Abstract
Objective
To observe the clinical efficacy of long-time needle retaining at Baihui (GV20) on post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) and its effects on the cognitive ability and living ability of the patients.
Methods
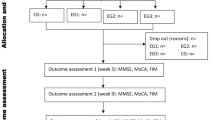
A total of 62 PSCI patients were divided into a control group and an observation group by the random number table method, with 31 cases in each group. The control group was treated with routine treatment for stroke in the recovery period plus cognitive training. The observation group received additional acupuncture at Baihui (GV20) with long-time needle retaining based on the same intervention in the control group. The Montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA) was used to evaluate the cognitive ability of patients. The activities of daily living (ADL) scale was used to evaluate the living ability of patients. And the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) scale was used to evaluate the mental state, concentration, language, and abstraction cognition of patients. After 4 weeks, the curative efficacy was observed, and the scores of cognitive level, living ability, mental state and concentration, language, and abstraction understanding ability were compared between the two groups.
Results
During the trial, 1 patient in each group dropped out due to personal reasons and was unable to continue the treatment. After 4 weeks of treatment, the total effective rate was 83.3% in the observation group and 66.7% in the control group, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05); the scores of MoCA, ADL, and MMSE, and scores of concentration, language ability, and abstraction understanding ability were all increased, and were statistically different from those before treatment in each group (P<0.05); the scores in the observation group were all higher than those in the control group, and the differences between the groups were statistically significant (P<0.05).
Conclusion
On the basis of routine treatment and cognitive training, the clinical efficacy of additional acupuncture at Baihui (GV20) with long-time needle retaining in the treatment of PSCI is better than that of routine treatment plus cognitive training; the treatment can better improve the cognitive function and mental state of patients, and improve their living ability.
摘要
目的
观察针刺百会穴久留针治疗中风后认知障碍(PSCI)的临床疗效, 以及对患者认知和生活能力的影响。
方法
将62例PSCI患者以随机数字表法分为对照组和观察组, 每组31例。对照组接受常规中风恢复期治疗联合认知训练, 观察组在对照组干预基础上加用针刺百会穴久留针。治疗前后采用蒙特利尔认知评估量表(MoCA)评估患者的认知水平; 采用日常生活活动(ADL)量表评估患者生活能力; 采用简易智力状态评价量表(MMSE)评估患者精神状态及注意力、语言能力和抽象认知能力。治疗4周后观察两组疗效; 比较两组认知水平、生活能力、精神状态以及注意力、语言、抽象理解等评分。
结果
研究过程中两组各有1例因个人原因无法继续治疗而退出研究。治疗4周后, 观察组总有效率为83.3%, 对照组为66.7%, 两组差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 两组MoCA、ADL、MMSE以及注意力、语言能力、抽象理解能力评分均增加, 与本组治疗前均有统计学差异(P<0.05), 且观察组各项评分均高于对照组, 组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
结论
在常规治疗及认知训练基础上加用针刺百会穴久留针治疗PSCI的临床疗效优于常规治疗联合认知训练, 可更好地改善患者认知功能和精神状态, 提高患者的生活能力。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SONG Y Y. Effect of acupuncture on blood lipid level in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Zhongguo Yejin Gongye Yixue Zazhi, 2018, 35(5): 596–597.
HUANG J, LI R Q, WU M L, LIU R C, FENG X D. Effects of electroacupuncture at Shenting and Baihui acupoints on learning and memory ability of rats with ischemia reperfusion and expression of autophagy related proteins. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2019, 37(4): 838–841.
BAN W G, TENG X Y, GONG F F, LU L N, XU W T, QI H. Effect of puncturing the thirteen ghost points combined with cluster needling at the scalp acupoints on the expression of miRNA-335 in patients with post-stroke cognitive impairment. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2021, 40(12): 1395–1400.
WANG H L, CUI Y X, HU F M, LIU G H, DUAN H B, YUAN C X. Observation on the efficacy of strengthened early shallow surround needling at Baihui acupoint in the treatment of depression after ischemic stroke. Xiandai Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2020, 29(4): 363–366.
JIANG X, CHEN S X, JI J. Effect of Xinglou Chengqi decoction on cognitive impairment in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke. Zhongguo Xiandai Yisheng, 2021, 59(34): 136–139.
YANG Q L, YU W J, ZHANG Z X, LI P, LÜ Q W, HU Z J. Advances in modern rehabilitation treatment of cognitive impairment after stroke. Anmo Yu Kangfu Yixue, 2022, 13(9): 72–76.
ZHU M Y, LU Y, DAI X Y, LIU Y B. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke cognitive impairment. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi, 2021, 36(12): 1555–1560.
WANG L, WANG Z X, SU L, SHI L Y. Regularity of acupoint selection in treatment of post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) with acupuncture in last 15 years based on data mining. Shijie Zhongyiyao, 2022, 17(3): 413–417, 423.
WANG X D, TAN T, MA H X, CHEN Y Q. Meta-analysis of pressing moxibustion at Baihui of vertigo. Zhongguo Yixue Chuangxin, 2022, 19(8): 160–165.
WANG K, DONG Q. Experts consensus on post-stroke cognitive impairment management 2021 Chinese society of vascular cognitive impairment. Zhongguo Cuzhong Zazhi, 2021, 16(4): 376–389.
China Stroke Association Round Table Expert Group on Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Research. Expert consensus on research on prevention and treatment of post-stroke cognitive impairment in China. Zhongguo Cuzhong Zazhi, 2020, 15(2): 158–166.
JI S Z, JIN X L, HAO Y, SHEN W, LIANG X, WANG J W, ZHAO J Y, ZHAO J J, CAO X L, ZHANG X Z, HOU X B, WANG S J, ZHANG H, YANG J, WANG L L, HU H, LIN A J, TIAN J B, WU Y Q, WU H, ZHANG Y L. Characteristic of change in cognitive function of stroke patients with NIHSS of 0 point and analysis on TCM syndrome element. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2016, 31(5): 1812–1815.
RONG Y H, TENG J. Discussion on YU Chang’s academic ideas of stroke disease and modern clinical application. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jizheng, 2022, 31(2): 345–347, 354.
WANG R, ZHANG R L. The effect of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with rehabilitation training on the sequelae of stroke and the effect of sleep quality. Shijie Shuimian Yixue Zazhi, 2022, 9(1): 55–56.
YANG F, LUO K T, ZHU J H, XU Y M. Effect of long-time needle retaining at Baihui (GV20) on cognitive impairment in post-stroke patients. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017, 15(6): 398–402.
CHEN L, JIAO P, LI F H. Acupuncture at Baihui, Shenting point and rehabilitation training for post-stroke cognitive dysfunction. Zhongguo Laonian Baojian Yixue, 2020, 18(2): 11–13.
CHEN X M, PANG L N, WANG Z F. Hippocampal anti-inflammatory effect of electroacupuncture at Baihui and Shenting on cognitive dysfunction induced by systemic inflammation. Kangfu Xuebao, 2021, 31(5): 415–419, 424.
QI C H, CUI L H, YUAN Y, TIAN Y, YANG J, XING X, ZHANG S, CHEN Y W. Efficacy observation of long-retaining scalp acupuncture plus interactive training for upper-extremity dysfunction after cerebral stroke. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2021, 19(1): 43–48.
CHEN F Y, LIU X P, BAO Y H, CHU J M, ZHU M, YU J, ZHANG W S. Effect of scalp acupuncture with long needle-retaining duration plus electroacupuncture by Brunnstrom stage on ambulation ability and quality of life in post-stroke hemiplegia. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2018, 37(9): 977–981.
HAN Q C, SUN Z R, YIN H N, LIU Y. Action mechanism of acupuncture in treatment of post-stroke cognitive impairment based on theory of brain-gut axis. Zhongyiyao Xinxi, 2022, 39(4): 10–15, 46.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project of Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (安徽省自然科学基金项目, No. 1808085MH278).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants or their relatives in this study.
Additional information
Author: WANG Jie, M.M., associate chief physician
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhu, T., Zhu, X. et al. Effects of long-time needle retaining at Baihui (GV20) on post-stroke cognitive impairment. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 21, 273–278 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-023-1385-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-023-1385-1
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Point, Baihui (GV20)
- Needle Retaining
- Poststroke Syndrome
- Cognitive Dysfunction
- Cognitive Training
- Activities of Daily Living