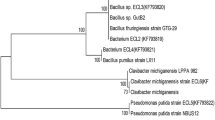
Abstract
Bacillus methylotrophicus CKAM obtained from root endosphere of healthy apple trees was selected on the basis of higher P-solubilisation (687 mg/L), nitrogenase activity (237.6 ηmole C2H4 h−1mg−1 protein), IAA (34 µg/mL), siderophore unit (96.4 %) and antifungal activity against F. oxysporum (88.22 %), Phytophthora sp. (70.00 %), D. necatrix (61.73 %), S. rolfsii (44.54 %) and P. aphanidermatum (62.56 %). We investigated the ability of isolate CKAM to solubilise insoluble P via two possible mechanisms: proton excretion by ammonium assimilation and organic acid production. There were no clear differences in pH and P-solubilisation between glucose–ammonium and glucose–nitrate media. P-solubilisation was significantly promoted with glucose compared with fructose. HPLC study showed that isolate CKAM produced mainly gluconic and oxalic acids with small amounts of 2-ketogluconic, formic acids. During the culture, the pH was reduced with increase in gluconic acid concentration and was inversely correlated with soluble P concentration. Analysis of antifungal compounds involved in their antagonistic activity showed that isolate CKAM produced chitinase, proteases, pectinase and the antibiotic lipopeptides surfactin, fengycin and iturin A. It was notable that isolate CKAM exhibited highest protection against S. rolfsii (58 %) followed by F. oxysporum (54.5 %), D. necatrix (52.7 %), P. aphanidermatum (36.3 %) and Phytophthora sp. (21.8 %) in biocontrol trials using the pathosystem tomato. Remarkable increase was observed in seed germination (27.07 %), shoot length (42.33 %) root length (52.6 %), shoot dry weight (62.01 %) and root dry weight (45.7 %) of tomato under net house condition. Isolate CKAM possessed traits related to plant growth promotion, therefore, could be a potential candidate for the development of biofertiliser or biocontrol agent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Babi AA, Anderson JD (1973) Vigour determination in soyabean seed by multiple criteria. Crop Sci 13:630–633
Ali B, Sabri AN, Hasnain S (2010) Rhizobacterial potential to alter auxin content and growth of Vigna radiata (L.). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:1379–1384
Altschul SF, Thomas LM, Alejandro AS, Jinghui Z (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSIBLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Baker AW, Schippers B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas spp. mediated plant growth stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457
Bakthavatchalu S, Shivakumar S, Sullia SB (2012) Identification of multi-trait PGPR isolates and evaluation of their potential as biocontrol agents. Acta Biologica Indica 1:61–67
Cazorla FM, Romero D, Garcıa Perez A, Lugtenberg BJJ, de Vicente, Bloemberg G (2007a) Isolation and characterization of antagonistic Bacillus subtilis strains from the avocado rhizoplane displaying biocontrol activity. J Appl Microbiol 103:1950–1959
Cazorla FM, Romero D, Garcia AP, Lugtenberg BJJ, Vincente A, Bloemberg G (2007b) Isolation and characterization of antagonistic B. subtilis strains from the avocado rhizoplane displaying biocontrol activity. J Appl Microbiol 103:1950–1959
Chatli Anshu S, Beri V, Sidhu BS (2008) Isolation and characterisation of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms from the cold desert habitat of Salix alba Linn. in trans Himalayan region of Himachal Pradesh. Indian J Microbiol 48:267–273
Chen YP, Rekha PD, Arun AB, Shen FT, Lai WA (2006) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tri-calcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl Soil Ecol 34:33–41
Collins DP, Jacobsen BJ (2003) Optimizing a Bacillus subtilis isolate for biological control of sugar beet cercospora leaf spot. Biol Control 26:153–161
Del Campillo SE, Van der Zee S, Torrent J (1999) Modeling long-term phosphorus leaching and changes in phosphorus fertility in excessively fertilized acid sandy soils. Eur J Soil Sci 50:391–399
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Glick BR (1995) The enhancement of plant growth by free living bacteria. Can J Microbiol 41:109–117
Hardy RWF, Holsten RD, Jacken EK (1968) The acetylene ethylene assay for N2- fixation-laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol 43:118–127
Jackson ML (1973) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall, New Delhi, pp 49–95
Jeffries S, Gianinazzi S, Perotto S, Turnau K, Barea JM (2003) The contribution of arbuscular mycorhizal fungi in sustainable maintenance of plant health and soil fertility. Biol Fertil Soils 37:1–16
Joshi R, McSpadden Gardener B (2006) Identification of genes associated with pathogen inhibition in different strains B. subtilis. Phytopathol 96:145–154
Kumar RS, Ayyadurai N, Pandiaraja P, Reddy AV, Venkateswarlu Y, Sakthivel OPN (2005) Characterization of antifungal metabolite produced by a new strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa PUPa3 that exhibits broad-spectrum antifungal activity and biofertilizing traits. J Appl Microbiol 98:145–154
Kumar D, Shivay YS, Dhar S, Kumar C, Prasad R (2013) Rhizospheric flora and the influence of agronomic practices on them—a review. Proc Natl Acad Sci India 83:1–14
McSpadden Gardener BB (2004) Ecology of Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp. in agricultural systems. Phytopathol 94:1252–1258
Mehta P, Chauhan A, Mahajan R, Mahajan PK, Shirkot CK (2010) Strain of Bacillus circulans isolated from apple rhizosphere showing plant growth promoting potential. Curr Sci 98:538–542
Mehta P, Walia A, Chauhan A, Shirkot CK (2013) Phosphate solubilization and plant growth promoting potential by stress tolerant Bacillus sp. isolated from rhizosphere of apple orchards in trans Himalayan region of Himachal Pradesh. Ann Appl Biol 163:430–443
Omar SA (1998) The role of rock-phosphate-solubilizing fungi and vesicular-arbuscular-mycorrhiza (VAM) in growth of wheat plants fertilized with rock phosphate. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:211–218
Ongena M, Jacques P, Toure Y, Destain J, Jabrane A, Thonart P (2005) Involvement of fengycin-type lipopeptides in the multifaceted biocontrol potential of Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:29–38
Park KH, Lee CY, Son HJ (2009) Mechanism of insoluble phosphate solubilization by Pseudomonas fluorescens RAF15 isolated from ginseng rhizosphere and its plant growth promoting activities. Lett Appl Microbiol 49:222–228
Patel DK, Archana G, Kumar GN (2008) Variation in the nature of organic acid secretion and mineral phosphate solubilization by Citrobacter sp. DHRSS in the presence of different sugars. Curr Microbiol 56:168–174
Penrose DM, Glick BR (2003) Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol Plant 118:10–15
Powers EM (1995) Efficacy of the Ryu nonstaining KOH technique for rapidly determining gram reactions of foodborne and water-borne bacteria and yeast. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3758–3765
Romero D, Perez-Garcia A, Rivera ME, Cazorla FM, de Vicente A (2004a) Isolation and evaluation of antagonistic bacteria towards the curcurbit powdery mildew fungus Podosphaera fusca. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:263–269
Romero D, Perez-Garcia A, Rivera ME, Cazorla FM, de Vicente A (2004b) Isolation and evaluation of antagonistic bacteria towards the curcurbit powdery mildew fungus Podosphaera fusca. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:263–269
Romero D, de Vicente A, Rakotoaly RV, Dufour SE, Veening JW, Arrebola E, Cazorla FM, Kuipers OP (2007) The iturin and fengycin families of lipopeptides are key factors in antagonism of Bacillus subtilis towards Podosphaera fusca. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:430–440
Roos W, Luckner M (1984) Relationships between protonextrusion and fluxes of ammonium ions and organic acid in Penicillium cyclopium. J Gen Microbiol 130:1007–1014
Sasser M, Wichman MD (1991) Identification of microorganisms through use of gas chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography. In: Balows A, Hausler WJ, Herrman KL, Isenberg HD, Shadomy HJ (eds) Manual of clinical microbiology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Stein T (2005) Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: structures, syntheses and specific functions. Mol Microbiol 56:845–857
Sundara Rao WVB, Sinha MK (1963) Phosphate dissolving microorganisms in the soil and rhizosphere. Indian J Agric Sci 33:272–278
Vassilev N, Vassileva M, Nikolaeva I (2006) Simultaneous P-solubilizing and biocontrol activity of microorganisms: potentials and future trends. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:137–144
Walia A, Mehta P, Chauhan A, Shirkot CK (2013) Effect of Bacillus subtilis strain CKT1 as inoculum on growth of tomato seedlings under net house conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci India. doi:10.1007/s40011-013-0189-3
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank ICAR (AINP on Soil Biodiversity & Biofertilizer), New Delhi, India, for providing the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Krolicka.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehta, P., Walia, A., Kakkar, N. et al. Tricalcium phosphate solubilisation by new endophyte Bacillus methylotrophicus CKAM isolated from apple root endosphere and its plant growth-promoting activities. Acta Physiol Plant 36, 2033–2045 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1581-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1581-1