Abstract
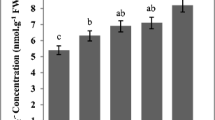
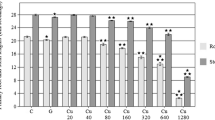
The effects of exposure of barley seedlings to different concentration (10−6 to 10−3 mol/l) of paraquat on seed germination, root length, antioxidant enzyme activities and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) profiles were investigated. The results revealed that malondialdehyde content significantly increased by exposing paraquat in a concentration-dependent manner (p < 0.05). A significant increase in peroxidase and catalase activities in seedlings was observed with increased concentration of paraquat, and then decreased when the value reached 10−3 mol/l, whereas the activities of superoxide dismutase gradually increased with increasing paraquat concentration. Germination and root elongation also decreased with the increase of paraquat concentration. On the other hand, alterations of DNA in barley seedlings were detected using RAPD technique. The changes occurring in RAPD profiles of seedlings following paraquat treatment included loss of bands found in DNA of control seedlings and appearance of new bands. The results of this study showed that paraquat induced DNA damage in a dose-dependent manner and the root cells of barley showed a defense against paraquat-induced oxidative stress by enhancing their antioxidant activities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Pandey V (2004) Antioxidant enzyme responses to NaCl stress in Cassia angustifoli. Biol Plant 48:555–560
Aksakal O, Aygun-Erturk F, Sunar S, Bozari S, Agar G (2013) Assessment of genotoxic effects of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on maize by using RAPD analysis. Ind Crop Prod 42:552–557
Asada K (1992) Ascobate peroxidase a hydrogen peroxide scavenging enzyme in plants. Physiol Plant 85:235–241
Bozari S, Aksakal O (2012) Application of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) to detect genotoxic effect of trifluralin on maize (Zea mays). Drug Chem Toxicol. doi:10.3109/01480545.2012.660948
Bus JS, Gibson JE (1984) Paraquat: model for oxidant-initiated toxicity. Environ Health Perspect 55:37–46
Cantavenera MJ, Catanzaro I, Loddo V, Palmisano L, Sciandrello G (2007) Photocatalytic degradation of paraquat and genotoxicity of its intermediate products. J Photochem Photobiol A 185:277–282
Chen Q, Niu Y, Zhang R, Guo H, Gao Y, Li Y, Liu R (2010) The toxic influence of paraquat on hippocampus of mice: involvement of oxidative stress. Neurotoxicology 31:310–316
D’souza UJA, Zain A, Raju S (2005) Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects in the bone marrow of rats exposed to a low dose of paraquat via the dermal route. Mutat Res 581:187–190
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Remião F, Carmo H, Duarte JA, Sanchez Navarro A, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2006) Paraquat exposure as an etiological factor of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 27:1110–1122
Havir EA, McHale NA (1987) Biochemical and development characterization of multiple forms of catalase in tobacco leaves. Plant Physiol 84:450–455
Holgrem A (2003) Redox regulation of genes and cell function. Crit Rev Oxid Stress Ag 2:102–111
Jalel CA, Manivannan P, Sankar B, Kishorekumar A, Panneerselvam R (2007) Calcium chloride effects on salinity induced oxidative stress, proline metabolism and indole alkaloid accumulation in Catharanthus roseus. C R Biol 330:674–683
Jovtchev G, Gateva S, Stergios M, Kulekova S (2009) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of paraquat in Hordeum vulgare and human lymphocytes in vitro. Environ Toxicol 25(3):295–303
Lin A, Zhang X, Zhu Y-G, Zhao F-J (2008) Arsenate-induced toxicity: effects on antioxidative enzymes and DNA damage in Vicia faba. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:413–419
Liu W, Yang YS, Zhou QX, Xie LJ, Li P, Sun T (2007) Impact assessment of cadmium contamination on rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings at molecular and population levels using multiple biomarkers. Chemosphere 67:1155–1163
Liu W, Yang YS, Li PJ, Zhou QX, Xie LJ, Han YP (2009) Risk assessment of cadmium-contaminated soil on plant DNA damage using RAPD and physiological indices. J Hazard Mater 161:878–883
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants, and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Mohammadi-Bardbori A, Ghazi-Khansari M (2008) Alternative electron acceptors: proposed mechanism of paraquat mitochondrial toxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26:1–5
Mohan BS, Hosetti BB (1997) Potential phytotoxicity of lead and cadmium to Lemna minor grown in sewage stabilization ponds. Environ Pollut 98:233–238
Suntres ZE (2002) Role of antioxidants in paraquat toxicity. Toxicology 180:65–77
Xue-mei Q, Pei-jun L, Wan L, Li-jing X (2006) Multiple biomarkers response in maize (Zea mays L.) during exposure to copper. J Environ Sci 18(6):1182–1188
Ye Y, Tam NFY, Wong YS, Lu CY (2003) Growth and physiological responses of two mangrove species (Bruguiera gymnorrhiza and Kandelia candel) to waterlogging. Environ Exp Bot 49:209–221
Zega G, Candiani S, Groppelli S, De Bernardi F, Pennati R (2010) Neurotoxic effect of the herbicide paraquat on ascidian larvae. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 29:24–31
Zhiyia R, Haowen Y (2004) A method for genotoxicity detection using random amplified polymorphism DNA with Danio rerio. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 58:96–103
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. Schleiff.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aksakal, O. Assessment of paraquat genotoxicity on barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings using molecular and biochemical parameters. Acta Physiol Plant 35, 2281–2287 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1265-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1265-2