) On the factor in Gibbs equation for ionic surfactants. J Phys Chem B 103:1045–1050
Naqvi AZ, Noori S, Kabir-ud-Din (2015) Effect of surfactant structure on the mixed micelle formation of cationic gemini–zwitterionic phospholipid systems. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 477:9–18
Alami E, Beinert G, Marie P, Zana R (1993) Alkanediyl-α,ω-bis(dimethylalkylammonium bromide) surfactants. 3. Behavior at the air–water interface. Langmuir 9:1465–1467
Chen Q, Zhang D, Li R, Liu H, Hu Y (2008) Effect of the spacer group on the behavior of the cationic gemini surfactant monolayer at the air/water interface. Thin Solid Films 516:8782–8787
Kang P, Xu H (2013) Synthesis and properties of dissymmetric gemini surfactants. J Surfact Deterg 16:921–925
Wettig SD, Verrall RE (2001) Thermodynamic studies of aqueous m-s-m gemini surfactant systems. J Colloids Interface Sci 235:310–316
Din Kabir-ud, Sheikh MS, Dar AA (2010) Analysis of mixed micellar and interfacial behavior of cationic gemini hexanediyl-1,6-bis(dimethylcetylammonium bromide) with conventional ionic and nonionic surfactants in aqueous medium. J Phys Chem B 114:6023–6032
Noori S, Naqvi AZ, Ansari WH, Kabir-ud-Din (2015) Interfacial and solution behavior of amphiphilic drug and counterion-coupled gemini (COCOGEM) surfactants. J Surfactants Deterg 18:55–66
Colichman E (1951) Spectral study of long chain quaternary ammonium salts in brom phenol blue solutions. J Am Chem Soc 73:3385–3388
Ghasemian E, Najafi M, Rafati AA, Felegari Z (2010) Effect of electrolytes on surface tension and surface adsorption of 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid in aqueous solution. J Chem Thermodyn 42:962–966
Rosendorfova J, Cermakova L (1980) Spectrophotometric study of the interaction of some triphenylmethane dyes and 1-carbethoxypentadecyltrimethylammonium bromide. Talanta 27:705–708
Kriwanek J, Miller R (1995) UV/vis spectroscopic investigations of micellisation of homologous N-alkyl betaines using the dye indicator ET(30). Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 105:233–242
El-Daly Samy A, Abdel-Kader Mahmoud H, Issa Raafat M, el-Sherbini el-Sayed A (2003) Influence of solvent polarity and medium acidity on the UV–Vis spectral behavior of 1-methyl-4-[4-amino-styryl] pyridinium iodide. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 59:405–411
Mandal AB, Dhathathreyan A, Jayakumar R, Ramasami T (1993) Characterisation of Boc-Lys(Z)-Tyr-NHNH2 dipeptide. Part 1.—Physico-chemical studies on the micelle formation of a dipeptide in the absence and presence of ionic surfactants. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 89:3075–3079
Lakowicz Joseph R (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Gargi BR, Indranil C, Satya PM (2006) Pyrene absorption can be a convenient method for probing critical micellar concentration (cmc) and indexing micellar polarity. J Colloids Interface Sci 294:248–254
Karpovich DS, Blanchard GJ (1995) Relating the polarity-dependent fluorescence response of pyrene to vibronic coupling. Achieving a fundamental understanding of the pyrene polarity scale. J Phys Chem 99:3951–3958
Dong DC, Winnik MA (1984) The pyrene scale of solvent polarities. Can J Chem 62:2560–2565
Zana R, Levy H, Kwetkat K (1998) Mixed micellization of dimeric (gemini) surfactants and conventional surfactants. I. Mixtures of an anionic dimeric surfactant and of the nonionic surfactants C12E5 and C12E8. J Colloid Interface Sci 197:370–376
Karukstis KK, McDonough JR (2005) Characterization of the aggregates of N-alkyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bromide surfactants in aqueous solution. Langmuir 21:5716–5721
Turro NJ, Yekta A (1978) Luminescent probes for detergent solutions. A simple procedure for determination of the mean aggregation number of micelles. J Am Chem Soc 100:5951–5952
Tachiya M (1975) Application of a generating function to reaction kinetics in micelles. Kinetics of quenching of luminescent probes in micelles. Chem Phys Lett 33:289–292
Tachiya M (1982) Kinetics of quenching of luminescent probes in micellar systems. J Chem Phys 76:340–348
Acknowledgments
UM is thankful for financial assistance by DST, Government of India (Project No. SR/FT/CS-014/2010) and NM is thankful for financial assistance by CSIR, Government of India (Project No. EMR-II/2545/2011). ZV acknowledges the financial assistance in the form of a Maulana Azad National Fellowship (F1-17.1/2012-13/MANF-2012-13-MUS-GUJ-10818). NM acknowledges Dr. Arvind Kumar, Scientist, CSMCRI for the DLS and Fluorescence measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
More, U., Kumari, P., Vaid, Z. et al. Interaction Between Ionic Liquids and Gemini Surfactant: A Detailed Investigation into the Role of Ionic Liquids in Modifying Properties of Aqueous Gemini Surfactant. J Surfact Deterg 19, 75–89 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-015-1747-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-015-1747-x