Abstract
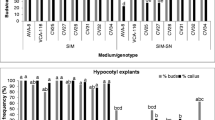
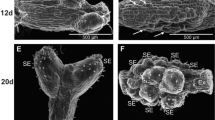
Flower buds, cotyledons and hypocotyls of Pharbitis nil were used as plant material. Flower buds (1–2 mm long) were excised from 3-week-old plants, grown in soil. Cotyledons of 7-day-old sterile seedlings were cut into 25 mm2 squares cotyledons whereas hypocotyls were cut to 1 mm long fragments. Explants were transferred into Petri dishes containing the Murashige and Skoog medium (MS), supplemented with either BA (11 µM·L−1) alone or BA (22 µM·L−1) and NAA (0.55 µM·L−1), and different sugars: sucrose, fructose, glucose, mannose or sorbitol (autoclaved or filter-sterilized). Addition of glucose instead of sucrose to the medium stimulated the induction of callus on flower buds and cotyledonary explants, but inhibited its growth on fragments of hypocotyls. The medium supplemented with fructose (especially filter-sterilized) stimulated the development of flower elements. Organogenesis of shoots and roots on explants was also observed. Flower buds and hypocotyls were able to regenerate both organs. Addition of fructose or glucose to the medium stimulated the organogenesis of shoots, whereas root organogenesis was inhibited on all explants used. Sorbitol strongly inhibited both induction of callus and organogenesis on all explants used.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
6-benzyladenine
- NAA:
-
naphthaleneacetic acid
References
Bach A., Pawłowska B. 1993. Effect of type of carbohydrates in regulation of Hyacinthus orientalis L. in long-term cultures. Folia Horti., 2: 3–11.
Bach A., Świderski A., 2000. The effect of light quality on organogenesis of Hyacinthus orientalis L. in vitro. Acta Biol. Cracoviensia, 42: 115–120.
Blanc G., Lardet L., Martin A., Jacob J.L., Carron M.P., 2002. Differential carbohydrate metabolism conducts morphogenesis in embryogenic callus of Havea brasiliensis (Müll. Arg.). J. Exp. Botany, 53: 1453–1462.
Bogunia H., Przywara L., 1999. Rola cukrowców w roślinnych kulturach in vitro. (Sugars in plant tissue culture.) Wiad. Bot., 43: 25–36.
Borkowska B., Szczerba J., 1995. Influence of different carbon sources on invertase activity and growth of sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) shoot cultures. J. Exp. Bot., 42: 911–915.
Chu C.C., Hill R.D., Brule-Babel A.L., 1990. High frequency of pollen embryoid formation and plant regeneration in Triticum aestvum L. on monosaccharide containing media. Plant Sci., 66: 255–262.
Cuenca B., Vietez A.M., 2000. Infuence of carbon sourse on shoot multiplication and adventitious bud regeneration in in vitro beech cultures. Plant Growth Regul., 32: 1–12.
Durdan S.F., Herbert R.J., Rogers H.J., Francis D., 2000. The determination time of the carpel whorl is differentially sensitive to carbohydrate supply in Pharbitis nil. Plant Physiol,. 123: 189–200.
El-Bakry A.A., 2002. Effect of genotype, growth regulators, carbon source, and pH on shoot induction and plant regeneration in tomato. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. — Plant, 38: 501–507.
Fuentes S.R.L., Calheiros M.B.P., Manetti-Filho J., Vieira L.G.E., 2000. The effects of silver nitrate and different carbohydrate sources on somatic embriogenesis in Coffea canephora. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 60: 5–13.
Fotopoulos S., Sotiropoulos T.E., 2004. In vitro propagation of the peach rootstock: the effect of different carbon sources and types of sealing material on rooting. Biol. Plant., 48: 629–631.
Gibson S.I., 2000. Plant sugar-response pathway. Part of complex regulatory web. Plant Physiol., 124: 1532–1539.
Harada H., Murai Y., 1996. Micropropagation of Prunus mume. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 46: 265–267.
Hita O., Gallego P., Villalobos N., Lanas I., Blazquez A., Martin J.P., Fernandez J., Martin L., Guerra H., 2003. Improvement of somatic embriogenesis in Medicago arborea. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 72: 13–18.
Jain N. Babbar S.B., 2003. Effect of carbon source on the shoot proliferation potential of epicotyl explants of Syzygium cuminii. Biol. Plant., 47: 133–136.
Jang J.C., Leon P., Zhou L., Sheen J., 1997. Hexokinase as a sugar sensor in higher plant. Plant Cell, 9: 5–19.
Kumria R., Waie B., Rajam M.V., 2001. Plant regeneration from transformed embryogenic callus of an elite indica rice via Agrobacterium. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 67: 63–71.
Kutschera U., Heiderich A., 2002. Sucrose metabolism and cellulose biosynthesis in sunflower hypocotyls. Physial. Plant., 114: 372–379.
Lemos E.E.P., Baker D.A., 1998. Shoot regeneration in response to carbon source on internodal explants of Annona muricata L. Plant Growth Regul., 25: 105–112.
Murashige T., Skoog, F., 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant., 15: 473–497.
Nowak B., Miczyński K., Hudy L., 2004. Sugar uptake and utilisation during adventitious buds differentiation on in vitro leaf explants of ‘Wegirka Zwykła’ plum (Prunus domestica) Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 76: 255–260.
Peterson K.K., Hansen J., Krogstrup P., 1999. Significance of different carbon source and sterilization methods on callus induction and plant regeneration of Miscanthus x ogiformis Honda ‘Giganteus’. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 58: 189–197.
Romano A., Noronha C., Martins-Loucao M.A., 1995. Role of carbohydrates in micropropagation of cork oak. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 40:159–167.
Sairam R.V., Franclin G., Hassel R., Smith B., Meeker K., Kashikar N., Parani M., Abes D.A., Ismail S., Berry K. Goldman S.L. 2003. A study on the effect of genotypes, plant growth regulatoes and sugars in promoting plant regeneration via organogenesis from soybean cotyledonary nodal callus. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 75: 79–85.
Shibli R., Ajlouni M.M., 2000. Somatic embriogenesis in the endemic black iris. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 61: 15–21.
Swedlund B., Locy R.D., 1993. Sorbitol as the primary carbon source for the growth of embryogenic callus of maize. Plant Physiol., 103: 1339–1346.
Tang W., 2000. High-frequency plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis and organogenesis and in vitro flowering of regenerated plantlets in Panax ginseng. Plant Cell Rep., 19: 727–732.
Trejgell A., Tretyn A., Nicos D., 1998. Attemt at regeneration of Pharbitis nil from fragments of vegetative organs. Acta Physiol. Plant., 20: 161–166.
Trejgell A., Wójciak A., Tretyn A., 2002. Photoperiodically independent flowering of Pharbitis nil plants regenerated from flower buds. In vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.- Plant, 38: 564–568.
Xiao W., Sheen J., Jang J-Ch., 2000. The role of hexokinase in plant sugar signal transduction and growth and development. Plant Mol. Biol., 44: 451–461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alina, T., Magdalena, J. & Andrzej, T. The effect of carbon source on callus induction and regeneration ability in Pharbitis nil . Acta Physiol Plant 28, 619–626 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-006-0058-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-006-0058-2