Abstract
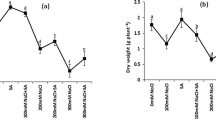
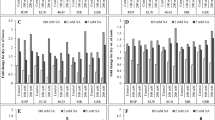
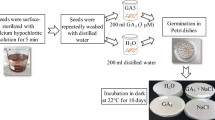
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a critical role in developmental and signal transduction processes during seed germination and early seedling establishment stages. Higher concentrations of ROS are known to have detrimental effects when the plant is under salt stress. In the present study, we aimed to test the early (1 h) and late (48 h) response of enzyme-driven ROS detoxification system in six peanut genotypes under salt stress at early seedling stage. Salt stress was imposed with three treatment concentrations of NaCl (50, 100 and 200 mM NaCl), all of which showed a reduction in seed germination and seedling vigour index. The 200 mM NaCl stress showed severe reduction of growth, while 100 mM NaCl stress resulted in rapid increase in O ·−2 and H2O2 contents. The O ·−2 content increased twofold in sensitive genotypes after 1 h of stress, whereas the tolerant genotypes showed ~ 60% rise. A prompt rise (> 50-fold) in SOD transcript was occurred within 1 h of salt stress in the tolerant genotypes (early response). But induction in SOD activity was observed only after 48 h of salt stress (late response). After 48 h of salt stress, the tolerant genotypes showed greater induction of POD activity, whereas in the sensitive genotypes CAT activity was more pronounced. We found POD and CAT played a greater role in H2O2 detoxification in tolerant and sensitive genotypes, respectively, during longer duration of the stress. This study summarizes the selective induction of different components of antioxidant enzyme system and their role in cellular fine tuning of ROS level in peanut under salt stress during seedling establishment stage.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- G p :
-
Germination percentage
- G r :
-
Germination rate
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- MGT:
-
Mean germination time
- SVI:
-
Seedling vigour index
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
References
Abogadallah GM (2010) Antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 5:369–374
Abogadallah GM, Serag MM, Quick WP (2010) Fine and coarse regulation of reactive oxygen species in the salt tolerant mutants of barnyard grass and their wild-type parents under salt stress. Physiol Plantarum 138:60–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2009.01297.x
Adem G, Roy SJ, Zhou M, Bowman JP, Shabala S (2014) Evaluating contribution of ionic, osmotic and oxidative stress components towards salinity tolerance in barley. BMC Plant Biol 14:113. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-113
Aebi H (1984) “[13] Catalase in vitro,” in Methods in Enzymology (Elsevier), 121-126
Ahmad P, Abdel Latef AA, Hashem A, Abd Allah EF, Gucel S, Tran LSP (2016) Nitric oxide mitigates salt stress by regulating levels of osmolytes and antioxidant enzymes in chickpea. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00347
Almansouri M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (2001) Effect of salt and osmotic stresses on germination in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.). Plant Soil 231:243–254. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010378409663
Amor NB, Jiménez A, Megdiche W, Lundqvist M, Sevilla F, Abdelly C (2006) Response of antioxidant systems to NaCl stress in the halophyte Cakile maritima. Physiol Plant 126:446–457
Arnao MB, Cano A, Acosta M (2001) The hydrophilic and lipophilic contribution to total antioxidant activity. Food Chem 73:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00324-1
Bailly C, Kranner I (2011) Methods for analyses of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in relation to seed longevity and germination. Methods Mol Biol 773:343–367
Bailly C, El-Maarouf-Bouteau H, Corbineau F (2008) From intracellular signaling networks to cell death: the dual role of reactive oxygen species in seed physiology. C R Biol 331:806–814
Bajji M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (2002) Osmotic and ionic effects of NaCl on germination, early seedling growth, and ion content of Atriplex halimus (Chenopodiaceae). Can J Bot 80:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1139/b02-008
Bor M, Özdemir F, Türkan I (2003) The effect of salt stress on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in leaves of sugar beet Beta vulgaris L. and wild beet Beta maritima L. Plant Sci 164:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00338-2
Bose J, Rodrigo-Moreno A, Shabala S (2014) ROS homeostasis in halophytes in the context of salinity stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 65:1241–1257. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert430
Cantliffe DJ (1991) Benzyladenine in the priming solution reduces thermo-dormancy of lettuce seeds. Hort Technol 1:95–97
Castillo FI, Penel I, Greppin H (1984) Peroxidase release induced by ozone in Sedum album leaves. Plant Physiol 74:846–851
Chaitanya KSK, Naithani SC (1994) Role of superoxide, lipid peroxidation and superoxide dismutase in membrane perturbation during loss of viability in seeds of Shorea robusta Gaertn. f. New Phytol 126:623–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1994.tb02957.x
Chakraborty K, Singh AL, Kalariya KA, Goswami N, Zala PV (2015) Physiological responses of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars to water deficit stress: status of oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activities. Acta Bot Croat 74:5. https://doi.org/10.1515/botcro-2015-0011
Chakraborty K, Bhaduri D, Meena HN, Kalariya K (2016a) External potassium (K+) application improves salinity tolerance by promoting Na+-exclusion, K+-accumulation and osmotic adjustment in contrasting peanut cultivars. Plant Phyiol Bioch 103:43–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.02.039
Chakraborty K, Bishi SK, Goswami N, Singh AL, Zala PV (2016b) Differential fine-regulation of enzyme driven ROS detoxification network imparts salt tolerance in contrasting peanut genotypes. Environ Exp Bot 128:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.05.001
Chakraborty K, Bose J, Shabala L, Shabala S (2016c) Difference in root K+ retention ability and reduced sensitivity of K+-permeable channels to reactive oxygen species confer differential salt tolerance in three Brassica species. J Exp Bot 67:461–4625. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw236
Cuartero J, Bolarin MC, Asins MJ, Moreno V (2006) Increasing salt tolerance in the tomato. J Exp Bot 57:1045–1058
de Azevedo Neto AD, Prisco JT, Enéas-Filho J, de Abreu CEB, Gomes-Filho E (2006) Effect of salt stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive maize genotypes. Environ Exp Bot 56:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.01.008
Demiral T, Turkan I (2005) Comparative lipid peroxidation, antioxidant defense systems and proline content in roots of two rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 53:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.03.017
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. Environ Exp Bot 32:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/32.1.93
Fan HF, Du CX, Ding L, Xu YL (2013) Effects of nitric oxide on the germination of cucumber seeds and antioxidant enzymes under salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 35:2707–2719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1303-0
Galvan-Ampudia CS, Julkowska MM, Darwish E, Gandullo J, Korver RA, Brunoud G, Michel AH, Teun M, Teva V, Christa T (2013) Halotropism is a response of plant roots to avoid a saline environment. Curr Biol 23:2044–2050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.08.042
Gruber BD, Giehl RFH, Friedel S, von Wiren N (2013) Plasticity of the Arabidopsis root system under nutrient deficiencies. Plant Physiol 163:161–179. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.218453
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
ISTA (2003) ISTA handbook on seedling evaluation. 3rd ed. International Seed Testing Association
Julkowska MM, Hoefsloot HCJ, Mol S, Feron R, de Boer GJ, Haring MA, Christa T (2014) Capturing Arabidopsis root architecture dynamics with ROOT-FIT reveals diversity in responses to salinity. Plant Phyiol 166:1387–1402. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.248963
Katembe W (1998) Effect of salinity on germination and seedling growth of two Atriplex species (Chenopodiaceae). Ann Bot 82:167–175. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1998.0663
Lafitte HR, Ismail A, Bennett J (2004) Abiotic stress tolerance in rice for Asia: progress and the future. In: Fischer T, Turner N, Angus J, McIntyre L, Robertson M, Borrell A (eds) New directions for a diverse planet: Proceedings of the 4th International Crop Science Congress. Brisbane, Australia
Läuchli A, Grattan SR (2007) Plant growth and development under salinity stress. In: Jenks MA, Hasegawa PM, Jain SM (eds) Advances in molecular breeding toward drought and salt tolerant crops. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–32
Levinsh G (2006) Biological basis of biological diversity: physiological adaptations of plants to heterogeneous habitats along a sea coast. Acta Univ Latv 710:53–79
Leymarie J, Vitkauskaité G, Hoang HH, Gendreau E, Chazoule V, Meimoun P, Corbineau F, El-Maarouf-Bouteau H, Bailly H (2011) Role of reactive oxygen species in the regulation of Arabidopsis seed dormancy. Plant Cell Physiol 53:96–106
Luo Q, Yu B, Liu Y (2005) Differential sensitivity to chloride and sodium ions in seedlings of Glycine max and G. soja under NaCl stress. J Plant Phy 162:1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2004.11.008
Machado Neto NB, Saturnino SM, Bomfim DC, Custódio CC (2004) Water stress induced by mannitol and sodium chloride in soybean cultivars. Braz Arch Biol Tech. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132004000400004
Miller GAD, Suzuki N, Sultan C, Mittler R (2010) Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant, Cell Environ 33:453–467
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02312-9
Mittova V (2004) Salinity up-regulates the antioxidative system in root mitochondria and peroxisomes of the wild salt-tolerant tomato species Lycopersicon pennellii. J Exp Bot 55:1105–1113. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh113
Mittova V, Tal M, Volokita M, Guy M (2002) Salt stress induces up-regulation of an efficient chloroplast antioxidant system in the salt-tolerant wild tomato species Lycopersicon pennellii but not in the cultivated species. Physiol Plant 115:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1150309.x
Müller K, Linkies A, Vreeburg RA, Fry SC, Krieger-Liszkay A, Leubner-Metzger G (2009) In vivo cell wall loosening by hydroxyl radicals during cress seed germination and elongation growth. Plant Physiol 150:1855–1865
Nakano Y, Asada K (1980) Spinach chloroplasts scavenge hydrogen peroxide on illumination. Plant Cell Physiol 21:1295–1307. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076105
Negrão S, Schmöckel SM, Tester M (2017) Evaluating physiological responses of plants to salinity stress. Ann Bot 119:1–11
Parihar P, Singh S, Singh R, Singh VP, Prasad SM (2015) Effect of salinity stress on plants and its tolerance strategies: a review. Environ Sci Pollut 22:4056–4075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3739-1
Rao MV, Paliyath G, Ormrod DP, Murr DP, Watkins CB (1997) Influence of salicylic acid on H2O2 production, oxidative stress, and H2O2-metabolizing enzymes (salicylic acid-mediated oxidative damage requires H2O2). Plant Physiol 115:137–149
Sandalio LM, Palma JM, Del Rio LA (1987) Localization of manganese superoxide dismutase in peroxisomes isolated from Pisum sativum L. Plant Sci 51:1–8
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Singh R, Issar D, Zala PV, Nautiyal PC (2007) Variation in sensitivity to salinity in groundnut cultivars during seed germination and early seedling growth. J SAT Agric Res 5(1)
Singh AL, Hariprassana K, Solanki RM (2008) Screening and selection of groundnut genotypes for tolerance of soil salinity. Aust J Crop Sci 1:69–77
Smith IK, Vierheller TL, Thorne CA (1988) Assay of glutathione reductase in crude tissue homogenates using 5,5′-dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid). Ann Biochem 175:408–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(88)90564-7
Werner JE, Finkelstein RR (1995) Arabidopsis mutants with reduced response to NaCl and osmotic stress. Physiol Plantarum 93:659–666. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1995.tb05114.x
Zhang X, Yin H, Chen S, He J, Guo S (2014) Changes in antioxidant enzyme activity and transcript levels of related genes in Limonium sinense Kuntze seedlings under NaCl stress. J Chem 1:6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/749047
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from Director, ICAR-DGR for the present study. We also acknowledge the technical support of Mr. CB Patel during the experiment. We acknowledge the help received from Ms. Ivanah Oliver, University of New England, Armidale (Australia) for necessary English editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Wojtaszek.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, K., Bishi, S.K., Goswami, N. et al. Salinity-induced changes in seed germination and the expression profile of antioxidant enzymes in peanut as early and late responses in emerging radicles. Acta Physiol Plant 41, 134 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2927-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2927-5