Abstract
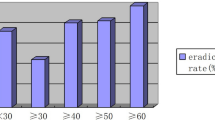
Helicobacter pylori eradication rate following standard triple therapy is decreasing. Identification of predictive factors of therapy success would be useful for H. pylori management in clinical practice. This study aimed to evaluate the role of different gastritis patterns on the efficacy of the currently suggested 14-day triple therapy regimen. One-hundred and seventeen, consecutive, non-ulcer dyspeptic patients, with H. pylori infection diagnosed at endoscopy, were enrolled. All patients received a 14-day, triple therapy with lansoprazole 30 mg, clarithromycin 500 mg and amoxicillin 1 g, all given twice daily. Bacterial eradication was assessed with 13C-urea breath test 4–6 weeks after completion of therapy. H. pylori infection was cured in 70.1% at ITT analysis and 83.7% at PP analysis. The eradication rate tended to be lower in patients with corpus-predominant gastritis as compared to those with antral-predominant gastritis at both ITT (66.1 vs 74.5%) and PP (80.4 vs 87.2%) analyses. The multivariate analysis failed to identify factors associated with therapy success. However, 14-day triple therapy does not achieve acceptable H. pylori cure rate in Italy, and should be not recommended in clinical practice.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kandulski A, Selgrad M, Malfertheiner P (2008) Helicobacter pylori infection: a clinical overview. Dig Liver Dis 40:619–626
Zullo A, Hassan C, Oliveti D, et al. (2011) Helicobacter pylori management in non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy patients in primary care. Intern Emerg Med. (Online First, 30 March 2011)
Annibale B, Capurso G, DelleFave G (2003) The stomach and iron deficiency anaemia: a forgotten link. Dig Liver Dis 35:288–295
Fujimura K (2005) Helicobacter pylori infection and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Int J Hematol 81:113–118
Franceschi F, Brisinda D, Buccelletti F, et al. (2011) Prevalence of virulent Helicobacter pylori strains in patients affected by idiopathic dysrhythmias. Intern Emerg Med (Online First, 11 May 2011)
Graham DY, Fischbach L (2010) Helicobacter pylori treatment in the era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Gut 59:1143–1153
Zullo A, Hassan C, Campo SMA et al (2004) Evolving therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection. Expert OpinTher Patents 14:1453–1464
De Francesco V, Zullo A, Margiotta M et al (2004) Sequential treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection does not share the risk factors of triple therapy failure. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19:407–414
Abdullahi M, Annibale B, Capoccia D et al (2008) The eradication of Helicobacter pylori is affected by body mass index (BMI). Obes Surg 18:1450–1454
Gatta L, Di Mario F, Vaira D et al (2011) Helicobacter pylori eradication: are we really all equal? A controlled study in native and immigrant population. Intern Emerg Med 6:35–39
Zullo A, Cristofari F, Bragazzi MC, Hassan C (2011) Helicobacter pylori in immigrants: a ‘‘foreign’’ bacterium? Intern Emerg Med 6:7–8
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH et al (1996) Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. Am J Surg Pathol 20:1161–1181
Georgopoulos SD, Ladas SD, Karatapanis S et al (2000) Factors that may affect treatment outcome of triple Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy with omeprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin. Dig Dis Sci 45:63–67
Severi C, Abdullahi M, Tari R et al (2009) High efficacy of bismuth subcitrate for Helicobacter pylori eradication in pangastritis. Dig Liver Dis 41:555–558
Zullo A, Perna F, Hassan C et al (2007) Primary antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori strains isolated in northern and central Italy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 25:1429–1434
Caselli M, Zullo A, Maconi G et al (2007) Cervia II Working Group Report 2006: guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in Italy. Dig Liver Dis 39:782–789
Megraud F, Malfertheiner P, O’Morain C et al (2007) Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht III Consensus Report. Gut 56:772–781
Scaccianoce G, Hassan C, Panarese A et al (2006) Helicobacter pylori eradication with either seve-day or 10-day triple therapies, and with ad 10-day sequential regimen. Can J Gastroenterol l20:113–117
Vaira D, Zullo A, Hassan C, et al. (2009) Sequential therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: the time is now! Ther Adv Gastroenterol 2317–2322
Goddard AF, Jessa MJ, Barrett DA et al (1996) Effect of omeprazole on the distribution of metronidazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin in human gastric juice. Gastroenterology 111:358–367
Lambert JR (1996) Pharmacology of the gastric mucosa: a rational approach to Helicobacter polytherapy. Gastroenterology 111:521–523
Perri F, Clemente R, Festa V et al (1998) Relationship between the results of pre-treatment urea breath test and efficacy of eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol 30:146–150
Maconi G, Parente F, Russo A et al (2001) Do some patients with Helicobacter pylori infection benefit from an extension to 2 weeks of a proton pump inhibitor-based triple eradication therapy? Am J Gastroenterol 96:359–366
Lai YC, Yang JC, Huang SH (2004) Pre-treatment urea breath test results predict the efficacy of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in patients with active duodenal ulcers. World J Gastroenterol 10:991–994
Zagari RM, Bianchi-Porro G, Fiocca R et al (2007) Comparison of one and 2 weeks of omeprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin treatment for Helicobacter pylori eradication: the HYPER study. Gut 56:475–479
Paoluzi P, Iacopini F, Crispino P et al (2006) 2-week triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection is better than 1-week in clinical practice: a large prospective single-center randomized study. Helicobacter 11:562–568
Buzas GM (2010) First-line eradication of Helicobacter pylori: are the standard triple therapies obsolete? A different perspective. World J Gastroenterol 16:3865–3870
Zullo A, De Francesco V, Hassan C et al (2007) The sequential therapy regimen for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a pooled-data analysis. Gut 56:1353–1357
Gatta L, Vakil N, Leandro G et al (2009) Sequential therapy or triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in adults and children. Am J Gastroenterol 104:3069–3079
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zullo, A., Severi, C., Vannella, L. et al. Role of gastritis pattern on Helicobacter pylori eradication. Intern Emerg Med 7, 517–522 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-011-0730-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-011-0730-4