Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of the combination of acupuncture and medication on orthostatic hypotension after incomplete cervical spinal cord injury.
Methods
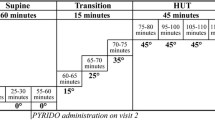
Ninety-two patients with orthostatic hypotension after incomplete cervical spinal cord injury were divided into two groups according to the random number table method, with 46 cases in each group. The control group was treated with oral midodrine hydrochloride on the basis of conventional treatment, and the observation group was treated with acupuncture in addition to the intervention used in the control group. Both groups were treated for 4 weeks. The changes in supine and orthostatic blood pressures, motor and sensory scores, quadriplegic function index score, clinical efficacy, and safety evaluation were observed.
Results
During the treatment, 2 cases dropped out in the observation group, and 3 cases dropped out in the control group. After 4 weeks of treatment, the clinical efficacy of the observation group was better than that of the control group (P<0.05). After treatment, the supine systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure in the two groups had no significant changes (P>0.05), while the orthostatic systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, the motor and sensory scores, and the quadriplegic function index score were significantly higher than those before treatment (P<0.05), and the scores in the observation group were higher than those in the control group (P<0.05). Adverse reactions were mild in both groups.
Conclusion
The combination of acupuncture and medication can significantly improve the orthostatic blood pressure, motor and sensory function and daily living ability of patients with orthostatic hypotension after incomplete cervical spinal cord injury, and it is safe and reliable.
摘要
目的
观察针药并用对颈髓不完全损伤后体位性低血压的影响。
方法
将92例颈髓不完全损伤后体位性低血 压患者根据随机数字表法分为两组, 每组46例。对照组在常规处理基础上采用口服盐酸米多君治疗, 观察组在对照组 干预基础上加用针刺治疗, 两组均治疗4周。观察两组治疗前后平卧位、直立位血压变化, 运动及感觉评分, 四肢瘫 功能指数评分以及临床疗效和安全性评价。
结果
治疗过程中观察组脱落2例, 对照组脱落3例。治疗4周后, 观察组 的临床疗效优于对照组(P<0.05)。治疗后, 两组患者平卧位的收缩压与舒张压未见明显变化(P>0.05), 而直立位的收缩 压和舒张压, 运动及感觉评分, 以及四肢瘫功能指数评分均显著高于本组治疗前(P<0.05), 观察组各项评分均高于对 照组(P<0.05)。两组的不良反应均轻微。
结论
针药并用可以明显提高颈髓不完全损伤后体位性低血压患者的直立位 血压, 运动及感觉功能和日常生活能力, 并且安全可靠。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LIU X L, CHEN Y D, SHU Q F, CAI M. Observation of the efficacy of acupuncture on orthostatic hypotension. Xinnaoxueguanbing Fangzhi, 2018,18(2): 163–171.
LU X L, ZHOU H J, LIU G L, ZHENG Y, HAO C X, ZHANG Y, KANG H Q, WEI B, WANG Y J, YUAN Y. Variation of blood pressure and heart rate after cervical spinal cord injury (review). Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun Yu Shijian, 2014, 20(2): 153–155.
Chinese Association of Orthopedic Surgeons, the Editorial Committee of the “Evidence-based Guideline for the Management of Acute Subaxial Cervical Spine Injury” of Chinese Association of Orthopedic Surgeons. Evidence-based guideline for the management of acute subaxial cervical spine injury. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi, 2019, 57(3): 161–165.
KANG H Q, ZHOU H J, LIU G L, ZHENG Y, HAO C X, ZHANG Y, WEI B, WANG Y J, LU X L, YUAN Y, MENG Q R. Modification and interpretation of the 2019 international standards for neurological classification of spinal cord injury worksheet. Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun Yu Shijian, 2019, 25(8): 983–985.
SHAW B H, GARLAND E M, BLACK B K. Optimal diagnostic thresholds for diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension with a sit-to-stand test. J Hypertens, 2017, 35(5): 1019–1025.
WANG Y X, WANG Y, DONG Y F. Research progress in diagnosis and treatment of orthostatic hypotension. Zhonghua Gaoxueya Zazhi, 2021, 29(10): 923–929.
YAO A M, GUAN H, ZHANG G P, LI X M, HU S J, HE H. A clinical study of the orthostatic hypotension after spinal cord injury. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi, 2005, 20(1): 47–50.
LIU J J, CHENG S M, XIONG Y Q. Research progress of orthostatic hypotension after spinal cord injury of Chinese and Western medicine. Jiangxi Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2022, 34(2): 115–119.
ZHANG X L, ZHANG J, ZHU J P, CHENG Z K, QIAN M H, WANG S Y. Clinical observations on proximate needling plus moxa stick pressure moxibustion for cervical vertigo. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2020, 39(10): 1290–1294.
JI H, LI F, LI T Y. Clinical observation of midodrine hydrochloride in treatment of orthostatic hypotension after incomplete cervical spinal cord injury. Zhongguo Linchuang Yaoxue Zazhi, 2010, 19(2): 74–77.
ZHANG J, HOU P H. Progress of traditional Chinese and Western medicine in the treatment of senile orthostatic hypotension. Zhongri Youhao Yiyuan Xuebao, 2014, 28(6): 361–363.
FAN H, LIN L L, MA S M, SHAO J K, WANG N, YANG J W, LIU C Z. Research progress on the mechanism of acupuncture in treating primary hypertension. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao, 2020, 31(4): 932–935.
DONG X Q, LI X Y, KONG X H, WU L J, HUANG Q F, YANG Y T, YANG L, YANG G, MA X P, SHI J R. Analysis of clinical application patterns in acupuncture-moxibustion treatment of Alzheimer disease. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2020, 16(3): 238–246.
DAI M Y. The present situation of clinical application and study of point Danzhong. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2004, 23(6): 30–31.
XIA Y, CAO Z L, LIU Y H, LOU B D, ZHANG W. Clinical observation on moxibustion therapy plus Tuina in treating children with recurrent respiratory tract infections due to Qi deficiency of spleen and lung. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2021, 19(5): 371–377.
WANG J, WU Z J, CAI R L, HE L, YU Q, LIU L, XU J, HU L. Effects of electroacupuncture at “Xinshu (BL15)-Shenmen (HT7)” on the expression of Glu, Asp and NR1 in the myocardial and hippocampal tissues of acute myocardial ischemia rat. Hunan Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2021, 41(1): 79–84.
ZHENG F Y, CHEN D, WANG C. Heat-sensitive moxibustion combined with Western medication intervening coronary heart disease coupled with left heart dysfunction: a randomized controlled trial. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2020, 39(6): 682–686.
ZHANG W J, CHEN Y G. Effects of acupuncture at Pishu (BL20) on distribution and metabolism of ginsenoside Rg3 in chronic fatigue rats’ model during different times. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2016, 31(4): 1482–1485.
ZHANG Z Y, XU D S, WANG H, SHE C, WANG J, CUI J J, BAI W Z. Neuronal correlation between acupoint Shenshu (Bl23) and the adrenal gland in rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2018, 43(7): 414–418.
ZHANG X L, HAO C H, ZHEN X C, ZHENG L Y, LI C R. Effect of acupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) on the expression of myocardial cells PKA in hemorrhagic hypotension rat. Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2009, 11(7): 194–195.
HUANG J J, YANG Q H, HAN D W, ZHU J, ZHANG L F. Specific research of acupoints to examine the efficacy of pressure that electric acupuncture was induced to hypotension rat of acupuncturing it’s Shuigou, Neiguan and Zusanli. Sichuan Zhongyi, 2009, 27(11): 40–43.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 345 Talent Project of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University (中国医科 大学附属盛京医院 345 优才工程).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the families of each participant.
First Author: LIU Jiye, doctor degree candidate, attending physician
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Meng, H. & Wang, J. Effects of the combination of acupuncture and medication on orthostatic hypotension after incomplete cervical spinal cord injury. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 21, 59–65 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-023-1359-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-023-1359-3
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Yin Needling
- Acupuncture Medication Combined
- Spinal Cord Injuries
- Cervical Cord
- Hypotension, Orthostatic