Abstract
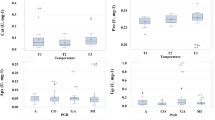
Platycodon grandiflorus (Jacq.) A.DC. (PG) is a traditional herb, and triterpenoid saponins are the main bioactive components of PG, including platycodin D, deapioplatycodin D, and platycodin D3. Our study aimed to explore the biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in responses to water regulation. PG samples were collected at different stages under full water (FW) and restricted-water (RW) conditions. Soil moisture, root weight, osmoregulatory substances including soluble sugar, soluble protein, and proline, as well as malondialdehyde were measured. Activities of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase, and catalase were detected. Expressions of key genes involved in the platycodin metabolism pathway and platycodin contents were determined, followed by correlation analysis. Significantly lower soil moisture as well as increased root dry matter content and malondialdehyde were observed in RW group. Soluble protein and proline were significantly higher in the RW group at the day 30, and 45, and higher levels of proline were also found at day 60, and 75. Soluble sugar content was rapidly increased in the RW group at day 30 and 60. Not only higher activities of peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase, but also high expressions of AACT, HMGR and HMGS were found in the late water regulation in RW group. Platycodin D content was rapidly increased in both groups, and the RW group had significantly higher platycodin D content. Linear mixed effects modeling analysis based on restricted maximum likelihood estimation revealed that proline, malondialdehyde, HMGR and platycodin D were negatively correlated with soil moisture. Platycodin D and deapioplatycodin D were positively correlated with AACT, HMGR, HMGS, SS, and UGT-1, and negatively correlated with β-AS. Platycodin D3 was positively correlated with IPPI, MVD and SS, while negatively correlated with β-AS. Our results presented here provide insights into the effects of water regulation on the biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in PG.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The raw data were collected and analyzed by the authors, and are not ready to share their data because the data have not been published.
References
Alhaithloul HA, Soliman MH, Ameta KL, El-Esawi MA, Elkelish A (2019) Changes in ecophysiology, osmolytes, and secondary metabolites of the medicinal plants of Mentha piperita and Catharanthus roseus subjected to drought and heat stress. Biomolecules 10(1):43
Alscher RG, Erturk N, Heath LS (2002) Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants. J Exp Bot 53(372):1331–1341
Augustin JM, Kuzina V, Andersen SB, Bak S (2011) Molecular activities, biosynthesis and evolution of triterpenoid saponins. Phytochemistry 72(6):435–457
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot 91(2):179–194
Blum A (2017) Osmotic adjustment is a prime drought stress adaptive engine in support of plant production. Plant Cell Environ 40(1):4–10
Boo HO, Park JH, Kim HH, Kwon SJ, Woo SH (2018) Evaluation of physiological functionalities and anti-inflammatory activity on in vitro cultured adventitious root of Platycodon grandiflorum. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 21(2):183–191
Cheng L, Han M, Yang L-M, Li Y, Sun Z, Zhang T (2018) Changes in the physiological characteristics and baicalin biosynthesis metabolism of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi under drought stress. Ind Crops Prod 122:473–482
Choi JH, Jin SW, Choi CY, Kim HG, Kim SJ, Lee HS, Chung YC, Kim EJ, Lee YC, Jeong HG (2017) Saponins from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum ameliorate high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Biomed Pharmacother 86:205–212
Chun J, Ha IJ, Kim YS (2013) Antiproliferative and apoptotic activities of triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum and their structure-activity relationships. Planta Med 79(8):639–645
Han SB, Park SH, Lee KH, Lee CW, Lee SH, Kim HC, Kim YS, Lee HS, Kim HM (2001) Polysaccharide isolated from the radix of Platycodon grandiflorum selectively activates B cells and macrophages but not T cells. Int Immunopharmacol 1(11):1969–1978
Haralampidis K, Trojanowska M, Osbourn AE (2002) Biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in plants. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 75:31–49
Jang KJ, Kim HK, Han MH, Oh YN, Yoon HM, Chung YH, Kim GY, Hwang HJ, Kim BW, Choi YH (2013) Anti-inflammatory effects of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorus in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int J Mol Med 31(6):1357–1366
Jia X, Sun C, Li G, Li G, Chen G (2015) Effects of progressive drought stress on the physiology, antioxidative enzymes and secondary metabolites of Radix astragali. Acta Physiol Plant 37(12):262
Jung SC, Kim W, Park SC, Jeong J, Park MK, Lim S, Lee Y, Im WT, Lee JH, Choi G, Kim SC (2014) Two ginseng UDP-glycosyltransferases synthesize ginsenoside Rg3 and Rd. Plant Cell Physiol 55(12):2177–2188
Kang Y, Kim K, Kim T, Yang C, Choe M (2015) Evaluation of the anti-obesity activity of Platycodon grandiflorum root and Curcuma longa root fermented with Aspergillus oryzae. Korean J Food Sci Technol 47:111–118
Kim TW, Song IB, Lee HK, Lim JH, Cho ES, Son HY, Park SJ, Kim JW, Yun HI (2012) Platycodin D, a triterpenoid sapoinin from Platycodon grandiflorum, ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 50(12):4254–4259
Kim YK, Kim JK, Kim YB, Lee S, Kim SU, Park SU (2013) Enhanced accumulation of phytosterol and triterpene in hairy root cultures of Platycodon grandiflorum by overexpression of Panax ginseng 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. J Agric Food Chem 61(8):1928–1934
Kliebenstein DJ, Osbourn A (2012) Making new molecules - evolution of pathways for novel metabolites in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15(4):415–423
Kong D-X, Li Y-Q, Bai M, He H-J, Liang G-X, Wu H (2017) Correlation between the dynamic accumulation of the main effective components and their associated regulatory enzyme activities at different growth stages in Lonicera japonica Thunb. Ind Crops Prod 96:16–22
Kuznetsova A, Brockhoff P, Christensen R (2017) lmerTest package: tests in linear mixed effects models. J Stat Softw 82(13):1–26
Li Y, Kong D, Fu Y, Sussman MR, Wu H (2020) The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 148:80–89
Ma CH, Gao ZJ, Zhang JJ, Zhang W, Shao JH, Hai MR, Chen JW, Yang SC, Zhang GH (2016) Candidate genes involved in the biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in platycodon grandiflorum identified by transcriptome analysis. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00673
Moses T, Papadopoulou KK, Osbourn A (2014) Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 49(6):439–462
Ncube B, Finnie J, Staden J (2012) Quality from the field: the impact of environmental factors as quality determinants in medicinal plants. S Afr J Bot 82:11–20
Parida AK, Dagaonkar VS, Phalak MS, Umalkar GV, Aurangabadkar LP (2007) Alterations in photosynthetic pigments, protein and osmotic components in cotton genotypes subjected to short-term drought stress followed by recovery. Plant Biotechnol Rep 1(1):37–48
Press CS (2017) China statistical yearbook.
Rahimi Y, Taleei A, Ranjbar M (2018) Long-term water deficit modulates antioxidant capacity of peppermint (Mentha piperita L.). Sci Hortic 237:36
Si C, Zhang JY, Xun HC (2014) Advances in studies on growth metabolism and response mechanisms of medicinal plants under drought stress. China J Chin Materia Med 39(13):2432–2437
Sivaramakrishnan S, Patell VZ, Flower DJ, Peacock JM (1988) Proline accumulation and nitrate reductase activity in contrasting sorghum lines during mid-season drought stress. Physiol Plant 74(3):418–426
Smirnoff N (2006) The role of active oxygen in the response of plants to water deficit and desiccation. New Phytol 125:27–58
Wang C, Zhang N, Wang Z, Qi Z, Zhu H, Zheng B, Li P, Liu J (2017a) Nontargeted metabolomic analysis of four different parts of platycodon grandiflorum grown in northeast China. Molecules 22(8):1280
Wang C, Zhang N, Wang Z, Qi Z, Zhu H, Zheng B, Li P, Liu J (2017b) Nontargeted metabolomic analysis of four different parts of platycodon grandiflorum grown in northeast China. Molecules 22(8):1280
Wei H, Cheng L, Wu P, Han M, Yang L-M (2019) Short-term water changes response of saponin biosynthesis process in Astragalus membranceus. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi 44:441–447
Weng JH (1990) Effects of water deficit on osmotic adjustment, photosynthesis and dry matter production of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. In: El Bassam N, Dambroth M, Loughman BC (eds) Genetic aspects of plant mineral nutrition. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 145–150
Yadav RK, Sangwan RS, Sabir F, Srivastava AK, Sangwan NS (2014) Effect of prolonged water stress on specialized secondary metabolites, peltate glandular trichomes, and pathway gene expression in Artemisia annua L. Plant Physiol Biochem 74:70–83
Yang LM, Zhang YG, Lin HM, Yang L (2012) Research advances on formation theories and control techniques of chinese medicinal materials quality. J Jilin Agric Univ 34(2):119–124
Yang L, Zhao Y, Zhang Q, Cheng L, Han M, Ren Y, Yang L (2019) Effects of drought–re-watering–drought on the photosynthesis physiology and secondary metabolite production of Bupleurum chinense DC. Plant Cell Rep 38(9):1181–1197
Yendo AC, de Costa F, Gosmann G, Fett-Neto AG (2010) Production of plant bioactive triterpenoid saponins: elicitation strategies and target genes to improve yields. Mol Biotechnol 46(1):94–104
Yoshioka H, Numata N, Nakajima K, Katou S, Kawakita K, Rowland O, Jones JD, Doke N (2003) Nicotiana benthamiana gp91phox homologs NbrbohA and NbrbohB participate in H2O2 accumulation and resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell 15(3):706–718
Zhang L, Wang Y, Yang D, Zhang C, Zhang N, Li M, Liu Y (2015) Platycodon grandifloras: an ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J Ethnopharmacol 164:147–161
Zhang LL, Huang MY, Yang Y, Huang MQ, Shi JJ, Zou L, Lu JJ (2020) Bioactive platycodins from platycodonis radix: phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, toxicology and pharmacokinetics. Food Chem 327(127029):19
Zhou J, Guo L, Zhang J, Yang G, Zhao M, Huang L (2010) Responses of medicinal plant to drought stress and controlled experiment. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 35(15):1919–1924
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the China Agriculture Research System (CN) (grant number: CARS-21) and Science and technology project of Jilin Provincial Education Department during the 13th five year plan (CN) (grant number: JJKH20190983KJ).
Funding
There is no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by A. Krolicka.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11738_2023_3519_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file1 High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) chromatogram of platycodin D, deapioplatycodin D, and platycodin D3. (A) Standard chromatogram; (B) Sample chromatogram. 1: platycodin D3; 2: deapioplatycodin D; 3: platycodin D. (JPG 107 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Cheng, L., Zhang, M. et al. Platycodon grandiflorus subjected to full- and restricted-water regimes show differential biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins. Acta Physiol Plant 45, 55 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-023-03519-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-023-03519-6