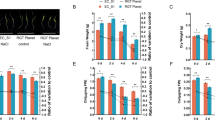
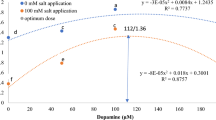
Abstract
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria can stimulate not only plant growth and development, but also alleviate the negative effects on plants caused by abiotic stresses. In this study, a novel halotolerant strain was isolated and identified as Glutamicibacter sp. (YD01) using 16S rDNA analysis. This strain tolerated up to 10% NaCl and showed two growth-promoting traits such as 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase enzyme activity and IAA production. Glutamicibacter sp. YD01 inoculation could enhance tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants to salt stress by regulation of plant ethylene production, ACC content, ACC oxidase activity and improving K+ acquisition. Moreover, strain YD01-inoculated rice exhibited lower levels of Na+ accumulation and electrolyte leakage under salt treatment compared to non-inoculated ones. Inoculated rice also showed higher transcript levels of genes encoding antioxidants and genes involved in salt tolerance than the plants with no inoculation. In summary, this study showed the important role of Glutamicibacter sp. YD01 in the alleviation of the adverse effects of salt stress on growth and development of rice plants through mediation of phytohormone (ethylene) and ROS accumulation, maintaining ion homeostasis, improving photosynthetic capacity and enhancing stress-responsive genes expression. This work provides an economic approach of promoting growth and development of plants under salt stress treatment.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkrim S, Jebara SH, Jebara M (2018) Antioxidant systems responses and the compatible solutes as contributing factors to lead accumulation and tolerance in Lathyrus sativus inoculated by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:427–436
Assaha DVM, Ueda A, Saneoka H, Al-Yahyai R, Yaish MW (2017) The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in glycophytes. Front Physiol 8:509
Barnawal D, Bharti N, Pandey SS, Pandey A, Chanotiya CS, Kalra A (2017) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance wheat salt and drought stress tolerance by altering endogenous phytohormone levels and TaCTR1/TaDREB2 expression. Physiol Plant 161(4):502–514
Barnawal D, Maji D, Bharti N, Chanotiya CS, Kalra A (2013) ACC deaminase-containing Bacillus subtilis reduces stress ethylene-induced damage and improves mycorrhizal colonization and rhizobial nodulation in Trigonella foenum-graecum under drought stress. J Plant Growth Regul 32(4):809–822
Bharti N, Pandey SS, Barnawal D, Patel VK, Kalra A (2016) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Dietzia natronolimnaea modulates the expression of stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress. Sci Rep 6:34768
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1):248–254
Cai R, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Lin Y, Peng X, Li Q, Chang Y, Jiang H, Xiang Y, Cheng B (2014) Overexpression of a maize WRKY58 gene enhances drought and salt tolerance in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 119(3):565–577
Chatterjee P, Kanagendran A, Samaddar S, Pazouki L, Sa T-M, Niinemets Ü (2019) Methylobacterium oryzae CBMB20 influences photosynthetic traits, volatile emission and ethylene metabolism in Oryza sativa genotypes grown in salt stress conditions. Planta 249(6):1903–1919
Chen L, Liu Y, Wu G, Veronican Njeri K, Shen Q, Zhang N, Zhang R (2016) Induced maize salt tolerance by rhizosphere inoculation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Physiol Plant 158(1):34–44
Chen L, Song Y, Li S, Zhang L, Zou C, Yu D (2012) (2012) The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant abiotic stresses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819(2):120–128
Chong J, Soufan O, Li C, Caraus I, Li S, Bourque G, Wishart DS, Xia J (2018) MetaboAnalyst 4.0: towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W486–W494
El-Esawi MA, Alaraidh IA, Alsahli AA, Alamri SA, Ali HM, Alayafi AA (2018a) Bacillus firmus (SW5) augments salt tolerance in soybean (Glycine max L.) by modulating root system architecture, antioxidant defense systems and stress-responsive genes expression. Plant Physiol Biochem 132:375–384
El-Esawi MA, Alaraidh IA, Alsahli AA, Alzahrani SM, Ali HM, Alayafi AA, Ahmad M (2018b) Serratia liquefaciens KM4 improves salt stress tolerance in maize by regulating redox potential, ion homeostasis, leaf gas exchange and stress-related gene expression. Int J Mol Sci 19(11):3310
Fahad S, Hussain S, Matloob A, Khan FA, Khaliq A, Saud S, Hassan S, Shan D, Khan F, Ullah N, Faiq M, Khan MR, Tareen AK, Khan A, Ullah A, Ullah N, Huang J (2015) Phytohormones and plant responses to salinity stress: a review. Plant Growth Regul 75(2):391–404
Guan C, Wang C, Li Q, Ji J, Wang G, Jin C, Tong Y (2019) LcSABP2, a salicylic acid binding protein 2 gene from Lycium chinense, confers resistance to triclosan stress in Nicotiana tabacum. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109516
Hashem A, Abd Allah EF, Alqarawi AA, Al-Huqail AA, Wirth S, Egamberdieva D (2016) The interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and endophytic bacteria enhances plant growth of Acacia gerrardii under salt stress. Front Microbiol 7:1089
He A-L, Niu S-Q, Zhao Q, Li Y-S, Gou J-Y, Gao H-J, Suo S-Z, Zhang J-L (2018) Induced salt tolerance of perennial ryegrass by a novel bacterium strain from the rhizosphere of a desert shrub Haloxylon ammodendron. Int J Mol Sci 19(2):469
Jaemsaeng R, Jantasuriyarat C, Thamchaipenet A (2018) Molecular interaction of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase (ACCD)-producing endophytic Streptomyces sp. GMKU 336 towards salt-stress resistance of Oryza sativa L. cv. KDML105. Sci Rep 8(1):1950
Jiang C, Belfield EJ, Cao Y, Smith JAC, Harberd NP (2013) An Arabidopsis soil-salinity—tolerance mutation confers ethylene-mediated enhancement of sodium/potassium homeostasis. Plant Cell 25(9):3535–3552
Kang S-M, Khan AL, Waqas M, You Y-H, Kim J-H, Kim J-G, Hamayun M, Lee I-J (2014) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria reduce adverse effects of salinity and osmotic stress by regulating phytohormones and antioxidants in Cucumis sativus. J Plant Interact 9(1):673–682
Lata C, Prasad M (2011) Role of DREBs in regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. J Exp Bot 62(14):4731–4748
Li Q, Wang G, Guan C, Yang D, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Ji J, Jin C, An T (2019a) Overexpression of LcSABP, an orthologous gene for salicylic acid binding protein 2, enhances drought stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Front Plant Sci 10:200
Li Q, Wang G, Wang Y, Dan Y, Guan C, Ji J (2019b) Foliar application of salicylic acid alleviate the cadmium toxicity by modulation the reactive oxygen species in potato. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 172:317–325
Lindemose S, Shea C, Jensen MK, Skriver K (2013) Structure, function and networks of transcription factors involved in abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 14(3):5842–5878
Lubna AS, Hamayun M, Khan AL, Waqas M, Khan MA, Jan R, Lee I-J, Hussain A (2018) Salt tolerance of Glycine max.L induced by endophytic fungus Aspergillus flavus CSH1, via regulating its endogenous hormones and antioxidative system. Plant Physiol Biochem 128:13–23
Niu S-Q, Li H-R, Paré PW, Aziz M, Wang S-M, Shi H, Li J, Han Q-Q, Guo S-Q, Li J, Guo Q, Ma Q, Zhang J-L (2016) Induced growth promotion and higher salt tolerance in the halophyte grass Puccinellia tenuiflora by beneficial Rhizobacteria. Plant Soil 407(1):217–230
Nunkaew T, Kantachote D, Kanzaki H, Nitoda T, Ritchie RJ (2014) Effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)-containing supernatants from selected Rhodopseudomonas palustris strains on rice growth under NaCl stress, with mediating effects on chlorophyll, photosynthetic electron transport and antioxidative enzymes. Electron J Biotechnol 17:4–4
Qin S, Feng W-W, Zhang Y-J, Wang T-T, Xiong Y-W, Xing K (2018) Diversity of bacterial microbiota of coastal halophyte Limonium sinense and amelioration of salinity stress damage by symbiotic plant growth-promoting actinobacterium Glutamicibacter halophytocola KLBMP 5180. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(19):e01533–e11518
Rabiei V, Kakavand F, Zaare-Nahandi F, Razavi F, Aghdam MS (2019) Nitric oxide and γ-aminobutyric acid treatments delay senescence of cornelian cherry fruits during postharvest cold storage by enhancing antioxidant system activity. Sci Hortic 243:268–273
Rong W, Qi L, Wang A, Ye X, Du L, Liang H, Xin Z, Zhang Z (2014) The ERF transcription factor TaERF3 promotes tolerance to salt and drought stresses in wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 12(4):468–479
Sapre S, Gontia-Mishra I, Tiwari S (2019) ACC deaminase-producing bacteria: a key player in alleviating abiotic stresses in plants. In: Kumar A, Meena VS (eds) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for agricultural sustainability: from theory to practices. Springer, Singapore, pp 267–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7553-8_14
Sarkar A, Ghosh PK, Pramanik K, Mitra S, Soren T, Pandey S, Mondal MH, Maiti TK (2018) A halotolerant Enterobacter sp. displaying ACC deaminase activity promotes rice seedling growth under salt stress. Res Microbiol 169(1):20–32
Turkan I (2018) ROS and RNS: key signalling molecules in plants. J Exp Bot 69(14):3313–3315
Upadhyay SK, Singh JS, Saxena AK, Singh DP (2012) Impact of PGPR inoculation on growth and antioxidant status of wheat under saline conditions. Plant Biol 14(4):605–611
Wang F, Cui X, Sun Y, Dong C-H (2013) Ethylene signaling and regulation in plant growth and stress responses. Plant Cell Rep 32(7):1099–1109
Win KT, Tanaka F, Okazaki K, Ohwaki Y (2018) The ACC deaminase expressing endophyte Pseudomonas spp. enhances NaCl stress tolerance by reducing stress-related ethylene production, resulting in improved growth, photosynthetic performance, and ionic balance in tomato plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 127:599–607
Wolf B (1982) A comprehensive system of leaf analyses and its use for diagnosing crop nutrient status. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 13(12):1035–1059
Yang C, Ma B, He S-J, Xiong Q, Duan K-X, Yin C-C, Chen H, Lu X, Chen S-Y, Zhang J-S (2015) MAOHUZI6/ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE1 and ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE2 regulate ethylene response of roots and coleoptiles and negatively affect salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol 169(1):148–165
Yang H, Yu C, Yan J, Wang X, Chen F, Zhao Y, Wei W (2014) Overexpression of the Jatropha curcas JcERF1 gene coding an AP2/ERF-type transcription factor increases tolerance to salt in transgenic tobacco. Biochemistry (Moscow) 79(11):1226–1236
Zamani Babgohari M, Ebrahimie E, Niazi A (2014) In silico analysis of high affinity potassium transporter (HKT) isoforms in different plants. Aquat Biosyst 10(1):9
Zerrouk IZ, Rahmoune B, Khelifi L, Mounir K, Baluska F, Ludwig-Müller J (2019) Algerian Sahara PGPR confers maize root tolerance to salt and aluminum toxicity via ACC deaminase and IAA. Acta Physiol Plant 41(6):91
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Tianjin Rice Industry Technology System Innovation Team Construction (ITTRRS2018007), Tianjin Science and Technology Research and Development Plan Project (19YFZCSN00280), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81901502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Q. Wang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, J., Yuan, D., Jin, C. et al. Enhancement of growth and salt tolerance of rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) by regulating ethylene production with a novel halotolerant PGPR strain Glutamicibacter sp. YD01 containing ACC deaminase activity. Acta Physiol Plant 42, 42 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-3034-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-3034-3