Abstract
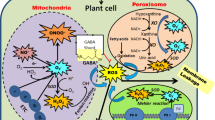
Environmental stimuli such as UV, paraquat, and H2O2 can induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and impair the cellular redox equilibrium. ROS are controlled by a complex network of ROS metabolizing enzymes and play a major signaling role in different compartments of plants cell. GABA, alanine, and glutamate are all GABA shunt-related metabolites that are accumulated in response to oxidative stress. In this study, T-DNA insertion mutants of 7 calmodulin genes (CAM) in Arabidopsis thaliana were used to determine the role of specific CaM in tolerance of plants to oxidative stress induced by ultraviolet (UVA and UVB) treatments. Seedlings growth, seeds germination, reactive oxygen species accumulation, and changes in GABA shunt metabolites levels were determined. Only cam4 mutants showed significant tolerance to UVA and UVB treatments over the other cam mutants during seed germination. Oxidative damage measured as level of MDA caused by UV treatment was found in root and shoot tissues of cam1, cam4, cam5-4, and cam6-1 of Arabidopsis cam mutants. In response to UVA treatment, the shunt metabolites accumulated in root and shoot tissues after 30 min. As a result of UVB treatment, GABA accumulated after 30 min while alanine and glutamate accumulated after 60 min only in root tissue. There was a significant increase in GABA, alanine, and glutamate levels after 30, 60, and 90 min UVA treatments in root and shoot tissue of cam1, cam3-2, cam4, cam5-1, cam5-2, cam6-1, cam7-1 mutants. On the other hand, all shunt metabolites levels were significantly accumulated in root of cam1, cam4, cam5-4, and cam6-1 and only in shoot tissue of cam5-4 and cam6-1 mutants in response to 30, 60, and 90 min UVB treatment. Our results show that cam mutants are sensitive to induced-oxidative stress in response to both UV treatments especially cam1, cam4, cam5-4, cam6-1, and cam7-1 mutants for seed germination and ROS accumulation. Accumulation of GABA shunt metabolites under induced-oxidative stress via UV treatments demonstrates that GABA shunt pathway, GABA metabolites accumulation, and Ca+2/CaM-mediating signaling mechanisms are major components of antioxidant machinery associated with ROS scavenging, H2O2 equilibrium, maintaining balance of cellular redox state, and acquiring tolerance in cellular signaling in response to UV stress in Arabidopsis seedlings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAM :
-
Calmodulin gene
- CaM:
-
Calmodulin protein
- Ca+2/CaM:
-
Calcium/calmodulin complex
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- GAD:
-
Glutamate decarboxylase
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric Acid
- MDA:
-
Malonaledehyde
- NAD+ :
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NADP+ :
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbiturate reactive substances
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet light (UVA or UVB)
References
AL-Quraan NA, Locy RD, Singh NK (2011) Implications of paraquat and hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress treatments on the GABA shunt pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin mutants. Plant Biotech Rep 5:225–234
AL-Quraan NA, Locy RD, Singh NK (2012) Heat and cold stresses phenotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin mutants: regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid shunt pathway under temperature stress. Int J Plant Biology 3(e2):9–17
Alscher RG, Donahue JH, Cramer CL (1997) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants: relationships in green cells. Physiol Plant 100:224–233
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Aurisano N, Bertani A, Reggiani R (1995) Involvement of calcium and calmodulin in protein and amino acid metabolism in rice roots under anoxia. Plant Cell Physiol 36:1525–1529
Bailly C (2004) Active oxygen species and antioxidants in seed biology. Seed Sci Res 14:93–107
Bailly C, Benamar A, Corbineau F, Côme D (2000) Antioxidant systems in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) seeds as affected by priming. Seed Sci Res 10:35–42
Bailly C, Bogatek-Leszczynska R, Côme D, Corbineau F (2002) Changes in activities of antioxidant enzymes and lipoxygenase during growth of sunflower seedlings from seeds of different vigour. Seed Sci Res 12:47–55
Bailly C, Leymarie J, Lehner A, Rousseau S, Côme D, Corbineau F (2004) Catalase activity and expression in developing sunflower seeds as related to drying. J Exp Bot 55:475–483
Bergmeyer HU (1983) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol I, 2nd edn. Weinheim:Verlag Chemie, Academic Press, New York, p 427
Bohnert HJ, Nelson DE, Jensen RG (1995) Adaptation to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 7:1099–1111
Bolwell GP, Bindschedler LV, Blee KA, Butt VS, Davies DR (2002) The apoplastic oxidative burst in response to biotic stress in plants: a three-component system. J Exp Bot 53:1367–1376
Bouche N, Fromm H (2004) GABA in plants: just a metabolite? Trend Plant Sci 9:110–115
Bouche N, Fait A, Bouchez D, Moller SG, Fromm H (2003) Mitochondrial succinic-semialdehyde dehydrogenase of the gamma-aminobutyrate shunt is required to restrict levels of reactive oxygen intermediates in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6843–6848
Bouche N, Fait A, Zik M, Fromm H (2004) The root-specific glutamate decarboxylase (gad1) is essential for sustaining gaba level in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 55:315–325
Bouche N, Yellin A, Snedden WA, Fromm H (2005) Plant-specific calmodulin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:435–466
Chen YL, Huang RF, Xiao YM, Lu P, Chen J, Wang XC (2004) Extracellular calmodulin-induced stomatal closure is mediated by heterotrimeric G protein and H2O2. Plant Physiol 136:4096–4103
Coleman ST, Fang TK, Rovinsky SA, Turano FJ, Moye-Rowley WS (2001) Expression of glutamate decarboxylase homologue is required for normal oxidative stress tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 276:244–250
Cuin TA, Shabala S (2007) Compatible solutes reduce ROS-induced potassium efflux in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell Environ 30:875–885
Desikan RA, Mackerness S, Hancock JT, Neill SJ (2001) Regulation of Arabidopsis transcriptome by oxidative stress. Plant Physiol 127:159–172
Dröge W (2002) Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev 82:47–95
Du L, Poovaiah BW (2005) Ca+2/calmodulin is critical for brassinosteroid biosynthesis and plant growth. Nature 437:741–745
Fait A, Yellin A, Fromm H (2005) GABA shunt deficiencies and accumulation of reactive oxygen intermediates: insight from Arabidopsis mutants. FEBS Lett 579:415–420
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2003) Redox sensing and signalling associated with reactive oxygen in chloroplasts, peroxisomes and mitochondria. Physiol Plant 119:355–364
Foyer CH, LopezDelgado H, Dat JF, Scott IM (1997) Hydrogen peroxide-and glutathione-associated mechanisms of acclimatory stress tolerance and signalling. Physiol Plant 100:241–254
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hendricks SB, Taylorson RB (1975) Breaking of seed dormancy by catalase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:306–309
Hong ZL, Lakkineni K, Zhang ZM, Verma DPS (2000) Removal of feedback inhibition of pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase results in increased proline accumulation and protection of plants from osmotic stress. Plant Physiol 122:1129–1136
Hu X, Jiang M, Zhang J, Zhang A, Lin F, Tan M (2007) Calcium-calmodulin is required for abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defense and functions both upstream and downstream of H2O2 production in leaves of maize (Zea mays) plants. New Phytol 173:27–38
Kalbina I, Strid A (2006) Supplementary ultraviolet-b irradiation reveals differences in stress responses between Arabidopsis thaliana ecotypes. Plant Cell Environ 29:754–763
Kwon SI, Lee H, An CS (2007) Differential expression of three catalase genes in the small radish (Rhaphanus sativus L. var. sativus). Mol Cells 24:37–44
Locy RD, Wu S-J, Bisnette J, Barger TW, McNabb D, Zik M, Fromm H, Singh NK, Cherry JH (2000) The regulation of GABA accumulation by heat stress in Arabidopsis. In: Cherry JH, Locy RD, Rychter A (eds) Plant tolerance to abiotic stresses in agriculture: role of genetic engineering. NATO advanced research workshop series in cell biology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 39–53
Ludewig F, Hüser A, Fromm H, Beauclair L, Bouché N (2008) Mutants of GABA transaminase (POP2) suppress the severe phenotype of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ssadh) mutants in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 3(10) e3383:1–10
Miller G, Suzuki N, Rizhsky L, Hegie A, Koussevitzky S, Mittler R (2007) Double mutants deficient in cytosolic and thylakoid ascorbate peroxidase reveal a complex mode of interaction between reactive oxygen species, plant development, and response to abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol 144:1777–1785
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trend Plant Sci 7:405–410
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trend Plant Sci 9:490–498
Moller IM (2001) Plant mitochondria and oxidative stress: electron transport, NADPH turnover, and metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:561–591
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:472–497
Murgia I, Tarantino D, Vannini C, Bracale M, Carravieri S, Soave C (2004) Arabidopsis thaliana plants overexpressing thylakoidal ascorbate peroxidase show increased resistance to paraquat-induced photooxidative stress and to nitric oxide-induced cell death. Plant J 38:940–953
Neill SJ, Desikan RA, Hancock JT (2002) Hydrogen peroxide signalling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:388–395
Niyogi KK (1999) Photoprotection revisited: genetic and molecular approaches. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:333–359
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:249–279
Oracz K, El-Maarouf BH, Farrant JM, Cooper K, Belghazi M, Job C, Job D, Corbineau F, Bailly C (2007a) ROS production and protein oxidation as a novel mechanism for seed dormancy alleviation. Plant J 50:452–465
Oracz K, Bailly C, Gniazdowska A, Côme D, Corbineau F, Bogatek R (2007b) Induction of oxidative stress by sunflower phytotoxins in germinating mustard seeds. J Chem Ecol 33:251–264
Oracz K, El-Maarouf BH, Kranner I, Bogatek R, Corbineau F, Bailly C (2009) The mechanisms involved in seed dormancy alleviation by hydrogen cyanide unravel the role of reactive oxygen species as key factors of cellular signaling during germination. Plant Physiol 150:494–505
Oracz K, Voegele A, Tarkowska´ D, Jacquemoud D, Tureckova´ V, Urbanova´ T, Strnad M, Sliwinska E, Leubner-Metzger G (2012) Myrigalone A inhibits Lepidium sativum seed germination by interference with gibberellin metabolism and apoplastic superoxide production required for embryo extension growth and endosperm rupture. Plant Cell Physiol 53:81–95
Pitzschke A, Forzani C, Hirt H (2006) Reactive oxygen species signaling in plants. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1757–1764
Prasad TK, Anderson MD, Martin BA, Stewart CR (1994) Evidence for chilling-induced oxidative stress in maize seedlings and a regulatory role for hydrogen peroxide. Plant Cell 6:65–74
Reggiani R, Cantu CA, Brambilla I, Bertani A (1988) Accumulation and interconversion of amino acids in rice roots under anoxia. Plant Cell Physiol 29:981–987
Rentel MC, Knight MR (2004) Oxidtaive stress-induced calcium signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 135:1471–1479
Rhoads DM, Umbach AL, Subbaiah CC, Siedow JN (2006) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: contribution to oxidative stress and interorganellar signaling. Plant Physiol 141:357–366
Rogozhin VV, Kuriliuk TT, Filippova NP (2000) Change in the reaction of the antioxidant system of wheat sprouts after UV-irradiation of seeds [article in Russian]. Biofizika 45:730–736
Scandalios JG (2005) Oxidative stress: molecular perception and transduction of signal triggering antioxidant gene defenses. Braz J Med Biol Res 38:995–1014
Serraj R, Shelp BJ, Sinclair T (1998) Accumulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid in nodulated soybean in response to drought stress. Physiol Plant 102:79–86
Shelp BJ, Walton CS, Snedden WA, Tuin LG, Oresnik IJ, Layzell DB (1995) GABA shunt In developing soybean seeds is associated with hypoxia. Physiol Plant 94:219–228
Shelp BJ, Bown AW, McLean MD (1999) Metabolism and functions of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Trend Plant Sci 4:446–452
Simontacchi M, Caro A, Fraga CG, Puntarulo S (1993) Oxidative stress affects [alpha]-tocopherol content in soybean embryonic axes upon imbibition and following germination. Plant Physiol 103:949–953
Snedden WA, Koutsia N, Baum G, Fromm H (1996) Activation of a recombinant Petunia glutamate decarboxylase by calcium/calmodulin binding domain. J Biol Chem 271:4148–4153
Turano FJ, Fang TK (1998) Characterization of two glutamate decarboxylase cDNA clones from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 117:1411–1421
Vranova E, Inze D, Van Breusegem F (2002) Signal transduction during oxidative stress. J Exp Bot 53:1227–1236
Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2002) Hydrogen peroxide homeostasis: activation of plant catalase by calcium/calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4097–4102
Yevtushenko DP, McLean MD, Peiris S, Van Cauwenberghe OR, Shelp BJ (2003) Calcium/calmodulin activation of two divergent glutamate decarboxylases from tobacco. J Exp Bot 54:2001–2002
Zhang G, Bown AW (1997) The rapid determination of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Phytochemistry 44:1007–1009
Zik M, Arazi T, Snedden WA, Fromm H (1998) Two isoforms of glutamate decarboxylase in Arabidopsis are regulated by calcium/calmodulin and differ in organ distribution. Plant Mol Biol 37:967–975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Z. Miszalski.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AL-Quraan, N.A. GABA shunt deficiencies and accumulation of reactive oxygen species under UV treatments: insight from Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin mutants. Acta Physiol Plant 37, 86 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1836-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1836-5