Abstract
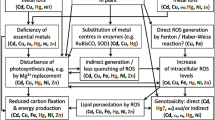
With the development of agricultural science and technology, the influence of nanomaterials on plants under low pressure is still not reported. Planting at the low-pressure place (in space or high-altitude areas of the Earth) is looking increasingly possible in the future. In this study, rice seedlings were cultured under low and atmospheric pressure, with the application of nanomaterials and Cd into the nutrient solution. We have investigated the influence of Cd, multi-walled carbon nanotubes, cerium oxide nanomaterials and their co-exposure effects on rice seedlings. Physiological parameters such as plant height and root length of rice remained non-significant under nanomaterials treatment. However, nanomaterials with Cd showed the inhibitory effect on plant height and root length as compared to control. Conversely, nanomaterials with Cd had no effects on rice biomass at atmospheric pressure but an average of 34.7% inhibit the biomass at low pressure. The low-pressure group showed that a low concentration of nanomaterials will promote the absorption of Cd in rice, and atmospheric pressure group showed that a high concentration of nanomaterials will promote the absorption of Cd. Transmission electron microscope images revealed that rice seedlings uptake the nanomaterials at both pressures. The results showed that low pressure would affect the growth and development of rice to a great extent, also affect the absorption of nanomaterials and Cd by rice.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbara HN, Dresler S, Matraszek R (2015) Exogenous malic and acetic acids reduce cadmium phytotoxicity and enhance cadmium accumulation in roots of sunflower plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 94:225–234
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, de Heer WA (2002) Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science 297:787–792
Begum P, Ikhtiari R, Fugetsu B (2014) Potential impact of multi-walled carbon nanotubes exposure to the seedling stage of selected plant species. Nanomaterials 4:203–221
Chen JW, Yu HJ, Li L, Qin MJ, Jiang M, Tan MP (2015) Mitigating effects of nano-TiO2 particles on growth inhibition of maize under cadmium stress. J Plant Physiol 51:1633–1639
Cui XF, Ding XD, Li SY, Liao XR, Liu CP, Xue SL, Wang DH, Wang RP (2012) Effects of the foliar application of silicon and cerium sol on relieving toxicity of Pb, Cd in the lettuce. J Saf Environ 5:7–12
Deng XY, Hu XL, Cheng W, Ma ZX, Gao K (2016) Study on the biological effects of nanometer cerium oxide on Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J Ecotoxicol 11(5):111–116
DalCorso G, Farinati S, Furini A (2010) Regulatory networks of cadmium stress in plants. Plant Signal Behav 5:663–667
Fleischer A, ONeiil MA, Ehwald R (1999) The pore size of non-graminaceous plant cell wall is rapidly decreased by borate ester cross-linking of the pectic polysaccharide rhamnogalacturonan II. Plant Physiol 121:829–838
Gui X, Zhang Z, Liu S, Ma Y, Zhang P, He X, Li Y, Zhang J, Li H, Rui Y et al (2015) Fate and phytotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles on lettuce cultured in the potting soil environment. PLoS ONE 10:
Hao Y, Yu FF, Lv RT, Ma CX, Zhang ZT, Rui YK, Liu LM, Cao WD, Xing BS (2016) Carbon nanotubes filled with different ferromagnetic alloys affect the growth and development of rice seedlings by changing the C:N ratio and plant hormones concentrations. PLoS ONE 11:e0157264
Hao Y, Yuan W, Ma CX, White JC, Zhang ZT, Adeel M, Zhou T, Rui YK, Xing BS (2018) Engineered nanomaterials suppress Turnip mosaic virus infection in tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana). Environ Sci Nano 5:1685–1693
Hao Y, Fang PH, Ma CX, White JC, Xiang ZQ, Wang HT, Zhang Z, Rui YK, Xing BS (2019) Engineered nanomaterials inhibit Podosphaera pannosa infection on rose leaves by regulating phytohormones. Environ Res 170:1–6
Iwabuchi K, Saito G, Goto E, Takakura T (1996) Effect of vapor pressure deficit on spinach growth under hypobaric conditions. Acta Hort 440:60–64
Ji Y, Zhou Y, Ma C, Feng Y, Hao Y, Rui Y, Wu W, Gui X, Han Y, Wang Y et al (2017) Jointed toxicity of TiO2 NPs and Cd to rice seedlings: NPs alleviated Cd toxicity and Cd promoted NPs uptake. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:82–93
Li YJ, Wen M, Li JK, Ma Y, Liang XX (2018) Progress in soil pollution remediation technology. Environ Monit Manag Technol 30(05):8–14
Ma YL, Niu J, Jiang ZY (2015) Effects of salicylic acid on CdCl2 stress-caused stomatal movement in Vicia Faba. J Shanxi Norm Univ (nat Sci Ed) 29:69–73
Mauter MS, Elimelech M (2008) Environmental applications of carbon-based nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 42:5843–5859
Moore MN (2006) Do nanoparticles present ecotoxicological risks for the health of the aquatic environment. Environ Int 32:967–976
Nair R, Varghese SH, Nair BG, Maekawa T, Yoshida Y, Kumar DS (2012) Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci 179:154–163
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao AJ, Quigg A, Santschi PH, Sigg L (2008) Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17:372–386
Qiao ZJ, Wang T, Jin ZP, Liu ZQ, Pei YX (2016) Hydrogen sulfide mediates Cd2+-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Shanxi Norm Univ (nat Sci Ed) 39:146–151
Rui MM, Ma CX, Hao Y, Guo J, Rui YK, Tang XL, Zhao Q, Fan X, Zhang ZT, Hou TQ, Zhu SY (2016) Iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Front Plant Sci 7:815
Sebastian A, Prasad MNV (2004) Vertisolprevent Cd accumulation in rice: analysis by ecophysiological toxicity markers. Chemosphere 108:85–92
Tang YK, Guo SS, Qin LF, Ai WD (2008) A study of growth and development of wheat under low atmospheric pressure. Space Med Med Eng 4:316–320
Tang YK, Guo SS, Lin S, Ai WD, Qin LF (2011) Review of advances on growth characteristics and adapting mechanism of plant at low atmospheric pressure. Chin J Plant Ecol 35:872–881
Tang YK, Gao F, Yang JS, Su HH (2018) Development of a small low-pressure vegetable culture device. Manned Spaceflight 24(03):404–410
Wang Z, Xie X, Zhao J, Liu X, Feng W, White JC, Xing B (2012) Xylem-and phloem-based transport of CuO nanoparticles in maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Sci Technol 46:4434–4441
Wang XJ, Wang WB, Yang L, Jin L, Song Yu, Jiang SJ, Qin LL (2015) Transport pathways of cadmium (Cd) and its regulatory mechanisms in plant. Acta Ecol Sin 35:7921–7929
Wang YY, Wang LQ, Ma CX, Wang KX, Hao Y, Chen Q, Mo Y, Rui YK (2019a) Effects of cerium oxide on rice seedlings as affected by co-exposure of cadmium and salt. Environ Pollut 252:1087–1096
Wei B, Shi Z, Xiao J et al (2017) In vivo and in vitro antibacterial effect of nano-structured titanium coating incorporated with silver oxide nanoparticles. J Biomater Tissue Eng 7(5):418–425
Wild E, Jones KC (2009) Novel method for the direct visualization of in vivo nanomaterials and chemical interactions in plants. Environ Sci Technol 43:5290–5294
Xing YG, Li WX, Wang Q, Li XL, Xu QL, Guo XL, Bi XF, Liu XC, Shui YR, Lin HB, Yang H (2019) Antimicrobial nanoparticles incorporated in edible coatings and films for the preservation of fruits and vegetables. Molecules 24(9):1695–1724
Yang XP, Zhao FJ (2013) A review of uptake, translocation and phytotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles in plants. Environ Sci 34:4495–4502
Yang J, Jiang F, Ma C, Rui Y, Rui M, Adeel M, Cao W, Xing B (2018) Alteration of crop yield and quality of wheat upon exposure to silver nanoparticles in a life cycle study. J Agric Food Chem 66:2589–2597
Yang SN, Liu L, Zheng LG (2019) Effects of combined contamination of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and cadmium on the growth of rice. Environ Chem 38(5):1113–1118
Yuan GQ, Gong JL, Zeng GM (2015) Phytotoxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes to rice seedling (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Sci Circum 35:4143–4149
Zhang MY, Wang Y, Zhao DY (2009) Mechanism of arsenic fixation of stabilized zero valence Fe, FeS, Fe3O4 nanoparticles in soil. Chin Sci Bull 54(23):3637–3644
Zhang M, Liu XC, Yuan LY, Wu KQ, Duan J, Wang XL, Yang LX (2012) Transcriptional profiling in Cd-treated rice seedling roots using suppressive subtractive hybridization. Plant Physiol Biochem 50:79–86
Zhao ZJ, Liang TB, Chen QS, Hu LW, Zhang YL, Yin QS (2017) The regulation of carbon nanomaterials on plant growth and development. Crops J 2:7–13
Zheng HC, Liu J, Wang H, Wang M (2019) Mechanism of plant cell absorb cadmium and its influence on stoma development. J Earth Environ 10(5):496–502
Zhu YQ, Yang ZQ (2018) Response of Leaf photosynthetic characteristics of different varieties of Grape to drought stress and recovery process after drought. Agrometeorol China 11:739–750
Wang C, Bi L, Pan G (2020) High-efficiency removal of heavy metal cadmium by manganese sulfide nanoparticles. Chin J Environ Eng 14(1):24–33
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0801103, 2017YFD0801300), NSFC-Guangdong Joint Fund (U1401234), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41371471) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41130526).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. P. Singh.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, K., Fu, D., Adeel, M. et al. Toxicities of nanomaterials and metals to rice under low atmospheric pressure. Acta Physiol Plant 44, 58 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03391-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03391-w