Abstract
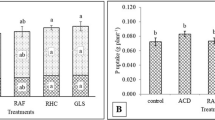
The arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) status and root phosphatase activities were studied in four vegetative Carica papaya L. varieties viz., CO-1, CO-2, Honey Dew and Washington. Standard techniques were used to ascertain information on spore density and species diversity of AM fungi. Although in case of estimation of root colonization and root phosphatase activities, the existing methods were slightly modified. Root colonization and spore density of AM fungi along with root phosphatase (acid and alkaline) activities varied significantly in four papaya varieties. The present study recorded higher acid root phosphatase activity when compared with alkaline root phosphatase activity under P-deficient, acidic soil conditions. The present study revealed that the root colonization of AM fungi influenced acid root phosphatase activity positively and significantly under P-deficient, acidic soil conditions. A total of 11 species of AM fungi belonging to five genera viz., Acaulospora, Dentiscutata, Gigaspora, Glomus and Racocetra were recovered from the rhizosphere of four papaya varieties.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen EB, Swenson W, Querejeta JI, Egerton-Waburton LM, Treseder KK et al (2003) Ecology of mycorrhizae: a conceptual framework for complex interactions among plants and fungi. Ann Rev Phytopathol 41:271–303
Allen MF, Sexton JC, Moore TS Jr, Christensen M et al (2006) Influence of phosphate source on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae of Bouteloua gracilis. New Phytol 87(4):687–694
Barea JM (1991) Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae as modifiers of soil fertility. In: Stewart BA (ed) Advances in soil science. Springer, New York, pp 1–40
Beena KR, Raviraja NS, Arun AD, Sridhar KR et al (2000) Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on coastal sand dunes of the West Coast of India. Curr Sci 79(10):1459–1465
Bethlenfalvay GJ, Linderman RG (1992) Mycorrhizae in sustainable agriculture. ASA Special Publication, Madison, p 124
Bethlenfalvay GJ, Schüepp H (1994) Arbuscular mycorrhizas and agrosystem stability. In: Gianinazzi S, Scheüpp H (eds) Impact of arbuscular mycorrhiza on sustainable agriculture and natural ecosystems. ALS, Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 117–131
Bonfante-Fasalo P (1984) Anatomy and morphology. In: Powell CL, Bagyaraj DJ (eds) VA mycorrhiza. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, pp 5–33
Bray RH, Kurtz LT (1945) Determination of total organic carbon and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci 59:39–45
Chauhan BS, Stewart JWB, Paul EA (1981) Effect of labile inorganic phosphate status and organic carbon additions on the microbial uptake of phosphorus in soils. Can J Soil Sci 61:373–385
Clarholm M, Rosengren-Brinck U (1995) Phosphorous and nitrogen fertilization of a Norway spruce forest-effect on needle concentrations and acid phosphatase activity in the humus layer. Plant Soil 175:239–249
Duff SMG, Sarath G, Plaxton WC (1994) The role of acid phosphatase in plant phosphorus metabolism. Physiol Plant 90:791–800
Fries LLM, Pacovsky RS, Safir GR, Kaminski J et al (1998) Phosphorus effect on phosphatase activity in endomycorrhizal maize. Physiol Plant 103(2):162–171
García-Gómez R, Chávez-Espinosa J, Mejía-Chávez A, Durán BC et al (2002) Short term effects of Glomus claroideum and Azospirillum brasilense on growth and root acid phosphatase activity of Carica papaya L. under phosphorus stress. Rev Latinoam Microbiol 44(1):31–37
Gaur A, Adholeya A (1994) Estimation of VAM spores in the soil—a modified method. Mycorrhiza News 6(1):10–11
Gemma JN, Koske RE, Carreiro M et al (1989) Seasonal dynamics of selected species of VA mycorrhizal fungi in a sand dune. Mycol Res 92:317–321
Gerdemann JW, Nicolson TH (1963) Spore density of Endogone species extracted from soil wet sieving and decanting. Trans Bri Mycol Soc 46:235–244
Gianinazzi S, Trouvelot A, Gianiazzi-Pearson V et al (1990) Role and use of mycorrhizas in horticulture crop production. XXII. International Horticulture Congress Florence, pp 25–30
Gilmore AE (1968) Phycomycetous mycorrhizal organisms collected by open pot cultures. Hilgardia 39:87–105
Giovannetti M, Mosse B (1980) An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytol 84:489–500
Goldstein AH, Baertlein DA, Mcdaniel RG (1988) Phosphate starvation inducible metabolism in Lycopersicon esculentum. I. Excretion of acid phosphatase by tomato plants and suspension-cultured cells. Plant Physiol 87:711–715
Hanway JJ, Heidel H (1952) Soil analysis method as used in Iowa State College Soil Testing Laboratory. Iowa Agric 57:1–31
Helal HM (1990) Varietal differences in root phosphatase activity as related to the utilization of organic phosphates. Plant Soil 123:161–163
Helal HM, Sauerbeck DR (1984) Influence of plant roots on carbon and phosphorus metabolism in soil. Plant Soil 76:175–182
Helal HM, Sauerbeck DR (1987) Direct and indirect influences of plant roots on organic matter and phosphorus turnover in soil. INTECOL Bull 15:49–58
Huttová J, Tamás L, Mistrík I (2002) Aluminum induced acid phosphatase activity in roots of Al-sensitive and Al-tolerant barley varieties. Rostlinná Výroba 48(12):556–559
Jackson ML (1971) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall, New Delhi
Joner EJ, Van Aarle IM, Vosatka M et al (2000) Phosphatase activity of extra- radical arbuscular mycorrhizal hyphae: a review. Plant Soil 226:199–210
Kapoor A, Singh VP, Mukerji KG (1989) Studies on the phosphatase of mycorrhizal and non mycorrhizal Trigonella roots. In: Mahadeva A, Raman A, Natarajan K et al (eds) Mycorrhizae for Green Asia. CAS, Madras, pp 125–127
Karangiannidis N, Velmis D, Stravropoulos N et al (1997) Root colonization and spore population by VA-mycorrhizal fungi in four grapevine rootstock. Vitis 36(2):57–60
Kesava Rao PS, Tilak KVBR, Arunachalam V et al (1990) Genetic variation of mycorrhiza-dependent phosphate mobilization in ground nut (Arachis hypogea L.). Plant Soil 121:291–294
Khade SW, Rodrigues BF (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with some pteridophytes from Western Ghat region of Goa. Trop Eco 43(2):251–256
Khade SW, Rodrigues BF (2003) Occurrence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in tree species from Western Ghats of Goa India. J Trop For Sci 15(2):320–331
Khade SW, Rodrigues BF (2008a) Ecology of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with Carica papaya L. in agro-based ecosystem of Goa, India. Trop Subtrop Agroecosyst 8:265–278
Khade SW, Rodrigues BF (2008b) Spatial variations in arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi associated with Carica papaya L. in a tropical agro-based ecosystem. Bio Agric Hort 26:149–174
Khade SW, Rodrigues BF (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with varieties of Carica papaya L. in tropical agro-based ecosystem of Goa, India. Trop Subtrop Agroecosyst 10(3):369–381
Khade SW, Bukhari MJ, Jaiswal V, Gaonkar UC, Rodrigues BF et al (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal status of medicinal plants: a field survey of AM fungal association in shrubs and trees. J Eco Tax Bot 26(3):571–578
Koske RE (1987) Distribution of VA mycorrhizal fungi along a latitudinal temperature gradient. Mycologia 79:55–68
Koske RE, Tessier B (1983) A convenient permanent slide mounting medium. Mycol Soc Am Newslett 34:59
Krishna KR, Bagyaraj DJ, Papavinashasundaram KG et al (1983) Acid and alkaline phosphatase activities in mycorrhizal and uninfected roots of Arachis hypogaea L. Ann Bot 51:551–553
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of DPTA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Am Soil Sci Soc J 42:421–488
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Fan AL, Randall RJ et al (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Machado CTT, Furlani AMC (2004) Root phosphatase activity, plant growth and phosphorus accumulation of maize genotypes. Sci Agric 61(2):216–223
Mc Gonigle TP, Miller MH, Evans DG, Fairchild GL, Swan JA et al (1990) A new method which gives an objective measure of colonization of roots by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 115:495–501
McArthur DAJ, Knowles NR (1993) Influence of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the response of potato to phosphorus deficiency. Plant Physiol 101(1):147–160
McLachlan KE (1980) Acid phosphate activity of intact roots and phosphorous nutrition in plants II: variation among wheat roots. Aust J Agric Res 31:441–448
Menge JA (1982) Utilization of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in agriculture. Can J Bot 61:1015–1024
Mercy MA, Shivashanker G, Bagyaraj DJ et al (1990) Mycorrhizal colonization in cowpea is dependent and heritable. Plant Soil 121:291–294
Mosse B (1975) A microbiologist’s view of root anatomy. In: Walker N (ed) Soil microbiology: a critical review. Butterworths, London, pp 39–66
Muthukumar T, Udaiyan K (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal composition in semi-arid soils of Western Ghats, southern India. Curr Sci 82(6):625–628
Oehl F, de Souza FA, Sieverding E (2008) Revision of Scutellospora and description of five new genera and three new families in the arbuscular mycorrhiza-forming Glomeromycetes. Mycotaxon 106:311–360
Phillips JM, Hayman DS (1970) Improved procedure for clearing roots and staining of mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans Bri Mycol Soc 55:158–161
Raju PS, Clark RB, Duncan JR, Maranville JW et al (1990) Benefit and cost analysis and phosphorus efficiency of VA-mycorrhizal fungi colonization with Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) genotypes grown at varied phosphorus levels. Plant Soil 124:199–204
Rhodes LH, Gerdemann JW (1975) Phosphate uptake zones of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal onions. New Phytol 75:555–561
Rubio R, Moraga E, Borie F et al (1990) Acid phosphatase activity and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection associated with roots of 4 wheat cultivars. J Plant Nutr 13(5):585–598
Schalamuk S, Velazquez H, Cabello CM et al (2006) Fungal spore diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with spring wheat: effects of tillage. Mycologia 98(1):16–22
Schenck NC, Perez Y (1990) Manual for identification of VA mycorrhizal fungi. INVAM, University of Florida, Gainesville, USA, pp 1–283
Smith SE, Walker NA (1981) A qualitative study of mycorrhizal plants in Trifolium: separate determination of the rates of infection and of mycelial growth. New Phytol 89:225–240
Speir TW, Ross DJ (1978) Soil phosphatase and sulphatase. In: Burns RG (ed) Soil enzymes. Academic Press, New York, USA, pp 197–250
St. John TV, Koske RE (1988) Statistical treatment of endogonaceous spore counts. Trans Bri Mycol Soc 91:117–121
Sukhada M (1992) Effect of VAM inoculation on plant growth, nutrient level and root phosphatase activity in papaya (Carica papaya cv. Coorg Honey Dew). Fert Res 31:263–267
Sylvia DM (1986) Spatial and temporal distribution of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with Uniola paniculata in Florida foredunes. Mycologia 78:728–734
Tews LL, Koske RE (1986) Towards a sampling strategy for vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizas. Trans Bri Mycol Soc 87(8):353–358
Acknowledgments
Shri Waman M. Khade Ex-director of Agriculture Department and Directorate of Agriculture, State Government of Goa are thanked for their assistance to carry out research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. Filek.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khade, S.W., Rodrigues, B.F. & Sharma, P.K. Arbuscular mycorrhizal status and root phosphatase activities in vegetative Carica papaya L. varieties. Acta Physiol Plant 32, 565–574 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0433-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0433-x