Abstract
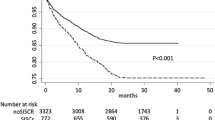
The objective of this study was to prospectively assess the prevalence, predictors and prognostic significance of microalbuminuria in a large cohort of consecutive acute cardiac patients, admitted to an intensive cardiac care unit from 1 January 2008 to 30 June 2009. In 815 acute cardiac patients, microalbuminuria is detectable in 39.3%. Microalbuminuria shows a significant negative correlation with left ventricular ejection fraction (Spearman’s ρ = −0.228; p < 0.001), while it is positively correlated with C-reactive protein (Spearman’s ρ = 0.239; p < 0.001), NT-pro-BNP (Spearman’s ρ = 0.306; p < 0.001) and glycemia (Spearman’s ρ = 0.191; p < 0.001). Microalbuminuria is an independent predictor for in-hospital mortality (1 μg/min step) (OR 1.015; 95% CI 1.008–1.023; p < 0.001). In the acute phase of cardiac patients, microalbuminuria is a common finding, and it represents an independent predictor for early mortality. It is strictly linked to the inflammatory activation (as indicated by C-reactive protein) and to acute glucose values, thus suggesting that it may be part of the acute response to stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pedersen LM (1999) Clinical significance of urinary albumin excretion in patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Br J Haematol 107:889–891
Pedersen LM, Milman N (1998) Microalbuminuria in patients with lung cancer. Eur J Cancer 34:76–80
Smith CT, Gosling P, Sanghera K et al (1994) Microproteinuria predicts the severity of systemic effects of reperfusion injury following infra renal aortic aneurysm surgery. Ann Vasc Surg 8:1–5
Shearman CP, Gosling P (1989) Walker KJ: Is low proteinuria an early predictor of severity of acute pancreatitis? J Clin Path 42:1132–1135
De Gaudio AR, Spina R (1999) Glomerular permeability and trauma: a correlation between microalbuminuria and injury severity score. Crit Care Med 27:2105–2108
Gopal S, Carr B, Nelson P (2006) Does microalbuminuria predict illness severity in critically ill patients on the intensive care unit? A systematic review. Crit Care Med 34(6):1805–1810
Abid O, Sun Q, Sugimoto K, Mercan D, Vincent JL (2001) Predictive value of microalbuminuria in medical ICU patients: results of a pilot study. Chest 120(6):1984–1988
Gosling P, Czyz J, Nightingale P, Manji M (2006) Microalbuminuria in the intensive care unit: Clinical correlates and association with outcomes in 431 patients. Crit Care Med 34(8):2158–2166
Thorevska N, Sabahi R, Upadya A, Manthous C, Amoateng-Adjepong Y (2003) Microalbuminuria in critically ill medical patients: prevalence, predictors, and prognostic significance. Crit Care Med 31(4):1075–1081
Donnelly R, Yeung JM, Manning G (2003) Microalbuminuria: a common, independent cardiovascular risk factor, especially but not exclusively in type 2 diabetes. J Hypertens Suppl 21:S7–S12
Lazzeri C, Valente S, Chiostri M, Sori A, Bernardo P, Gensini GF (2010) Uric acid in the acute phase of ST elevation myocardial infarction submitted to primary PCI: its prognostic role and relation with inflammatory markers: a single center experience. Int J Cardiol 138(2):206–209
Valente S, Lazzeri C, Chiostri M, Giglioli C, Sori A et al (2009) NT-proBNP on admission for early risk stratification in STEMI patients submitted to PCI. Relation with extension of STEMI and inflammatory markers. Int J Cardiol 132(1):84–89
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, Coresh J, CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150(9):604–612
European Association for Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions, Wijns W, Kolh P, Danchin N, Di Mario C, Falk V, Folliguet T, Garg S, Huber K, James S, Knuuti J, Lopez-Sendon J, Marco J, Menicanti L, Ostojic M, Piepoli MF, Pirlet C, Pomar JL, Reifart N, Ribichini FL, Schalij MJ, Sergeant P, Serruys PW, Silber S, Sousa Uva M, Taggart D; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines, Vahanian A, Auricchio A, Bax J, Ceconi C, Dean V, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hobbs R, Kearney P, McDonagh T, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Sechtem U, Sirnes PA, Tendera M, Vardas PE, Widimsky P; EACTS Clinical Guidelines Committee, Kolh P, Alfieri O, Dunning J, Elia S, Kappetein P, Lockowandt U, Sarris G, Vouhe P, Kearney P, von Segesser L, Agewall S, Aladashvili A, Alexopoulos D, Antunes MJ, Atalar E, Brutel de la Riviere A, Doganov A, Eha J, Fajadet J, Ferreira R, Garot J, Halcox J, Hasin Y, Janssens S, Kervinen K, Laufer G, Legrand V, Nashef SA, Neumann FJ, Niemela K, Nihoyannopoulos P, Noc M, Piek JJ, Pirk J, Rozenman Y, Sabate M, Starc R, Thielmann M, Wheatley DJ, Windecker S, Zembala M (2010) Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: the task force on myocardial revascularization of the european society of cardiology (esc) and the european association for cardio-thoracic surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J 31(20):2501–55
ACC/AHA Guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non st-elevation myocardial infarction guidelines Medicine Circulation (2007) 116: e148–e304
Sharon AH, William TA, Marshall HC et al (2009) Focused update incorporated into the acc/aha 2005 guidlines for the diagnosis and management of heart failure in adults. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:e1–e90
Stehouwer CD, Smulders YM (2006) Microalbuminuria and risk for cardiovascular disease: analysis of potential mechanisms. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(8):2106–2111
Borch-Johnsen K, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Strandgaard S (1999) Urinary albumin excretion: an independent predictor of ischemic heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:1992–1997
Masson S, Latini R, Milani V, Moretti L, Rossi MG, Carbonieri E, Frisinghelli A, Minneci C, Valisi M, Maggioni AP, Marchioli R, Tognoni G, Tavazzi L, GISSI-HF Investigators (2010) Prevalence and prognostic value of elevated urinary albumin excretion in patients with chronic heart failure: data from the GISSI-Heart Failure trial. Circ Heart Fail. 3(1):65–72
Taskiran M, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Jensen GB, Jensen JS (1998) Urinary albumin excretion in hospitalized patients with acute myocardial infarction. Prevalence of microalbuminuria and correlation to left ventricle wall thickness. Scand Cardiovasc J 32(3):163–166
Gosling P, Hughes EA, Reynolds TM, Fox JP (1991) Microalbuminuria is an early response following acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 12(4):508–513
Berton G, Citro T, Palmieri R, Petucco S, De Toni R, Palatini P (1997) Albumin excretion rate increases during acute myocardial infarction and strongly predicts early mortality. Circulation 96(10):3338–3345
Lekatsas I, Koulouris S, Triantafyllou K, Chrisanthopoulou G, Moutsatsou-Ladikou P, Ioannidis G et al (2006) Prognostic significance of microalbuminuria in non-diabetic patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 106(2):218–223
Berton G, Cordiano R, Mbaso S, De Toni R, Mormino P, Palatini P (1998) Prognostic significance of hypertension and albuminuria for early mortality after acute myocardial infarction. J Hypertens 16(4):525–530
Lazzeri C, Valente S, Chiostri M, Picariello C, Gensini GF (2010) Microalbuminuria in hypertensive nondiabetic patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 11(10):748–753
The MONICA/KORA Myocardial Infarction Registry, Meisinger C, Heier M, von Scheidt W, Kuch B (2010) Admission C-reactive protein and short- as well as long-term mortality in diabetic versus non-diabetic patients with incident myocardial infarction. Clin Res Cardiol 99(12):817–823
Araújo JP, Lourenço P, Azevedo A, Friões F, Rocha-Gonçalves F, Ferreira A, Bettencourt P (2009) Prognostic value of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in heart failure: a systematic review. J Card Fail 15(3):256–266
He LP, Tang XY, Ling WH, Chen WQ, Chen YM (2010) Early C-reactive protein in the prediction of long-term outcomes after acute coronary syndromes: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Heart 96(5):339–346
Genest J (2010) C-reactive protein: risk factor, biomarker and/or therapeutic target? Can J Cardiol 26(Suppl A):41A–44A
Struthers A, Lang C (2007) The potential to improve primary prevention in the future by using BNP/N-BNP as an indicator of silent ‘pancardiac’ target organ damage: BNP/N-BNP could become for the heart what microalbuminuria is for the kidney. Eur Heart J 28(14):1678–1682
Uno H, Ishikawa J, Hoshide S, Kabutoya T, Ishikawa S, Shimada K, Kario K (2008) Effects of strict blood pressure control by a long-acting calcium channel blocker on brain natriuretic peptide and urinary albumin excretion rate in Japanese hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 31(5):887–896
Saliba Y, Chouery E, Mégarbané A, Jabbour H, Fares N (2010) Microalbuminuria versus brain natriuretic peptide in cardiac hypertrophy of hypertensive rats. Physiol Res 59(6):871–880
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valente, S., Lazzeri, C., Chiostri, M. et al. Prevalence, predictors and prognostic significance of microalbuminuria in acute cardiac patients: a single center experience. Intern Emerg Med 8, 327–331 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-011-0619-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-011-0619-2