Abstract
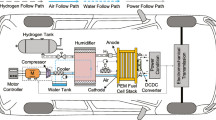
To prevent the oxygen starvation and improve the system output performance, an adaptive inverse control (AIC) strategy is developed to regulate the air supply flow of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) system in this paper. The PEMFC stack and the air supply system including a compressor and a supply manifold are modeled for the purpose of performance analysis and controller design. A recurrent fuzzy neural network (RFNN) is utilized to identify the inverse model of the controlled system and generates a suitable control input during the abrupt step change of external disturbances. Compared with the PI controller, numerical simulations are performed to validate the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed AIC strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li C H, Zhu X J, Cao G Y, Sui S, Hu M R. Identification of the Hammerstein model of a PEMFC stack based on least squares support vector machines [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 175(1): 303–316.
Wang F C, Yang Y P, Huang C W, Chang H P, Chen H T. System identification and robust control of a portable proton exchange membrane fuel-cell system [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 164(2): 704–712.
Methekar R N, Prasad V, Gudi R D. Dynamic analysis and linear control strategies for proton exchange membrane fuel cell using a distributed parameter model [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 165(1): 152–170.
Danzer M A, Wilhelm J, Aschemann H, Hofer E P. Model-based control of cathode pressure and oxygen excess ratio of a PEM fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 176(2): 515–522.
Lu Zhi-gang, Wu Shi-chang, Yu Ling-hui. Nonlinear adaptive inverse control and its application [M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2004: 1–27 (in Chinese).
Miao Q, Cao G Y, Zhu X J. Performance analysis and fuzzy neural networks modeling of direct methanol fuel cell [J]. Journal of Shanghai University (English Edition), 2007, 11(1): 84–87.
Lin C M, Hsu C F. Supervisory recurrent fuzzy neural network control of wing rock for slender delta wings [J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2004, 12(5): 733–742.
Correa J M, Farret F A, Canha L N, Simoes M G. An electrochemical-based fuel-cell model suitable for electrical engineering automation approach [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2004, 51(5): 1103–1112.
Mann R F, Amphlett J C, Hooper M A I, Jensen H M, Peppley B A, Roberge P R. Development and application of a generalised steady-state electrochemical model for a PEM fuel cell [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 86(1–2): 173–180.
Brown R N. Compressors: selection and sizing [M]. Houston: Gulf Professional Publishing, 1997: 125–165.
Pukrushpan J T, Stefanopoulou A G, Peng H. Modeling and control for PEM fuel cell stack system [C]// Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Anchorage, USA. 2002: 3117–3122.
Li C H, Zhu X J, Cao G Y, Sui S, Hu M R. Dynamic modeling and sizing optimization of stand-alone photovoltaic power systems using hybrid energy storage technology [J]. International Journal of Renewable Energy, 2009, 34(3): 815–826.
Kim K. Dynamic proton exchange membrane fuel cell system synthesis/design and operation/control optimization under uncertainty [D]. Doctoral dissertation, Virginia: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 2008: 78–87.
Larminie J, Dicks A. Fuel cell systems explained [M]. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, 2003: 263–270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.20576071), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No.08ZR1409800)
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Ch., Zhu, Xj., Sui, S. et al. Adaptive inverse control of air supply flow for proton exchange membrane fuel cell systems. J. Shanghai Univ.(Engl. Ed.) 13, 474–480 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11741-009-0610-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11741-009-0610-3