Abstract
Objective
To observe the effects of electroacupuncture (EA) at Neiguan (PC6) on arrhythmia during acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion and the expression of connexin 43 (Cx43) in rats.
Methods
A total of 40 Sprague-Dawley male rats were used. Ten rats were randomly selected as the blank group, and the remaining 30 rats were randomly divided into a model group and an EA group, with 15 rats in each group. Before modeling, rats in the EA group received one session of EA intervention at bilateral Neiguan (PC6) for 30 min; the other groups were treated with the same grasping and anesthesia for 30 min without intervention. PowerLab physiological recorder was used to record electrocardiograph within 30 min of infarction. After the experiment, cardiac tissue and serum were collected from rats. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was used to observe the morphological changes of myocardial tissue in the ventricular infarction area of rats in each group. The expression of Cx43 protein in the myocardium of each group was detected by Western blotting (WB). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to determine the activity of Na+-K+-ATPase in myocardial tissue and the serum content of endogenous digitalis-like factor (EDLF) in rats.
Results
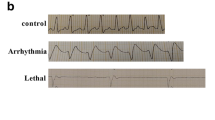
There was no statistical difference in arrhythmia score between the EA group and the model group, but the total duration and average duration of arrhythmia in the EA group were decreased (P<0.01). HE staining showed that compared with the blank group, myocardial cells in the model group were disorganized and seriously damaged. The pathological changes in the EA group were similar to those in the model group, but the damage was relatively minor. The results of WB showed that compared with the blank group, the Cx43 expression in myocardial tissue of the model group was decreased (P<0.01); compared with the model group, the Cx43 expression in the EA group was increased (P<0.01); compared with the blank group, the Na+-K+-ATPase activity in myocardial tissue of the model group was significantly decreased (P<0.01); compared with the model group, the Na+-K+-ATPase activity in the EA group was increased (P<0.01). ELISA results showed that compared with the blank group, the serum EDLF content in the model group was significantly increased (P<0.01); compared with the model group, the EDLF content in the EA group was decreased (P<0.01).
Conclusion
EA at Neiguan (PC6) can delay and reduce the onset of arrhythmia during myocardial infarction in the rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Its mechanism of action may be related to the regulation of the Cx43 expression in myocardial tissue, improvement of the activity of Na+-K+-ATPase in myocardial tissue, and increase in the content of serum EDLF.
摘要
目的
观察电针内关穴对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注急性期心律失常及心室缝隙连接蛋白43(Cx43)表达的影响。
方 法
共选用40只Sprague-Dawley雄性大鼠。随机选取10只作为空白组, 剩余的30只大鼠被随机分为模型组和电针组, 每组15只。电针组大鼠于造模前接受双侧内关单次30 min电针干预; 其余组不予干预但进行同样方法抓取和30 min 的麻醉。使用PowerLab生理记录仪记录梗死30 min内心电图, 实验结束后取大鼠的心肌组织与血清。采用苏木素-伊红(HE)染色观察各组大鼠心室梗死区心肌组织形态变化; 采用免疫印迹法(WB)检测各组大鼠心肌组织中Cx43蛋白 表达情况; 酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)检测大鼠心肌组织Na+-K+-ATP酶活性和大鼠血清内源性类洋地黄因子(EDLF)含 量。
结果
电针组与模型组大鼠心律失常分数无统计学差异, 但电针组心律失常的总时长和平均每次心律失常的持 续时间均减少(P<0.01)。HE染色结果显示, 与空白组相比, 模型组心肌细胞排列紊乱, 损伤严重; 电针组病理变化与模 型组相似, 但损伤程度相对较轻。WB结果显示, 与空白组相比, 模型组大鼠心肌组织Cx43的表达降低(P<0.01); 与模型 组相比, 电针组大鼠Cx43表达升高(P<0.01); 与空白组相比, 模型组大鼠心肌组织Na+-K+-ATP酶活性显著下降(P<0.01); 与模型组相比, 电针组Na+-K+-ATP酶活性有所提高(P<0.01)。ELISA结果显示, 与空白组相比, 模型组大鼠血清EDLF含量 显著提高(P<0.01); 与模型组相比, 电针组EDLF含量下降(P<0.01)。
结论
电针内关穴可延缓和减少心肌缺血再灌注大 鼠心肌梗死期间心律失常的发作; 其作用机制可能与调控心肌组织中Cx43的表达, 改善大鼠心肌组织Na+-K+-ATP酶活 性以及提高血清EDLF含量有关。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
VANWORMER A M, LINDQUIST R, SENDELBACH S E. The effects of acupuncture on cardiac arrhythmias: a literature review. Heart Lung, 2008, 37(6): 425–431.
LIN Y, PENG C, YANG S Q, GU C L, GE D Y, DONG R J, CHENG K. Effect of acupuncture at different layers of local “Neiguan” (PC6) tissue on arrhythmia and expression of myocardial Cx43 in rabbits. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2020, 45(4): 269–274.
CHU S N, TSAI C T, LIN L Y, HUANG S C, CHEN Y S, WANG J K, WU M H, LAI L P, LIN J L. Repolarization alternans and ventricular arrhythmia in a repaired tetralogy of Fallot animal model. J Am Heart Assoc, 2015, 4(12): e002173.
LIU Y, ZHAO H Y, ZHAO H F, LIU M J, ZHANG Z, WANG H, ZHI D M. Application rule of acupuncture for arrhythmia based-on data mining analysis. Changchun Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2016, 32(4): 759–761.
Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on the administration of laboratory animals (draft amendment) (2006-09-30) [2021-08-03] https://www.most.gov.cn/tztg/202108/W020210803581700415090.doc.
LI Z R. Experimental Acupuncture Science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2003.
RAVINGEROVA T, TRIBULOVA N, SLEZAK J, CURTIS M J. Brief, intermediate and prolonged ischemia in the isolated crystalloid perfused rat heart: relationship between susceptibility to arrhythmias and degree of ultrastructural injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 1995, 27(9): 1937–1951.
SKAU E, HENRIKSEN E, WAGNER P, HEDBERG P, SIEGBAHN A, LEPPERT J. GDF-15 and TRAIL-R2 are powerful predictors of long-term mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Prev Cardiol, 2017, 24(15): 1576–1583.
CALLANS D J, MOORE E N, SPEAR J F. Effect of coronary perfusion of heptanol on conduction and ventricular arrhythmias in infarcted canine myocardium. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 1996, 7(12): 1159–1171.
GREENER I D, SASANO T, WAN X, IGARASHI T, STROM M, ROSENBAUM D S, DONAHUE J K. Connexin 43 gene transfer reduces ventricular tachycardia susceptibility after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2012, 60(12): 1103–1110.
CABO C, BOYDEN P A. Heterogeneous gap junction remodeling in reentrant circuits in the epicardial border zone of the healing canine infarct. Cardiovasc Res, 2006, 72(2): 241–249.
BRANDENBURGER T, HUHN R, GALAS A, PANNEN B H, KEITEL V, BARTHEL F, BAUER I, HEINEN A. Remote ischemic preconditioning preserves connexin 43 phosphorylation in the rat heart in vivo. J Transl Med, 2014, 12: 228.
SMYTH J W, SHAW R M. Autoregulation of connexin 43 gap junction formation by internally translated isoforms. Cell Rep, 2013, 5(3): 611–618.
BOENGLER K, SCHULZ R. Connexin 43 and mitochondria in cardiovascular health and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 982: 227–246.
PETERS N S, GREEN C R, POOLE-WILSON P A, SEVERS N J. Cardiac arrhythmogenesis and the gap junction. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 1995, 27(1): 37–44.
AKANUMA S I, HIGASHI H, MARUYAMA S, MURAKAMI K, TACHIKAWA M, KUBO Y, HOSOYA K I. Expression and function of connexin 43 protein in mouse and human retinal pigment epithelial cells as hemichannels and gap junction proteins. Exp Eye Res, 2018, 168: 128–137.
ALESUTAN I, VOELKL J, STÖCKIGT F, MIA S, FEGER M, PRIMESSNIG U, SOPJANI M, MUNOZ C, BORST O, GAWAZ M, PIESKE B, METZLER B, HEINZEL F, SCHRICKEL J W, LANG F. AMP-activated protein kinase α1 regulates cardiac gap junction protein connexin 43 and electrical remodeling following pressure overload. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2015, 35(1): 406–418.
SAVI M, BOCCHI L, ROSSI S, FRATI C, GRAIANI G, LAGRASTA C, MIRAGOLI M, DI PASQUALE E, STIRPARO G G, MASTROTOTARO G, URBANEK K, DE ANGELIS A, MACCHI E, STILLI D, QUAINI F, MUSSO E. Antiarrhythmic effect of growth factor-supplemented cardiac progenitor cells in chronic infarcted heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2016, 310(11): H1622–H1648.
LINDSEY M L, ESCOBAR G P, MUKHERJEE R, GOSHORN D K, SHEATS N J, BRUCE J A, MAINS I M, HENDRICK J K, HEWETT K W, GOURDIE R G, MATRISIAN L M, SPINALE F G. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 affects connexin-43 levels, electrical conduction, and survival after myocardial infarction. Circulation, 2006, 113(25): 2919–2928.
KÖLBEL F, SCHREIBER V. The endogenous digitalis-like factor. Mol Cell Biochem, 1996, 160–161: 111–115.
BAGROV A Y, KUZNETSOVA E A, FEDOROVA O V. Endogenous digoxin-like factor in acute myocardial infarction. J Intern Med, 1994, 235(1): 63–67.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (国家自然科学基金 项目, No. 81974583); Youth Fund Project of Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (南京中医药大学校自然青年基金项目, No. NZY81704169).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria in this experiment.
First Author: XIA Xuefeng, master degree candidate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, X., Xu, S., Lu, S. et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) on arrhythmia during myocardial infarction in a rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 21, 1–9 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-023-1352-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-023-1352-x
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Point, Neiguan (PC6)
- Myocardial Ischemia
- Myocardial Infarction
- Arrhythmia, Cardiac
- Connexin 43
- Rats