Abstract
Objective
To compare the efficacy difference between moxibustion at sensitized-acupoints and non-sensitized-acupoints using the same group of acupoints.
Methods
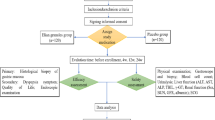
A total of 139 patients with chronic superficial gastritis were divided into a sensitized acupoint group (102 cases) and a non-sensitized acupoint group (37 cases) based on whether acupoint sensitization occurred. The SPSS version 19.0 statistical software propensity score matching function was used to balance the baseline data between the groups. Finally, 29 pairs of matched patients were included, namely 29 cases in the sensitized acupoint group and 29 cases in the non-sensitized acupoint group. Both groups were treated with moxibustion therapy. The treatment lasted for 30 min per time, and was performed every other day for 8 weeks. Changes in the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) symptom score and the short-form 36-item health survey (SF-36) score in both groups were observed before and after treatment, as well as the clinical efficacy.
Results
The covariates of age, course of disease, TCM symptom score and SF-36 score in the two groups were balanced after matching (all P<0.05). After treatment, the total effective rate was 100.0% in the sensitized acupoint group and 79.3% in the non-sensitized acupoint group. The difference in the total effective rate between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.01). After treatment and at the 4-week follow-up, the TCM symptom scores in the sensitized acupoint group were significantly lower than those in the non-sensitized acupoint group (all P<0.01); the SF-36 scores in the sensitized acupoint group were significantly higher than those in the non-sensitized acupoint group (all P<0.01).
Conclusion
With the same group of acupoints, the sensitized acupoints have a better therapeutic effect and long-term efficacy than the non-sensitized acupoints in the treatment of chronic superficial gastritis.
摘要
目的:艾灸同一组腧穴, 比较穴位敏化与穴位非敏化之间的疗效差异。方法:将139 例慢性浅表性胃炎 患者依据是否出现穴位敏化, 分为穴位敏化组(102 例)和穴位非敏化组(37 例)。采用SPSS 19.0 统计软件倾向匹配 评分功能均衡组间基线资料, 最终纳入29 对匹配患者, 即穴位敏化组29 例和穴位非敏化组29 例。两组均采用 艾灸治疗, 每次30 min, 隔日1 次, 连续治疗8 周。观察两组治疗前后中医症状评分和简明健康测量量表(SF-36) 评分的变化, 并观察两组临床疗效。结果:两组患者年龄、病程、中医症状评分和SF-36 评分在组间不均衡的协 变量经匹配后均达到均衡(均P<0.05)。治疗后, 穴位敏化组总有效率为100.0%, 穴位非敏化组总有效率为79.3%, 两组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。治疗后与4 个月随访, 穴位敏化组中医症状评分均显著低于穴位非敏化组 (均P<0.01); 穴位敏化组SF-36 评分均显著高于穴位非敏化组(均P<0.01)。结论:同一组腧穴, 艾灸敏化态穴位 治疗慢性浅表性胃炎患者的临床疗效优于艾灸非敏化态穴位, 且远期疗效更好。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chinese Society of Gastroenterology. Consensus on chronic gastritis in China (2017, Shanghai). Wei Chang Bing Xue, 2017, 22(11): 670–687.
Du KT, Xie H. Clinical study on acupuncture plus moxibustion for chronic superficial gastritis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2015, 34(10): 908–910.
She C. Comparative Study Between Moxibustion and Acupuncture on Gastric Mucosa Protection and Stomach Tissue of Metabonomics in Chronic Atrophic Gastric Rats. Changsha: Doctor Thesis of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2017.
Li Y, Du YH, Shi L, Xiong J, Yang LH, Zhang LL. Acupuncture and moxibustion therapy for chronic superficial gastritis: a meta-analysis. Zhenjiu Linchuang Zazhi, 2011, 27(2): 1–6.
Zhou M, Luo J, Chen RX. Academic thought and clinical application of Deqi (arrival of qi) of moxibustion of Professor Chen Rixin. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2019, 38(11): 1290–1294.
Lin Y, Yang HY. Research progress on heat-sensitive characteristics of acupoints and heat-sensitive moxibustion. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2017, 36(8): 1021–1024.
Ye GP, Huang YF, Zhu DY, Zhang YY, Zhang LY, Wu MX. Exploring on the different state of acupoints and its clinical significance based on “body surface and Zang-fu organs correlation” acupoint sensitization. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2019, 34(5): 2298–2301.
Feng XX, Chen L, Zhang Y, Ma GZ, Ying J, Shen XY. Infrared thermogram of Yangming Meridian acupoints in patients with idiopathic facial paralysis in acute stage. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2019, 38(2): 127–130.
Zhang SY, Li HJ, Zhang L, Zeng YW. Clinical study on heat-sensitive point moxibustion plus external application of Chinese herbal medicine for knee osteoarthritis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2018, 37(11): 1291–1296.
Liu Z, Yang JS, Wu Y, Yang L, Chai X, Xiao T, Chen M, Wang YY. Acupuncture for tobacco cessation: comparison of treatment effects in randomized and cohort study based on propensity score matching. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2019, 34(1): 114–119.
Zhu DC, Leng C, Xiong J, Ye WG. Thermosensitive moxibustion induces a better therapeutic effect in the treatment of facial paralysis patients. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2018, 43(10): 666–669.
Chen RX, Chen MR, Kang MF. Practical Book of Heat-sensitive Moxibustion. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2009: 54–56.
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Guiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 124–129.
Yuan J, Wang N. Study on the efficacy of triple medications (omeprazole + clarithromycin + amoxicillin) plus moxibustion for chronic superficial gastritis. Dangdai Yiyao Luncong, 2018, 16(1): 125–126.
Zeng TK. Therapeutic study on “experienced ten acupoints” therapy plus Banxia Xiexin decoction for chronic superficial gastritis due to dampness-heat of spleen and stomach. Sichuan Zhongyi, 2018, 36(7): 180–182.
Xie H, Liu M, Chang XR, Yan J, Yi Z, Yi SX, Yue ZH, Lin YP, Song J. Clinical observation on therapeutic effects of mild moxibustion in superficial gastritis patients with spleen-stomach deficiency-cold pattern. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2012, 37(4): 318–323.
Du Y, Yi SX, Lin YP, Hong JB, Peng H, Huang Y, Chang XR, Wu HG. Effect of moxibustion on heat shock protein and related inflammatory cells in rats with acute gastric mucosal injury. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2010, 29(5): 269–272.
Li L. Experimental Study on the Mechanism of Electro-acupuncture at Zusanli (ST 36), Zhongwan (CV 12) and Neiguan (PC 6) on Acute Gastric Mucosal Injury in Rats. Shenyang: Master Thesis of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2002.
Ying ZH. Research on Microcirculation of Brain and Tumor in the Field of Integrated TCM and Western Medicine. Jinan: Master Thesis of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007.
Zhu B. The sensitization phenomenon of acupoint and biological significances. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2019, 39(2): 115–121.
Ding N, Jiang J, Wang QX, Qin PP, Xu YY, Liu XX, Hu JT, Li ZG. Research advances in biophysical properties of acupoint sensitization. Zhenjiu Linchuang Zazhi, 2017, 33(2): 69–72.
Gao CM. Explore the treatment outcome of Xue Shuan Xin Mai Ning tablet for coronary heart disease based on propensity score method. Zhonghua Xinzang Yu Xinlü Dianzi Zazhi, 2016, 4(1): 48–49.
Xiong J, Jiao L, Xie DY, Chi ZH, Zhang B, Fu Y, Chen RX. Effects of heat-sensitive moxibustion in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (swelling phase) based on propensity score: a prospective cohort study. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2016, 31(6): 2295–2298.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 国家重点基础研究发展 计划, No. 2015CB554502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patients in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Feng, F., Wang, J. et al. Effect of moxibustion at sensitized-acupoints on quality of life in patients with chronic superficial gastritis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 18, 425–430 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-020-1210-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-020-1210-z
Keywords
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Moxa Stick Moxibustion
- Heat-sensitive Moxibustion
- Gastritis, Superficial
- Quality of Life
- Propensity Score Matching
- Cohort Study