Abstract
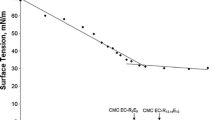
In the present study, quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) equations were derived using the logarithm of the octanol/water partition co-efficient for the prediction of acute aquatic toxicity of mixed surfactant systems. Further mixed surfactant systems of an anionic surfactant (sodium lauryl sulfate) and several nonionic surfactants (alkyl polyglucoside) of different hydrophobic chain lengths were taken together to calculate the parameter pEC50. Quantitative structure-properties relationship (QSPR) equations based on pC20, \( \Delta G^{{\text{ $ ^\circ $ }}}_{{{\text{ad}}}} \) and A min were developed from the surface tension data to predict pEC50 values and compared with QSAR derived pEC50 values to understand the probable mechanisms of action of the mixed surfactants blends for aquatic toxicity. The established QSAR and QSPR equations for mixed surfactants indicate that given blends of surfactants act as a polar narcotic.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SLS:
-
Sodium lauryl sulfate
- APG:
-
Alkyl polyglucoside
- \( \Delta G^{^\circ }_{{{\text{ad}}}} \) :
-
Gibbs free energy for adsorption
- A min :
-
Area minimum
- QSAR:
-
Quantitative structure activity relationship
- QSPR:
-
Quantitative structure property relationship
- log P :
-
Octanol/water patrician co-efficient
References
Roberts DW, Marshall SJ (1995) Applications of hydrophobicity parameters to prediction of acute aquatic toxicity of commercial surfactants mixtures. SAR QSAR Environ Res 4:167
Uppagrad L, Lindgren A, Sjostrom M, Wold S (2003) Multivariante quantitative structure activity relationships for the aquatic toxicity of technical nonionic surfactants. J Surf Detg 3:33–41
Collander R (1951) The partition of organic compounds between higher alcohols and water. Acta Chem Scand 5:774–780
Escher BI, Schwarzenbach RP (2000) Evaluation of liposome–water partitioning of organic acids and bases, development of a sorption model. Environ Sci Technol 34:3954–3961
Joshi VY, Sawant MR (2006) Study on dissolution rate enhancement of poorly water soluble drug: contributions of solubility enhancement and relatively low micelle diffusivity. J Dispers Sci Technol 27:1141–1150
Takagi Y, Ebata S, Takei T (1999) Toxicology and ecotoxicology of detergent chemicals. Surfactant Science Series, Marcel Dekker, New York
Zhang J, Li G-Z (2004) Phase behaviour of the APG/Alcohol/Alkane/H2O system. J Dispers Sci Technol 25:27–34
Busch P, Hensen H, Tesmann H (1993) Alkylpolyglucoside-eine newe tensid generation fur die kosmetik. Tenside Surf Det 30:11675
Abe M, Ogino K (1992) Mixed surfactant systems. Surfactant Science Series vol 46. Marcel Dekker, New York
Joshi VY, Sawant MR (2006) A convenient stereo selective synthesis of β-d-glucopyranosides. Indian J Chem 45B:461
Rubingh DN (1979) Solution chemistry of surfactants. In: Mittal KL (ed) vol 3. Plenum, New York, p 337
Clint JH (1975) Micellization of mixed nonionic surface active agents. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 73:1327
Roberts DW (2000) Aquatic toxicity: are surfactant properties relevant? J surfactants and detergents 3:309–315
Leo AJ, Hansch C (1979) Substitute constants for correlation analysis in chemistry and biology. Wiely, New york
Konemann H (1981) Quantitative structure-activity relationships in fish toxicity studies. Part 1: Relationship for 50 industrial pollutants. Toxicology 19(3):209–221
Saarikoski J, Viluksela M (1982) Relation between physicochemical properties of phenols and their toxicity and accumulation in fish. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 6:501–512
Roberts DW, Cosello JF (2003) Mechanisms of action for general and polar narcosis: a difference in dimension. QSAR and Combinat Sci 22:226–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, V.Y., Kadam, M.M. & Sawant, M.R. Comparison of QSAR and QSPR Based Aquatic Toxicity for Mixed Surfactants. J Surfact Deterg 10, 25–34 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-007-1013-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-007-1013-y