Abstract
Objective
To observe the impact of Tiao Shen Tong Du (regulating the mind and unblocking the Governor Vessel) Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage) on neuropsychological development of premature infants, discover effective early-stage intervention techniques, and improve the prognosis of premature infants.
Methods
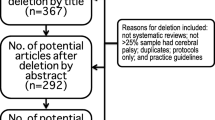
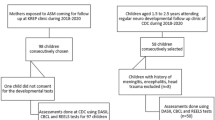
A total of 115 eligible premature infants were recruited and divided into a control group of 59 cases and an observation group of 56 cases based on different interventions. The control group received three-month physical therapy (PT) and conventional early-stage intervention, and the observation group received additional Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina treatment. Before and after treatment and at the one-year follow-up, the Gesell developmental schedule was adopted to evaluate neuropsychological development.
Results
After treatment, the gross motor development quotient (DQ) was higher in the observation group than in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); there were no significant differences in the other four domains between the two groups (P>0.05). At the one-year follow-up, the observation group showed more notable improvements in all five domains’ DQs than the control group, and the between-group differences were statistically significant (P<0.05 or P<0.01).
Conclusion
Based on conventional intervention, Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina can significantly improve the gross motor function of premature infants in the short term, alongside valid long-term efficacy for gross motor function, fine motor function, adaptive behaviors, language, and personal-social behaviors.
摘要
目的
观察调神通督推拿治疗对早产儿神经心理发育的影响, 探索有效的早产儿早期干预技术, 改善早产儿预后。
方法
收集符合入组标准的早产儿115例, 根据干预方式分为对照组59例和观察组56例。对照组接受物理治疗(PT)及常规早期干预治疗, 观察组在对照组治疗基础上加用调神通督推拿治疗, 共治疗3个月。治疗前后及治疗结束后1年随访时采用Gesell发育量表进行神经心理发育评估。
结果
治疗后观察组粗大运动发育商(DQ)高于对照组, 两组差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 其余四个能区两组均无统计学差异(P>0.05)。治疗后1年随访, 观察组五个能区DQ均较对照组改善明显, 组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。
结论
常规干预基础上加用调神通督推拿改善早产儿粗大运动方面的近期疗效明显, 对早产儿粗大运动、精细动作、社会适应、语言及个人社交方面的远期疗效肯定。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CAO Y. Treatment and prognosis of extremely/ultra-premature infants: from enhancing survival rate to emphasizing quality of life. Zhonghua Weichan Yixue Zazhi, 2018, 21(6): 367–375.
JIAN Y, MI H Y, SHI X L, YANG J H, YANG Y M, TIAN Y F. Analysis of risk factors and effects of early intervention on physical and neuro development of premature infants. Kunming Yike Daxue Xuebao, 2020, 41(6): 120–126.
SUN Y, ZHANG Y P, JIA W Z, KUAI Y B, XIAO H Y, LI J L, LI H X. Influence of early intervention on cognitive development of early and late preterm infants. Zhongguo Fuyou Jiankang Yanjiu, 2019, 30(3): 275–278.
CHE D, WU J L. Influence of early implementation of comprehensive training on physical development and developmental quotient of premature infants. Zhongguo Dangdai Yiyao, 2018, 25(35): 92–94.
XIE J S, LI Y Y, YAN X L, XUN J P, JIN B X. Clinical observation on spleen-invigorating and Qi-benefiting pediatric massage for treating recurrent respiratory tract infection in children with cerebral palsy due to Qi deficiency of spleen and lung. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2021, 19(2): 110–116.
LIU Z H, DING J Y. Clinical observation of Chinese massage in the prevention from sequela in high-risk infantile brain injury. Shijie Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2010, 5(2): 130–136.
General Office of the National Health and Family Planning Commission. Healthcare work specifications for premature infants. Zhonghua Weichan Yixue Zazhi, 2017, 20(6): 401406.
LIU M J, WANG J G. Pediatric Massage. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012.
SHEN X Y. Science of Meridians and Acupoints. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2009.
XU S Q, WU X L. Value of Gesell developmental schedule in evaluating the treatment of infantile cerebral palsy. Zhongguo Fuyou Baojian, 2017, 32(8): 1685–1687.
JIANG D Y, WANG J R, LIU C G, LIU C Y, HAN J R. A study of the origin and development of fetal debility. Jiangsu Zhongyiyao, 2020, 52(6): 81–83.
LIU B, YE X L, YE X Y. YE Xinmiao’s experience in treating fetal debility based on syndrome differentiation. Zhejiang Zhongyi Zazhi, 2019, 54(4): 297.
YING Y H, YUAN S, XIAN D. The status and factors of language impairment in children with autism spectrum disorder. Zhongguo Tingli Yuyan Kangfu Kexue Zazhi, 2020, 18(3): 208–210.
WANG Y J, PAN Q, ZHONG N, LU Y, WANG H. Follow-up study on neuropsychological behavior development of preterm and low birth weight infants. Zhonghua Xingwei Yixue Yu Naokexue Zazhi, 2016, 25(9): 842–846.
LI S T, YANG J Z. Study of the experience of LIU Yanling’s experience of treating allergic rhinitis with mind-regulating Zang-Fu-meridian Tuina. Hebei Zhongyiyao Xuebao, 2020, 35(6): 46–49.
YANG JZ, LI S T. Study of Prof. LIU Yanling’s experience of treating infantile eczema with Tuina based on mind-regulating theory. Hebei Zhongyiyao Xuebao, 2021, 36(1): 50–54.
WANG H Q, YAO B Z. Progress of neurodevelopmental characteristics and clinical diagnosis and treatment in premature infants. Zhongguo Ertong Baojian Zazhi, 2021, 29(8): 877–880.
LIU Y X, XU F L, DUAN W L, DONG H F, WANG Y J, ZHANG Y, ZHANG R. A multicenter study of the birth condition of preterm infants and the causes of preterm birth in Henan Province, China. Zhongguo Dangdai Erke Zazhi, 2021, 23(2): 121–126.
HU B, WANG C J, CHANG Q, YANG W, ZHANG Y P. Retrospective study of Gesell development scale of premature infants at different gestational age. Zhongguo Fuyou Jiankang Yanjiu, 2018, 29(9): 1067–1070.
SUN S Y, GAO X T, XIAO L, LIU M N. Gesell mental assessment study of 160 late preterm infants. Shaanxi Yixue Zazhi, 2019, 48(9): 1171–1174.
XU J H, FU J H. Study progress of the long-term prognosis of ultra-premature infants. Zhonghua Xinshengerke Zazhi, 2019, 34(6): 469–472.
LI W, YANG X M, DAI S J, CHEN H. Research progress of long-term neuropsychological development in late preterm infants. Yixue Zongshu, 2019, 25(22): 4468–4472.
ZHANG Y, LI Y H, LIANG J, LI J, JI Y L, GAO H, WANG Z H. Cohort study on neuropsychological development in preterm infants under 2 years old. Zhongguo Ertong Baojian Zazhi, 2020, 28(6): 703–705.
ZHANG X N, YI B. Developmental outcome of premature infants. Zhongguo Ertong Baojian Zazhi, 2020, 28(8): 870–874.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Plan Project of Baoding City, Hebei Province (河北省保定 市科技计划项目, No. 2041ZF142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
First Author: CHEN Jie, M.M., attending physician
Conflict of Interest
There is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the guardians of the recruited children in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Li, X., Chong, Y. et al. Clinical observation of Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina in promoting neuropsychological development of premature infants. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 20, 482–488 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-022-1349-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-022-1349-x