Abstract
Objective
To observe the effects of electroacupuncture (EA) on the protein and gene expressions of Bax, Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in cerebral cortex of type 2 diabetic rats with cognitive impairment (CI), and to explore the mechanism of EA in improving the learning and memory abilities.
Methods
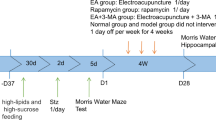
A total of 100 Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were divided into a normal group (n=10) and a model group (n=90) by random number table method. Rats in the model group were intraperitoneally injected with a small dose of streptozotocin (STZ) to establish the type 2 diabetic models, after being fed with high-fat and high-sugar diet for 1 month. Twenty CI rats were selected from the 50 successful model rats by the Morris water maze (MWM) test and randomly divided into a model group and an EA group according to the blood glucose level and MWM data (n=10). Rats in the EA group received acupuncture at Zusanli (ST 36), Neiting (ST 44) and Yishu (Extra), of which Zusanli (ST 36) and Neiting (ST 44) were stimulated by EA apparatus, 20 min/time, once a day for 6 d a week and 4 consecutive weeks. The rats in the model and the normal groups were fixed without treatment. After 4-week treatment, the random blood glucose level of the rats was measured; the learning and memory abilities of rats were measured by MWM; terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay was used to detect apoptotic cells; Western blot (WB) and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) were used to detect the protein and gene expressions of Bax, Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in cerebral cortex.
Results
After modeling, the random blood glucose level and the escape latency tested by MWM were significantly increased, and the number of crossing the platform tested by the MWM was decreased in the EA and model groups, and were significantly different from those in the normal group (P<0.05 or P<0.01), while the differences between the model group and the EA group were not statistically significant (all P>0.05). After 4-week treatment, the random glucose level and the escape latency tested by MWM were significantly increased (both P<0.05), and the number of crossing the original platform tested by the MWM was significantly reduced (P<0.01), the protein and gene expressions of Bax and Caspase-3 were significantly increased (all P<0.001), the protein and gene expressions of Bcl-2 were significantly reduced (both P<0.001), and the number of neuron apoptosis was significantly increased (P<0.001) in the model group than in the normal group; the random blood glucose level was significantly reduced (P<0.05), the escape latency tested by MWM was significantly shortened (P<0.05), and the number of crossing the original platform tested by MWM was significantly increased (P<0.05), the protein and gene expressions of Bax and Caspase-3 were significantly reduced (all P<0.001), the protein and gene expressions of Bcl-2 were significantly increased (both P<0.001), and the number of neuron apoptosis was significantly reduced (P<0.001) in the EA group than in the model group.
Conclusion
EA can improve the learning and memory damages induced by type 2 diabetic model rats with CI; the action mechanism may be achieved via anti-apoptosis.
摘要
目的
观察电针对2型糖尿病认知障碍大鼠大脑皮质Bax、Caspase-3、Bcl-2蛋白及基因表达的影响, 探讨电针改善其学习记忆的作用机制.
方法
将100只Sprague-Dawley(SD)大鼠采用随机数字表法分为正常组10只和造模组90只.造模组大鼠以高脂高糖饲料喂养1个月后, 采用小剂量链脲佐菌素(STZ)腹腔注射法建立2型糖尿病大鼠模型.将造模成功的50只大鼠通过Morris水迷宫实验(MWM)筛选出认知障碍大鼠20只, 按照血糖值与MWM数据随机分为模型组和电针组, 每组10只.电针组大鼠针刺足三里、内庭及胰俞, 其中足三里和内庭加电针刺激, 每日治疗1次, 每次20 min.每周治疗6 d, 连续治疗4周.模型组与正常组大鼠只固定不治疗.治疗4周后, 测定大鼠随机血糖值; MWM测定大鼠学习与记忆能力; 末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶介导的dUTP 缺口末端标记测定(TUNEL)法检测凋亡细胞; Western blot (WB)及实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(RT-qPCR)法检测大脑皮质Bax、Caspase-3、Bcl-2蛋白及基因的表达.
结果
造模后, 电针组和模型组大鼠随机血糖值和MWM逃避潜伏期明显增高, MWM通过平台次数减少, 与正常组差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01), 而模型组与电针组之间差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05).治疗4周后, 与正常组相比, 模型组随机血糖值及MWM逃避潜伏期明显升高(均P<0.05), MWM穿越原平台次数明显减少(P<0.01), Bax、Caspase-3蛋白及基因表达明显升高(均P<0.001); Bcl-2蛋白及基因表达明显降低(均P<0.001), 神经细胞的凋亡数显著增加(P<0.001); 与模型组比较, 电针组随机血糖值明显降低(P<0.05), MWM逃避潜伏期明显缩短(P<0.05), MWM穿越原平台次数明显增多(P<0.05), Bax、Caspase-3蛋白及基因表达明显降低(均P<0.001); Bcl-2蛋白及基因表达明显升高(均P<0.001), 神经细胞的凋亡数明显减低(P<0.001).
结论
电针可以改善大鼠2型糖尿病造成的学习记忆能力损伤, 其作用机制可能是通过抗细胞凋亡作用完成.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fradkin JE, Cowie CC, Hanlon MC, Rodgers GP. Celebrating 30 years of research accomplishments of the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study. Diabetes, 2013, 62(12): 3963–3967.
Shan Y, Wang JJ, Wang ZQ, Zhao ZL, Zhang M, Xu JY, Han Y, Li KC, Lu J. Neuronal specificity of acupuncture in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment patients: a functional MRI study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2018, 2018: 7619197.
Li T, Wu HG, Soto-Aguliar F, Huang L, Li WT, Lao LX, Xu SF. Efficacy of electrical acupuncture on vascular cognitive impairment with no dementia: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials, 2018, 19(1): 52.
De Felice FG, Ferreira ST. Inflammation, defective insulin signaling, and mitochondrial dysfunction as common molecular denominators connecting type 2 diabetes to Alzheimer disease. Diabetes, 2014, 63(7): 2262–2272.
Fu XZ, Feng XP, Huang WH, Li CY, Li XC, Qiu HX, Wang QL, Ban FD. Effect of Jiangtang Shuxin recipe on endoplasmic reticulum stress c-JNK apoptosis pathway in diabetic myocardium. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2018, 36(10): 2423–2427.
Chen QQ, Yuan AH, Yang J, Zha BX, Zhang M. Effect of acupuncture on the endoplasmic reticulum stress IRE1-CHOP pathway and the expression levels of Bax and Bcl-2 protein as well as genes in pancreatic tissue of rats with diabetes mellitus. Shijie Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2017, 27(1): 41–46.
Yuan AH, Zha BX, Wu JP, Huang RL. Effects of acupuncture on pancreatic ERS PERK-CHOP pathway and Bax/Bcl-2 mRNA expressions in diabetic rats. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2017, 32(3): 1291–1294.
Zhang ZY, Liu Z, Deng HH, Chen Q. Effects of acupuncture on vascular dementia (VD) animal models: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2018, 18(1): 302.
Tian HM, Yan H, Zhang J, He P, Chen CT. Effect of acupuncture on neurological function and related differentially-depressed profiles in the brain of middle cerebral artery occlusion rats using antibody chips technique. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2016, 41(6): 479–485.
Li S, Tan J, Zhang H, Huang GL, Deng DX, Guo KK, Liu JQ, Liu TY, Wu YY. Effect of catgut implantation on spatial learning-memory ability, expression of hippocampal protein kinase C interacting protein 1 and GluR2 and Ca2+ content in rats with chronic ischemic cognitive impairment. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2018, 43(6): 347–352.
Li ZR. Experimental Acupuncture Science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2003.
Du SQ, Wang XR, Zhu W, Ye Y, Yang JW, Ma SM, Ji CS, Liu CZ. Acupuncture inhibits TXNIP-associated oxidative stress and inflammation to attenuate cognitive impairment in vascular dementia rats. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2018, 24(1): 39–46.
Yang JW, Wang XR, Zhang M, Xiao LY, Zhu W, Ji CS, Liu CZ. Acupuncture as a multifunctional neuroprotective therapy ameliorates cognitive impairment in a rat model of vascular dementia: a quantitative iTRAQ proteomics study. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2018, 24(12): 1264–1274.
Mansur RB, Lee Y, Zhou AJ, Carmona NE, Cha DS, Rosenblat JD, Bruins R, Kakar R, Rasgon NL, Lovshin JA, Wroolie TE, Sim K, Brietzke E, Gerstein HC, Rong C, McIntyre RS. Determinants of cognitive function in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Ann Clin Psychiatry, 2018, 30(1): 38–50.
Podolski N, Brixius K, Predel HG, Brinkmann C. Effects of regular physical activity on the cognitive performance of type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review. Metab Syndr Relat Disord, 2017, 15(10): 481–493.
Yuan XY, Wang XG. Mild cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus and related risk factors: a review. Rev Neuro sci, 2017, 28(7): 715–723.
Mehta BK, Singh KK, Banerjee S. Effect of exercise on type 2 diabetes-associated cognitive impairment in rats. Int J Neurosci, 2019, 129(3): 252–263.
Liu XH, Liu H, Zheng Q, Liu H, Mai WL. Effects of EGCG on cognitive disorder of type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2018, 20(4): 48–50.
Xu XD, Huang Z, Xing QF, Wang J, Zhang YB. Clinical study on nimodipine plus oxiracetam capsules for type 2 diabetes mellitus with mild vascular cognitive impairmen. Zhongguo Shiyong Shenjing Jibing Zazhi, 2017, 20(6): 107–109.
Lai XS, Wang L. Effect of electroacupuncture on learning and memory and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in vascular dementia rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2003, 28(4): 245–250.
Luo Y, Dong WW. Electroacupuncture can down-regulate apoptotic gene Bax protein expression in cerebral cortex during focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 1999, 24(4): 274–277.
Tang SS, Ren Y, Xu LJ, Cao JR, Hong H, Ji H, Hu QH. Activation of ERα and/or ERβ ameliorates cognitive impairment and apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Horm Behav, 2018, 105: 95–103.
Puzzo D, Bizzoca A, Loreto C, Guida CA, Gulisano W, Frasca G, Bellomo M, Castorina S, Gennarini G, Palmeri A. Role of F3/contactin expression profile in synaptic plasticity and memory in aged mice. Neurobiol Aging, 2015, 36(4): 1702–1715.
Li M, Peng J, Song YL, Liang H, Mei YW, Fang Yuan. Electroacupuncture combined with transcranial magnetic stimulation improves learning and memory function of rats with cerebral infarction by inhibiting neuron cell apoptosis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci, 2012, 32(5): 746–749.
Jin MY, Cui ZH, Piao CL, Mi J, Liu XR, Han F, Pan WW. Analysis of regulating mechanism of Jiedu Tongluo Tiaogan formula on type 2 diabetes based on IRE1α/JNK pathway. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2018, 33(12): 5353–5357.
Fitrullah, Rousdy A. Effectiveness of acupressure at the Zusanli (ST 36) acupoint as a comfortable treatment for diabetes mellitus: a pilot study in Indonesia. J Acupunct Meridian Stud, 2017, 10(2): 96–103.
Zhang CC, Lin YP, Peng Y, Chen HJ, Yang JW, Liu WW, Liu L. Study on the mechanisms of electroacupuncture for promoting gastrointestinal motility in rats with diabetic gastroparesis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017, 15(3): 158–164.
Zhang Y, Chen DQ, Zhao FX, Su B, Lin CX. Effect of low frequency electroacupuncture Zusanli (ST 36) on glycometabolism in type 2 diabetes rats. Xiandai Zhongyi Linchuang, 2015, 22(1): 49–52, 55.
Cai SK, Li YB, Yang F, Fan YZ, Dong JL, Wu Q, Cai Y. Effect of electroacupuncture on hypothalamic IRS-1 in rat moedel of T2DM. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2018, 37(3): 330–334.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (国家自然科学基金, No. 81202769); Yang Jun’s Inheritance Studio of National Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Experts (全国名老中医药专 家杨骏传承工作室); 2016–2018 Anhui University Research and Innovation Platform Team Construction Project (2016-2018 年安徽高校科研创新平台团队建设项目, No. 2015TD033, No. 2015TD033); International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of Anhui Province (安 徽 省 对 外 科 技 合 作 计 划, No. 1604b0602020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Jp., Yuan, Ah., Yang, J. et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on the learning and memory abilities in type 2 diabetic model rats with cognitive impairment. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 18, 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-020-1150-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-020-1150-7
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2
- Cognitive Disorders
- Maze Learning
- Apoptosis
- Caspases
- Rats